Physical and Chemical equilibrium
... equal to its stoichiometric coefficient as represented by the balanced chemical equation For example aA + bB ⇌ cC + dD According to law of active mass action Rate of forward reaction rf ∝ [A]a [B]b Rate of backward reaction rb ∝ [C]c [D]d Active mass of a substance is simply number of moles dissolve ...
... equal to its stoichiometric coefficient as represented by the balanced chemical equation For example aA + bB ⇌ cC + dD According to law of active mass action Rate of forward reaction rf ∝ [A]a [B]b Rate of backward reaction rb ∝ [C]c [D]d Active mass of a substance is simply number of moles dissolve ...
1 Acids and Bases
... As with any other ion, a hydrogen ion dissolved in water will be closely associated with one or more water molecules. This fact is sometimes indicated explicitly by writing the hydronium ion, H3 O+ , in place of the hydrogen ion, H+ . Many chemists still use H+ (aq) to represent this situation, but ...
... As with any other ion, a hydrogen ion dissolved in water will be closely associated with one or more water molecules. This fact is sometimes indicated explicitly by writing the hydronium ion, H3 O+ , in place of the hydrogen ion, H+ . Many chemists still use H+ (aq) to represent this situation, but ...
Copper Chemistry
... introduced into the system in the early stages and persists in the subsequent stages of the process. The effects of these contaminants are considerable and include: increased phase separation time at stages when organic and aqueous solvents are mixed. lack of complete phase separation after extracti ...
... introduced into the system in the early stages and persists in the subsequent stages of the process. The effects of these contaminants are considerable and include: increased phase separation time at stages when organic and aqueous solvents are mixed. lack of complete phase separation after extracti ...
In_Class_Practice Chapter 17 PreAP
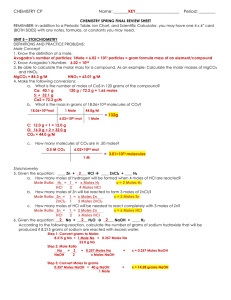
... 6. Use Le Châtelier’s principle to predict how each of the following changes would affect this equilibrium. C2H4O(g) CH4(g) + CO(g) a. adding CH4(g) to the system b. removing CO(g) from the system c. removing C2H4O(g) from the system 7. How would decreasing the volume of the reaction vessel affect ...
... 6. Use Le Châtelier’s principle to predict how each of the following changes would affect this equilibrium. C2H4O(g) CH4(g) + CO(g) a. adding CH4(g) to the system b. removing CO(g) from the system c. removing C2H4O(g) from the system 7. How would decreasing the volume of the reaction vessel affect ...
Solubility Equilibria
... Ionic compounds can be either: o soluble in water. (We do not need to study the solubility of this type) o nonsoluble or very slightly soluble in water. Different ionic compounds have different degrees of solubility in water. (Exploring the solubility of this type of compounds is useful) One ...
... Ionic compounds can be either: o soluble in water. (We do not need to study the solubility of this type) o nonsoluble or very slightly soluble in water. Different ionic compounds have different degrees of solubility in water. (Exploring the solubility of this type of compounds is useful) One ...
B.Sc. Industrial Chemistry
... The course on B.Sc. Industrial Chemistry was introduced in the University of Delhi in 1984 and since then this course has undergone many changes and has become more comprehensive and relevant. The importance of industrial chemistry hardly needs any emphasis. It basically deals with the development, ...
... The course on B.Sc. Industrial Chemistry was introduced in the University of Delhi in 1984 and since then this course has undergone many changes and has become more comprehensive and relevant. The importance of industrial chemistry hardly needs any emphasis. It basically deals with the development, ...
chemistry sp.indd
... One chlorofluorocarbon which was widely used as a solvent is CCl2FCClF2. Large stocks of it remain. One process to use up these stocks is to convert it into the fluorocarbon CH2FCF3 by the following route. ...
... One chlorofluorocarbon which was widely used as a solvent is CCl2FCClF2. Large stocks of it remain. One process to use up these stocks is to convert it into the fluorocarbon CH2FCF3 by the following route. ...
AVOGADRO EXAMS 1991 - 2002 PRACTICE BOOKLET
... 25. Assume that argon, at a constant temperature and pressure, behaves as an ideal gas. Which of the following is correct? (a) All argon atoms move with the same speed (b) All argon atoms collide with the container walls with the same force (c) Temperature is determined solely by the collision freq ...
... 25. Assume that argon, at a constant temperature and pressure, behaves as an ideal gas. Which of the following is correct? (a) All argon atoms move with the same speed (b) All argon atoms collide with the container walls with the same force (c) Temperature is determined solely by the collision freq ...
Liquid–liquid extraction

Liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) consists in transferring one (or more) solute(s) contained in a feed solution to another immiscible liquid (solvent). The solvent that is enriched in solute(s) is called extract. The feed solution that is depleted in solute(s) is called raffinate.Liquid–liquid extraction also known as solvent extraction and partitioning, is a method to separate compounds based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids, usually water and an organic solvent. It is an extraction of a substance from one liquid into another liquid phase. Liquid–liquid extraction is a basic technique in chemical laboratories, where it is performed using a variety of apparatus, from separatory funnels to countercurrent distribution equipment. This type of process is commonly performed after a chemical reaction as part of the work-up.The term partitioning is commonly used to refer to the underlying chemical and physical processes involved in liquid–liquid extraction, but on another reading may be fully synonymous with it. The term solvent extraction can also refer to the separation of a substance from a mixture by preferentially dissolving that substance in a suitable solvent. In that case, a soluble compound is separated from an insoluble compound or a complex matrix.Solvent extraction is used in nuclear reprocessing, ore processing, the production of fine organic compounds, the processing of perfumes, the production of vegetable oils and biodiesel, and other industries.Liquid–liquid extraction is possible in non-aqueous systems: In a system consisting of a molten metal in contact with molten salts, metals can be extracted from one phase to the other. This is related to a mercury electrode where a metal can be reduced, the metal will often then dissolve in the mercury to form an amalgam that modifies its electrochemistry greatly. For example, it is possible for sodium cations to be reduced at a mercury cathode to form sodium amalgam, while at an inert electrode (such as platinum) the sodium cations are not reduced. Instead, water is reduced to hydrogen. A detergent or fine solid can be used to stabilize an emulsion, or third phase.