Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... disappear, or become a liquid - the composition can vary from one sample to another. Pure substances have constant composition. Salt water samples from different seas or lakes have different amounts of salt ...
... disappear, or become a liquid - the composition can vary from one sample to another. Pure substances have constant composition. Salt water samples from different seas or lakes have different amounts of salt ...
Review Final 111 Lect
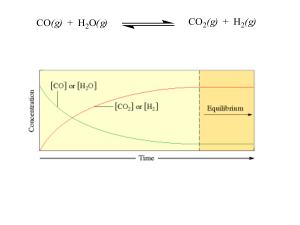
... c. The concentration of the fluoride ions will decrease. d. The concentration of Ca2+ ions will increase. e. The concentration of NO3- will have no effect on the solubility of CaF2 (s). f. All of the above will happen g. None of (a) to (e) will happen. 5. The equilibrium concentration of HSO3- is mu ...
... c. The concentration of the fluoride ions will decrease. d. The concentration of Ca2+ ions will increase. e. The concentration of NO3- will have no effect on the solubility of CaF2 (s). f. All of the above will happen g. None of (a) to (e) will happen. 5. The equilibrium concentration of HSO3- is mu ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Aqueous Solutions (aq) 5. Properties: Clear or transparent but may be colored, Solute doesn’t settle on standing, Can’t be separated by filtering, Components are not in a definite ratio 6. Example: NaCl(aq) ...
... Aqueous Solutions (aq) 5. Properties: Clear or transparent but may be colored, Solute doesn’t settle on standing, Can’t be separated by filtering, Components are not in a definite ratio 6. Example: NaCl(aq) ...
Solutions - iBioKaare
... mole fraction of solvent (d) less than that of water An aqueous solution of methanol in water has vapour pressure (a) equal to that of water (b) equation to that of methanol (c) more than that of water (d) less than that of water An ozeotropic mixture of two liquids boils at a lower temperature than ...
... mole fraction of solvent (d) less than that of water An aqueous solution of methanol in water has vapour pressure (a) equal to that of water (b) equation to that of methanol (c) more than that of water (d) less than that of water An ozeotropic mixture of two liquids boils at a lower temperature than ...
Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization of Norbornene by Cp
... Olefin metathesis reactions are widely used in industry.1 The largest application of this reaction is found in the Shell higher olefin process (SHOP), which produces more than 105 tons of C10-C20 alkenes annually.2 One subset of olefin metathesis reactions is known as ringopening metathesis polymeri ...
... Olefin metathesis reactions are widely used in industry.1 The largest application of this reaction is found in the Shell higher olefin process (SHOP), which produces more than 105 tons of C10-C20 alkenes annually.2 One subset of olefin metathesis reactions is known as ringopening metathesis polymeri ...
chem 100 class notes - Louisiana Tech University
... Most of the chemical compounds can be classified either as an acid, a base or a salt. Acids: Acids are compounds that increase the hydrogen ion concentration when dissolved in water. They usually have at least one removable hydrogen atom attached to an oxygen atom. These hydrogen are called acidic h ...
... Most of the chemical compounds can be classified either as an acid, a base or a salt. Acids: Acids are compounds that increase the hydrogen ion concentration when dissolved in water. They usually have at least one removable hydrogen atom attached to an oxygen atom. These hydrogen are called acidic h ...
Class XII Chemistry IMPORTANT QUESTIONS and COMMON
... Ans.Dissolution of gas is exothermic process. Hence according to LeChatelier‘s principle, the solubility of gas should decrease with rise in temperature 7. Mention a large scale use of the phenomenon called ‘reverse osmosis’. Ans. Desalination of Sea water. 8 .Why it is advised to add ethylene glyco ...
... Ans.Dissolution of gas is exothermic process. Hence according to LeChatelier‘s principle, the solubility of gas should decrease with rise in temperature 7. Mention a large scale use of the phenomenon called ‘reverse osmosis’. Ans. Desalination of Sea water. 8 .Why it is advised to add ethylene glyco ...
Untitled
... The [H3O+] of any aqueous solution is a very important characteristic, and we often need to talk about it. It is inconvenient to talk about the concentration in units such as 4.50 x 10-12 M or numbers similar to this form. So scientist defined a new number called _____ to talk about the concentratio ...
... The [H3O+] of any aqueous solution is a very important characteristic, and we often need to talk about it. It is inconvenient to talk about the concentration in units such as 4.50 x 10-12 M or numbers similar to this form. So scientist defined a new number called _____ to talk about the concentratio ...
Solution Definition and Speciation Calculations
... mmol Na2CO3 to a kilogram of water. What is the pH of the solution? Hint: The solution definition contains Na and C. 2. Define a solution made by adding 1 mmol of NaHCO3 and 1 mmol Na2CO3 to a kilogram of water that was then titrated to pH 7 with pure HCl. How much chloride was added? Hint: The solu ...
... mmol Na2CO3 to a kilogram of water. What is the pH of the solution? Hint: The solution definition contains Na and C. 2. Define a solution made by adding 1 mmol of NaHCO3 and 1 mmol Na2CO3 to a kilogram of water that was then titrated to pH 7 with pure HCl. How much chloride was added? Hint: The solu ...
Sulfuric Acid
... 4. The absorption tower has enough water so that 60% nitric acid will result, and also enough air to convert all remaining NO to NO2. The pressure is 10 atm. to give more efficient absorption. A more concentrated acid is obtained by distillation. The yield is 94-95% nitric acid. The product is 60% H ...
... 4. The absorption tower has enough water so that 60% nitric acid will result, and also enough air to convert all remaining NO to NO2. The pressure is 10 atm. to give more efficient absorption. A more concentrated acid is obtained by distillation. The yield is 94-95% nitric acid. The product is 60% H ...
AP Chemistry: Bonding Multiple Choice
... (B) consist of positive and negative ions that are strongly attracted to each other (C) are giant molecules in which each atom forms strong covalent bonds with all of its neighboring atoms (D) are formed under extreme conditions of temperature and pressure (E) contain orbitals or bands of delocalize ...
... (B) consist of positive and negative ions that are strongly attracted to each other (C) are giant molecules in which each atom forms strong covalent bonds with all of its neighboring atoms (D) are formed under extreme conditions of temperature and pressure (E) contain orbitals or bands of delocalize ...
Liquid–liquid extraction

Liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) consists in transferring one (or more) solute(s) contained in a feed solution to another immiscible liquid (solvent). The solvent that is enriched in solute(s) is called extract. The feed solution that is depleted in solute(s) is called raffinate.Liquid–liquid extraction also known as solvent extraction and partitioning, is a method to separate compounds based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids, usually water and an organic solvent. It is an extraction of a substance from one liquid into another liquid phase. Liquid–liquid extraction is a basic technique in chemical laboratories, where it is performed using a variety of apparatus, from separatory funnels to countercurrent distribution equipment. This type of process is commonly performed after a chemical reaction as part of the work-up.The term partitioning is commonly used to refer to the underlying chemical and physical processes involved in liquid–liquid extraction, but on another reading may be fully synonymous with it. The term solvent extraction can also refer to the separation of a substance from a mixture by preferentially dissolving that substance in a suitable solvent. In that case, a soluble compound is separated from an insoluble compound or a complex matrix.Solvent extraction is used in nuclear reprocessing, ore processing, the production of fine organic compounds, the processing of perfumes, the production of vegetable oils and biodiesel, and other industries.Liquid–liquid extraction is possible in non-aqueous systems: In a system consisting of a molten metal in contact with molten salts, metals can be extracted from one phase to the other. This is related to a mercury electrode where a metal can be reduced, the metal will often then dissolve in the mercury to form an amalgam that modifies its electrochemistry greatly. For example, it is possible for sodium cations to be reduced at a mercury cathode to form sodium amalgam, while at an inert electrode (such as platinum) the sodium cations are not reduced. Instead, water is reduced to hydrogen. A detergent or fine solid can be used to stabilize an emulsion, or third phase.