Acids and Bases
... How can we identify an acid or a base simply by looking at the chemical formula? Since we have defined acids and bases by the ions they release in solution, the first requirement is that they contain H or OH, respectively. However, there are plenty of compounds that contain oxygen and hydrogen atoms t ...
... How can we identify an acid or a base simply by looking at the chemical formula? Since we have defined acids and bases by the ions they release in solution, the first requirement is that they contain H or OH, respectively. However, there are plenty of compounds that contain oxygen and hydrogen atoms t ...
REACTIONS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION
... sugar (sucrose) in a cup of water (! FIGURE 4.2). Both solutions are clear and colorless, but they possess very different electrical conductivities: the salt solution is a good conductor of electricity, whereas the sugar solution is not. In order for the bulb in the device of Figure 4.2 to light up, ...
... sugar (sucrose) in a cup of water (! FIGURE 4.2). Both solutions are clear and colorless, but they possess very different electrical conductivities: the salt solution is a good conductor of electricity, whereas the sugar solution is not. In order for the bulb in the device of Figure 4.2 to light up, ...
IChO_Comp_Prob_Answ 1997
... routine material studied in most high schools around the world. But this is how it should be since the competitors involved are among the best that our countries have to offer. However, it is felt that even these topics and the level of expertise expected can be mastered by our students without sign ...
... routine material studied in most high schools around the world. But this is how it should be since the competitors involved are among the best that our countries have to offer. However, it is felt that even these topics and the level of expertise expected can be mastered by our students without sign ...
Disproportionation of Gold(II)
... the PCM methodology (a simplistic solvation model for atomic metal ions)36 to simulate an aqueous reaction field, it is calculated that solvation substantially alters the energetics of the disproportionation reaction. The gas-phase energy of eq 3 calculated by B3PW91/LANL2DZ(2f,p)* is more than halv ...
... the PCM methodology (a simplistic solvation model for atomic metal ions)36 to simulate an aqueous reaction field, it is calculated that solvation substantially alters the energetics of the disproportionation reaction. The gas-phase energy of eq 3 calculated by B3PW91/LANL2DZ(2f,p)* is more than halv ...
odd - WWW2
... The three classes are ionic, covalent, and metallic. Ionic carbides are formed by the most electropositive metals. These may contain the dicarbide(2 ) ion, C22 , or the true carbide ion C4 . Both types of ionic carbides react with water to produce the appropriate hydrocarbon. Covalent carbides are f ...
... The three classes are ionic, covalent, and metallic. Ionic carbides are formed by the most electropositive metals. These may contain the dicarbide(2 ) ion, C22 , or the true carbide ion C4 . Both types of ionic carbides react with water to produce the appropriate hydrocarbon. Covalent carbides are f ...
Chemical Reaction Equations
... A chemical reaction equation that includes only reacting entities (molecules, atoms and/or ions) and omits any that do not change Writing Net Ionic Equations: 1) Write a complete balanced chemical equation 2) Dissociate all high-solubility ionic compounds, and ionize all strong acids to show the com ...
... A chemical reaction equation that includes only reacting entities (molecules, atoms and/or ions) and omits any that do not change Writing Net Ionic Equations: 1) Write a complete balanced chemical equation 2) Dissociate all high-solubility ionic compounds, and ionize all strong acids to show the com ...
Complete Set
... • The ocean contains a variety of forms of CO32– and CO2 with a variety of acid-base and solubility equilibria determining their concentrations. There is concern that increasing levels of CO2 will lead to increased dissolution of CaCO3 and critically affect the survival of life forms that rely on a ...
... • The ocean contains a variety of forms of CO32– and CO2 with a variety of acid-base and solubility equilibria determining their concentrations. There is concern that increasing levels of CO2 will lead to increased dissolution of CaCO3 and critically affect the survival of life forms that rely on a ...
General and Inorganic Chemistry
... 4.1.1. III.4.1.1 Limit of detection of different types of balances .......................... 31 4.1.2. III.4.1.2 Rules to be followed when using analytical balance .................... 32 4.1.3. III.4.1.3 Experimental task: Determination of mass of objects. Weighing of solid compounds on laboratory ...
... 4.1.1. III.4.1.1 Limit of detection of different types of balances .......................... 31 4.1.2. III.4.1.2 Rules to be followed when using analytical balance .................... 32 4.1.3. III.4.1.3 Experimental task: Determination of mass of objects. Weighing of solid compounds on laboratory ...
www.iitvidya.com salt analysis assignment 1. A compound on
... 3 (B) Elementals (C) 37. Identify the following : Na2CO3 SO (D) Also mention the oxidation state of S in all the compounds : 38. How is boron obtained from borax ? Give chemical equations with reaction conditions ? Write the structure of B2H6 and its reaction with HCl. 39. A metallic c ...
... 3 (B) Elementals (C) 37. Identify the following : Na2CO3 SO (D) Also mention the oxidation state of S in all the compounds : 38. How is boron obtained from borax ? Give chemical equations with reaction conditions ? Write the structure of B2H6 and its reaction with HCl. 39. A metallic c ...
Experimental Chemistry I
... 1. rinse burette with calibration solution (1.000M) NaOH and fill it up to zero-mark; close stopcock before filling with titrant and clamp burette onto the stand; 2. pipet 25ml of Standardized Acid into the 0.25L Erlenmeyer flask and add approx. 0.1L of deionized water; 3. add 1 drop of PP-indicator ...
... 1. rinse burette with calibration solution (1.000M) NaOH and fill it up to zero-mark; close stopcock before filling with titrant and clamp burette onto the stand; 2. pipet 25ml of Standardized Acid into the 0.25L Erlenmeyer flask and add approx. 0.1L of deionized water; 3. add 1 drop of PP-indicator ...
Chapter 4
... nitrate [Ca(NO3)2], are strong electrolytes. It is interesting to note that human body fluids contain many strong and weak electrolytes. Water is a very effective solvent for ionic compounds. Although water is an electrically neutral molecule, it has a positive region (the H atoms) and a negative re ...
... nitrate [Ca(NO3)2], are strong electrolytes. It is interesting to note that human body fluids contain many strong and weak electrolytes. Water is a very effective solvent for ionic compounds. Although water is an electrically neutral molecule, it has a positive region (the H atoms) and a negative re ...
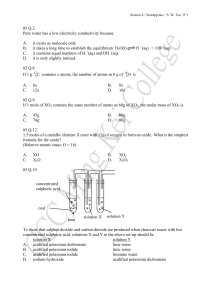
85 Q.2 Pure water has a low electricity conductivity because A. it
... Which of the following statements concerning 25 cm3 of 1M hydrochloric acid and 25 cm3 of 1M ethanoic acid is / are correct? (1) They give the same colour change when the same quantity to universal indicator is added. (2) They react with marble chips at the same rate when the initial temperatures ar ...
... Which of the following statements concerning 25 cm3 of 1M hydrochloric acid and 25 cm3 of 1M ethanoic acid is / are correct? (1) They give the same colour change when the same quantity to universal indicator is added. (2) They react with marble chips at the same rate when the initial temperatures ar ...
Chapter 4: Types of Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Example: If a solution containing potassium chloride is added to a solution containing ammonium nitrate, will a precipitate form? KCl(aq) + NH4NO3(aq) → K+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + NH4+(aq) + NO3-(aq) Possible reaction products are KCl and NH4NO3, NH4Cl and KNO3. All are soluble, so there is no precipitate. ...
... Example: If a solution containing potassium chloride is added to a solution containing ammonium nitrate, will a precipitate form? KCl(aq) + NH4NO3(aq) → K+(aq) + Cl-(aq) + NH4+(aq) + NO3-(aq) Possible reaction products are KCl and NH4NO3, NH4Cl and KNO3. All are soluble, so there is no precipitate. ...
F:\Users\Steven\Documents\Chemistry\CHEM120\Problem Set
... a) Please write the NET ionic reaction that occurred. b) How many grams of solid were made? c) What is the concentration of all the ions left in solution? 3) When 100 mL of 0.40M NaOH is added to 75 mL of 0.6 M Zn(NO3)2 a white solid forms. a) Please write the NET ionic reaction that occured. b) How ...
... a) Please write the NET ionic reaction that occurred. b) How many grams of solid were made? c) What is the concentration of all the ions left in solution? 3) When 100 mL of 0.40M NaOH is added to 75 mL of 0.6 M Zn(NO3)2 a white solid forms. a) Please write the NET ionic reaction that occured. b) How ...
EDEXCEL A LeveL - Hodder Education
... Relative atomic masses show that one atom of carbon is 12 times heavier than one atom of hydrogen. This means that 12 g of carbon contains the same number of atoms as 1 g of hydrogen. Similarly, one atom of oxygen is 16 times as heavy as one atom of hydrogen, so 16 g of oxygen also contains the same ...
... Relative atomic masses show that one atom of carbon is 12 times heavier than one atom of hydrogen. This means that 12 g of carbon contains the same number of atoms as 1 g of hydrogen. Similarly, one atom of oxygen is 16 times as heavy as one atom of hydrogen, so 16 g of oxygen also contains the same ...
Liquid–liquid extraction

Liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) consists in transferring one (or more) solute(s) contained in a feed solution to another immiscible liquid (solvent). The solvent that is enriched in solute(s) is called extract. The feed solution that is depleted in solute(s) is called raffinate.Liquid–liquid extraction also known as solvent extraction and partitioning, is a method to separate compounds based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids, usually water and an organic solvent. It is an extraction of a substance from one liquid into another liquid phase. Liquid–liquid extraction is a basic technique in chemical laboratories, where it is performed using a variety of apparatus, from separatory funnels to countercurrent distribution equipment. This type of process is commonly performed after a chemical reaction as part of the work-up.The term partitioning is commonly used to refer to the underlying chemical and physical processes involved in liquid–liquid extraction, but on another reading may be fully synonymous with it. The term solvent extraction can also refer to the separation of a substance from a mixture by preferentially dissolving that substance in a suitable solvent. In that case, a soluble compound is separated from an insoluble compound or a complex matrix.Solvent extraction is used in nuclear reprocessing, ore processing, the production of fine organic compounds, the processing of perfumes, the production of vegetable oils and biodiesel, and other industries.Liquid–liquid extraction is possible in non-aqueous systems: In a system consisting of a molten metal in contact with molten salts, metals can be extracted from one phase to the other. This is related to a mercury electrode where a metal can be reduced, the metal will often then dissolve in the mercury to form an amalgam that modifies its electrochemistry greatly. For example, it is possible for sodium cations to be reduced at a mercury cathode to form sodium amalgam, while at an inert electrode (such as platinum) the sodium cations are not reduced. Instead, water is reduced to hydrogen. A detergent or fine solid can be used to stabilize an emulsion, or third phase.