* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Radiation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
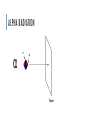
TYPES OF RADIATION ALPHA RADIATION n p Paper ALPHA RADIATION Greek Letter: α Representative Picture (labeled): 4 Symbol: 2𝐻𝑒 ALPHA RADIATION Definition: A positively charged particle that consists of two protons and two neutrons bound together. It is emitted by an atomic nucleus undergoing radioactive decay and is identical to the nucleus of a helium atom. Because of their relatively large mass, alpha particles are the slowest and least penetrating forms of nuclear radiation. How does alpha radiation change an atom? Since a helium nucleus is being emitting, it will drop the mass number by four (2 p + 2 n) and the atomic number by two (2 p). LEARNING CHECK: TRUE OR FALSE: ALPHA PARTICLES CONSIST OF TWO PROTONS AND TWO NEUTRONS A. True B. False BETA DECAY Paper Aluminum BETA RADIATION Greek Letter: β Representative Picture (labeled): 0 Symbol: −1𝑒 e- BETA RADIATION Definition: A high-speed electron or positron (positive electron), usually emitted by an atomic nucleus undergoing radioactive decay is a beta particle. Beta radiation occurs when a neutron decays into a proton and emits an electron. Beta radiation also occurs when a proton decays into a neutron and emits a positron. Beta particles have greater speed and penetrating power than alpha particles but can be stopped by a sheet of aluminum. How does beta radiation change an atom? Since a proton and a neutron have the same relative mass, the mass number of an atom will stay the same. The atomic number will increase by one when a neutron decays and it will decrease by one when a proton decays. LEARNING CHECK: THE MASS OF A BETA PARTICLE IS… A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D. 4 GAMMA RADIATION GAMMA RADIATION Greek Letter: γ Representative Picture (labeled): 0 Symbol: 0γ GAMMA RADIATION Definition: A stream of high-energy electromagnetic radiation given off by an atomic nucleus undergoing radioactive decay. How does gamma radiation change an atom? Gamma radiation does not change the nucleus but lowers the energy of the atom to become more stable. LEARNING CHECK: WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING DOES NOT CHANGE THE NUCLEUS OF AN ATOM? A. Alpha radiation B. Beta radiation C. Gamma radiation D. All of the above