Accelerator Terms
... measured by an area intercepted by particles on six dimensional phase space. In any accelerator design, low emittance will allow most of the particles to be confined into small area that fits into beam pipe and magnets that make up the system. Collider beam accelerator also needs small emittance to ...
... measured by an area intercepted by particles on six dimensional phase space. In any accelerator design, low emittance will allow most of the particles to be confined into small area that fits into beam pipe and magnets that make up the system. Collider beam accelerator also needs small emittance to ...
StandardModel
... Up to this we have found the 12 (6 quarks + 6 leptons) fundamental particles as well as four basic forces in nature and also the mediator particles of interactions respectively. What will happen if we try to bring it all together ? ----This synthesis of current knowledge, without any doubt is known ...
... Up to this we have found the 12 (6 quarks + 6 leptons) fundamental particles as well as four basic forces in nature and also the mediator particles of interactions respectively. What will happen if we try to bring it all together ? ----This synthesis of current knowledge, without any doubt is known ...
Wave as particle 2
... When photon with energy above the rest mass of two electrons ( 2me c 2 ) interact with the electric field of a nucleus, this photon may be turned into a pair of electron and positron. This process is called pair production through which energy gets turned into mass. Positron is the anti-particle of ...
... When photon with energy above the rest mass of two electrons ( 2me c 2 ) interact with the electric field of a nucleus, this photon may be turned into a pair of electron and positron. This process is called pair production through which energy gets turned into mass. Positron is the anti-particle of ...
Assignment for Physics 295 – Professor Thomson – due May 2 2005
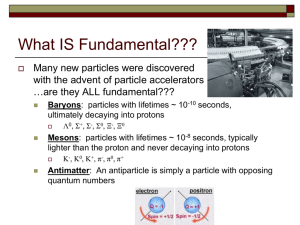
... particles? Electrons and positrons are fundamental particles, ie they are not made of anything else. When an electron moving in one direction collides with a positron moving with equal speed in the opposite direction, they completely annihilate and twice the beam-energy is available to make new part ...
... particles? Electrons and positrons are fundamental particles, ie they are not made of anything else. When an electron moving in one direction collides with a positron moving with equal speed in the opposite direction, they completely annihilate and twice the beam-energy is available to make new part ...
CHAPTER 3: The Experimental Basis of Quantum
... A positron passing through matter will likely annihilate with an electron. The electron and positron can form an atom-like configuration first, called positronium. Pair annihilation in empty space produces two photons to conserve momentum. Annihilation near a nucleus can result in a single photon. ...
... A positron passing through matter will likely annihilate with an electron. The electron and positron can form an atom-like configuration first, called positronium. Pair annihilation in empty space produces two photons to conserve momentum. Annihilation near a nucleus can result in a single photon. ...
The top quark
... What is dark matter made of ? Why is gravity so different ? What explains the required (extreme) tuning of parameters ? ...
... What is dark matter made of ? Why is gravity so different ? What explains the required (extreme) tuning of parameters ? ...
From electrons to quarks - FSU High Energy Physics
... Performs new experiments; protons ejected not only from hydrogen, but also from other light elements; measures energy of ejected protons (by mesuring their range), results not compatible with assumption that unknown radiation consists of gamma radiation (contradiction with energy-momentum conservati ...
... Performs new experiments; protons ejected not only from hydrogen, but also from other light elements; measures energy of ejected protons (by mesuring their range), results not compatible with assumption that unknown radiation consists of gamma radiation (contradiction with energy-momentum conservati ...
Types of Radiation
... Definition: A positively charged particle that consists of two protons and two neutrons bound together. It is emitted by an atomic nucleus undergoing radioactive decay and is identical to the nucleus of a helium atom. Because of their relatively large mass, alpha particles are the slowest and least ...
... Definition: A positively charged particle that consists of two protons and two neutrons bound together. It is emitted by an atomic nucleus undergoing radioactive decay and is identical to the nucleus of a helium atom. Because of their relatively large mass, alpha particles are the slowest and least ...
NASA Space Radiation Laboratory
... heavy ion beams from the AGS Booster synchrotron. The AGS Booster is an ideal accelerator for space radiation studies due to the good overlap between the available ion masses and energies with those encountered in space. A variety of heavy high energy (HZE) particles are available with energies rang ...
... heavy ion beams from the AGS Booster synchrotron. The AGS Booster is an ideal accelerator for space radiation studies due to the good overlap between the available ion masses and energies with those encountered in space. A variety of heavy high energy (HZE) particles are available with energies rang ...
Theory of electrons and positrons P A. M. D
... Of these, I shall deal almost entirely with the electrons and the positrons - not because they are the most interesting ones, but because in their case the theory has been developed further. There is, in fact, hardly anything that can be inferred theoretically about the properties of the others. The ...
... Of these, I shall deal almost entirely with the electrons and the positrons - not because they are the most interesting ones, but because in their case the theory has been developed further. There is, in fact, hardly anything that can be inferred theoretically about the properties of the others. The ...
STRUCTURE OF ATOMS
... Neutrons and electrons are known from particle physics — they're made of even smaller particles like quarks, those three particles will do for a thorough study of chemistry. The table below shows the relative sizes, masses and charges of our three particles. The important things to note are that pro ...
... Neutrons and electrons are known from particle physics — they're made of even smaller particles like quarks, those three particles will do for a thorough study of chemistry. The table below shows the relative sizes, masses and charges of our three particles. The important things to note are that pro ...
Modern Physics
... Interactions with the Higgs Field are theorized to give all the particles their masses LHC detectors should be able to confirm or disprove initial hints for Higgs at E=115 GeV ...
... Interactions with the Higgs Field are theorized to give all the particles their masses LHC detectors should be able to confirm or disprove initial hints for Higgs at E=115 GeV ...
DESY
The Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron (english German Electron Synchrotron) commonly referred to by the abbreviation DESY, is a national research center in Germany that operates particle accelerators used to investigate the structure of matter. It conducts a broad spectrum of inter-disciplinary scientific research in three main areas: particle and high energy physics; photon science; and the development, construction and operation of particle accelerators. Its name refers to its first project, an electron synchrotron. DESY is publicly financed by the Federal Republic of Germany, the States of Germany, and the German Research Foundation (DFG). DESY is a member of the Helmholtz Association and operates at sites in Hamburg and Zeuthen.