Mechanistic Studies of the Reactions of Silicon
... (selected) deuterium kinetic isotope effects for the addition of water, methanol, ethanol, 2-propanol, tert-butyl alcohol, and acetic acid have been determined at 23 °C in acetonitrile solution. Silene quenching follows a linear dependence on quencher concentration over the range investigated in all ...
... (selected) deuterium kinetic isotope effects for the addition of water, methanol, ethanol, 2-propanol, tert-butyl alcohol, and acetic acid have been determined at 23 °C in acetonitrile solution. Silene quenching follows a linear dependence on quencher concentration over the range investigated in all ...
- Catalyst
... The Solubility of Covalent Compounds in Water Polar covalent compounds are very soluble in water. They often have OH groups that can form “hydrogen bonds” with water. Examples are table sugar (C12H22O11), ethanol (C2H5OH), ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) in antifreeze, and methanol (CH3OH). These also are ...
... The Solubility of Covalent Compounds in Water Polar covalent compounds are very soluble in water. They often have OH groups that can form “hydrogen bonds” with water. Examples are table sugar (C12H22O11), ethanol (C2H5OH), ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) in antifreeze, and methanol (CH3OH). These also are ...
Mock Examination (2016/2017) CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 SECTION B
... write in the margins. Answers written in the margins will not be marked. ...
... write in the margins. Answers written in the margins will not be marked. ...
Chapter 1 questions
... nicotine is approximately 160. Quantitative analysis of this compound yields the following percentages by mass of its constituent elements: carbon 74.1%, hydrogen 8.7%, nitrogen 17.2% Calculate the empirical and molecular formulae of nicotine. Q10. 0.8361g of an organic compound is analysed and foun ...
... nicotine is approximately 160. Quantitative analysis of this compound yields the following percentages by mass of its constituent elements: carbon 74.1%, hydrogen 8.7%, nitrogen 17.2% Calculate the empirical and molecular formulae of nicotine. Q10. 0.8361g of an organic compound is analysed and foun ...
CIS Exam Questions
... Which of the following statements about the experiment is correct? A 0·05 mol of zinc reacts. B 0·05 mol of silver is displaced. C Silver nitrate is in excess. D All of the zinc reacts. 25. 0·5 mol of copper(II) chloride and 0·5 mol of copper(II) sulphate are dissolved together in water and made up ...
... Which of the following statements about the experiment is correct? A 0·05 mol of zinc reacts. B 0·05 mol of silver is displaced. C Silver nitrate is in excess. D All of the zinc reacts. 25. 0·5 mol of copper(II) chloride and 0·5 mol of copper(II) sulphate are dissolved together in water and made up ...
Insertion of SO2 into the Metal−Carbon Bonds of Rhodium and
... proposed that still holds in the majority of cases.1a While current interest in this reaction has decreased, SO2 remains the subject of numerous studies2 because of its diverse coordination properties and its role in acid rain production. In this paper, we present two new systems that are able to cl ...
... proposed that still holds in the majority of cases.1a While current interest in this reaction has decreased, SO2 remains the subject of numerous studies2 because of its diverse coordination properties and its role in acid rain production. In this paper, we present two new systems that are able to cl ...
Amino Acid Synthesis in a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide
... one of the essential materials for chemical evolution in early Earth. The prebiotic synthesis by electric discharge in reducing gasses (CH4, NH3, H2, and H2O) through Miller’s experiment has given experimental support to the chemical evolution [2]. After Miller’s report, many prebiotic syntheses in ...
... one of the essential materials for chemical evolution in early Earth. The prebiotic synthesis by electric discharge in reducing gasses (CH4, NH3, H2, and H2O) through Miller’s experiment has given experimental support to the chemical evolution [2]. After Miller’s report, many prebiotic syntheses in ...
Unit 3 Exam Level Questions
... 10. The Avogadro Constant is the same as the number of A ions in 1 mol of NaCl B atoms in 1 mol of hydrogen gas C electrons in 1 mol of helium gas D molecules in 1 mol of oxygen gas. 11. The Avogadro Constant is the same as the number of A molecules in 16 g of oxygen B electrons in 1 g of hydrogen C ...
... 10. The Avogadro Constant is the same as the number of A ions in 1 mol of NaCl B atoms in 1 mol of hydrogen gas C electrons in 1 mol of helium gas D molecules in 1 mol of oxygen gas. 11. The Avogadro Constant is the same as the number of A molecules in 16 g of oxygen B electrons in 1 g of hydrogen C ...
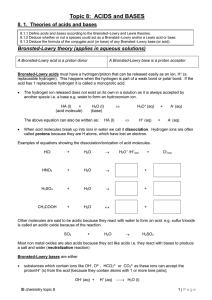
Topic 8: ACIDS and BASES
... Example: a hydrochloric acid solution and an ethanoic acid solution of the same concentration (eg 0.1M) will have different hydrogen concentrations - and therefore different pH’s - because of their different strengths: the pH of the hydrochloric acid will be lower than the pH of the ethanoic acid ...
... Example: a hydrochloric acid solution and an ethanoic acid solution of the same concentration (eg 0.1M) will have different hydrogen concentrations - and therefore different pH’s - because of their different strengths: the pH of the hydrochloric acid will be lower than the pH of the ethanoic acid ...
Study Modules XII Chemistry 2017
... In metals with increase of temperature, the kernels start vibrating and thus offer resistance to the flow of electrons.Hence conductivity decreases. In case of semiconductors, with increase of temperature, more electrons can shift from valence band to conduction band. Hence conductivity increases. 8 ...
... In metals with increase of temperature, the kernels start vibrating and thus offer resistance to the flow of electrons.Hence conductivity decreases. In case of semiconductors, with increase of temperature, more electrons can shift from valence band to conduction band. Hence conductivity increases. 8 ...
Oxidation of benzoin with anchored vanadyl and
... Bu’O,H oxidant was of interest since Bu’O,H is one of the best sources of oxygen atoms from the point of view of economics, selectivity and safety. Bu’O,H is essentially inert to most organic molecules in the absence of catalysts and so catalysts can be used to push the oxidation reaction in pre-det ...
... Bu’O,H oxidant was of interest since Bu’O,H is one of the best sources of oxygen atoms from the point of view of economics, selectivity and safety. Bu’O,H is essentially inert to most organic molecules in the absence of catalysts and so catalysts can be used to push the oxidation reaction in pre-det ...
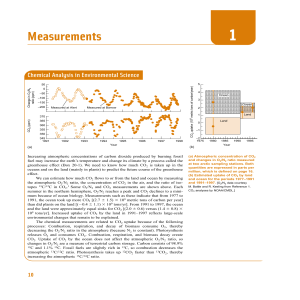
Measurements
... We can estimate how much CO2 flows to or from the land and ocean by measuring the atmospheric O2/N2 ratio, the concentration of CO2 in the air, and the ratio of isotopes 13C/12C in CO2.1 Some O2/N2 and CO2 measurements are shown above. Each summer in the northern hemisphere, O2/N2 reaches a peak and ...
... We can estimate how much CO2 flows to or from the land and ocean by measuring the atmospheric O2/N2 ratio, the concentration of CO2 in the air, and the ratio of isotopes 13C/12C in CO2.1 Some O2/N2 and CO2 measurements are shown above. Each summer in the northern hemisphere, O2/N2 reaches a peak and ...
Review on N acylation reaction
... base R1NH2. So the acylation of an equimolar mixture of two amines usually observed the conversion of weaker amine to amide and hydrochloride of the stronger amine in number of solvents. In some cases the selectivity of acylation was also found to depend on steric effect such as in acylation of mixt ...
... base R1NH2. So the acylation of an equimolar mixture of two amines usually observed the conversion of weaker amine to amide and hydrochloride of the stronger amine in number of solvents. In some cases the selectivity of acylation was also found to depend on steric effect such as in acylation of mixt ...
Laboratory Practices from Physical Chemistry
... 4 Determination of molar mass of volatile liquids Aim To determine molar mass of volatile liquid sample by means of Meyer and Dumas methods. Theoretical part In the case of volatile liquid, their behavior can be described in terms of the equation of state for a perfect gas, if the temperature is a ...
... 4 Determination of molar mass of volatile liquids Aim To determine molar mass of volatile liquid sample by means of Meyer and Dumas methods. Theoretical part In the case of volatile liquid, their behavior can be described in terms of the equation of state for a perfect gas, if the temperature is a ...
Document
... 2. There is only one correct answer to each question. 3. Any rough working should be done on the additional space for answers and rough work at the end of this booklet. Sample Question To show that the ink in a ball-pen consists of a mixture of dyes, the method of separation would be: A ...
... 2. There is only one correct answer to each question. 3. Any rough working should be done on the additional space for answers and rough work at the end of this booklet. Sample Question To show that the ink in a ball-pen consists of a mixture of dyes, the method of separation would be: A ...
Liquid–liquid extraction

Liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) consists in transferring one (or more) solute(s) contained in a feed solution to another immiscible liquid (solvent). The solvent that is enriched in solute(s) is called extract. The feed solution that is depleted in solute(s) is called raffinate.Liquid–liquid extraction also known as solvent extraction and partitioning, is a method to separate compounds based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids, usually water and an organic solvent. It is an extraction of a substance from one liquid into another liquid phase. Liquid–liquid extraction is a basic technique in chemical laboratories, where it is performed using a variety of apparatus, from separatory funnels to countercurrent distribution equipment. This type of process is commonly performed after a chemical reaction as part of the work-up.The term partitioning is commonly used to refer to the underlying chemical and physical processes involved in liquid–liquid extraction, but on another reading may be fully synonymous with it. The term solvent extraction can also refer to the separation of a substance from a mixture by preferentially dissolving that substance in a suitable solvent. In that case, a soluble compound is separated from an insoluble compound or a complex matrix.Solvent extraction is used in nuclear reprocessing, ore processing, the production of fine organic compounds, the processing of perfumes, the production of vegetable oils and biodiesel, and other industries.Liquid–liquid extraction is possible in non-aqueous systems: In a system consisting of a molten metal in contact with molten salts, metals can be extracted from one phase to the other. This is related to a mercury electrode where a metal can be reduced, the metal will often then dissolve in the mercury to form an amalgam that modifies its electrochemistry greatly. For example, it is possible for sodium cations to be reduced at a mercury cathode to form sodium amalgam, while at an inert electrode (such as platinum) the sodium cations are not reduced. Instead, water is reduced to hydrogen. A detergent or fine solid can be used to stabilize an emulsion, or third phase.