Lab Manual (Eng. Medium)
... harmful/corrosive liquids. It is used as follows: 1. Insert the adaptor into the top end of the pipette. 2. Dip the pipette tip in the liquid. 3. Press the adaptor to force the air out and then release to suck the liquid into the pipette. 4. Fill the pipette to just above the calibration mark. 5. Ad ...
... harmful/corrosive liquids. It is used as follows: 1. Insert the adaptor into the top end of the pipette. 2. Dip the pipette tip in the liquid. 3. Press the adaptor to force the air out and then release to suck the liquid into the pipette. 4. Fill the pipette to just above the calibration mark. 5. Ad ...
Name:
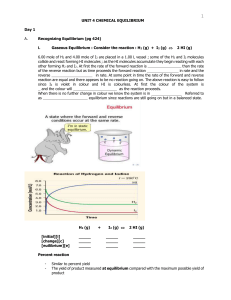
... H2O(g) Cl2O(g) 2HOCl(g) 3. Determine the equilibrium constant for the following reaction, based on the equilibrium concentrations below. 3NO(g) N2O(g) NO2(g) [NO] 0.060 mol/L [N2O] 0.015 mol/L [NO2] 0.025 mol/L 4. 0.150 mol of SO3 and 0.150 mol of NO are placed in a 1 L container and a ...
... H2O(g) Cl2O(g) 2HOCl(g) 3. Determine the equilibrium constant for the following reaction, based on the equilibrium concentrations below. 3NO(g) N2O(g) NO2(g) [NO] 0.060 mol/L [N2O] 0.015 mol/L [NO2] 0.025 mol/L 4. 0.150 mol of SO3 and 0.150 mol of NO are placed in a 1 L container and a ...
Appendix
... 1. Which of the following condiments do you think has the lowest salt content? a. mustard ...
... 1. Which of the following condiments do you think has the lowest salt content? a. mustard ...
Photo-oxidation of pinonaldehyde at low NOx
... chemistry of pinonaldehyde and similar compounds in the literature (Glasius et al., 1997). Though we recently described SOA chemistry under highNOx conditions (Chacon-Madrid and Donahue, 2011), it is important to explore its chemistry in low-NOx conditions because products of biogenic species are co ...
... chemistry of pinonaldehyde and similar compounds in the literature (Glasius et al., 1997). Though we recently described SOA chemistry under highNOx conditions (Chacon-Madrid and Donahue, 2011), it is important to explore its chemistry in low-NOx conditions because products of biogenic species are co ...
Novel Methods and Materials in Development of Liquid Carrier
... primary thesis work were generated. One brainchild here and another there led into quite time consuming proposal writing: without a „bunch of bucks” no research can be done. There were proposals on microreactors, on membrane reactor and two on molecular modelling - one in the field of crystallisatio ...
... primary thesis work were generated. One brainchild here and another there led into quite time consuming proposal writing: without a „bunch of bucks” no research can be done. There were proposals on microreactors, on membrane reactor and two on molecular modelling - one in the field of crystallisatio ...
LABORATORY MANUAL FOR CHEMISTRY 102
... the experimentally determined exponents for each species. (The overall order of the reaction is equal to the sum of x + y + z +... .) The term k is known as the rate constant for the reaction. Usually, when a reaction is initiated, the rate (known as the initial rate) is found to be at its maximum v ...
... the experimentally determined exponents for each species. (The overall order of the reaction is equal to the sum of x + y + z +... .) The term k is known as the rate constant for the reaction. Usually, when a reaction is initiated, the rate (known as the initial rate) is found to be at its maximum v ...
Module 2
... Definition of the first law of thermodynamics is: Energy can neither be created nor destroyed but only changed from one form to another or The energy of a system that is isolated from its surroundings is constant. If an amount of heat Q flows into a system from the surroundings, then the internal en ...
... Definition of the first law of thermodynamics is: Energy can neither be created nor destroyed but only changed from one form to another or The energy of a system that is isolated from its surroundings is constant. If an amount of heat Q flows into a system from the surroundings, then the internal en ...
Reactions in Aqueous Solution
... When weak electrolytes9 dissolve, they produce relatively few ions in solution. This does not mean that the compounds do not dissolve readily in water; many weak electrolytes contain polar bonds and are therefore very soluble in a polar solvent such as water. They do not completely dissociate to for ...
... When weak electrolytes9 dissolve, they produce relatively few ions in solution. This does not mean that the compounds do not dissolve readily in water; many weak electrolytes contain polar bonds and are therefore very soluble in a polar solvent such as water. They do not completely dissociate to for ...
Chapter 4 "Reactions in Aqueous Solution"
... When weak electrolytes9 dissolve, they produce relatively few ions in solution. This does not mean that the compounds do not dissolve readily in water; many weak electrolytes contain polar bonds and are therefore very soluble in a polar solvent such as water. They do not completely dissociate to for ...
... When weak electrolytes9 dissolve, they produce relatively few ions in solution. This does not mean that the compounds do not dissolve readily in water; many weak electrolytes contain polar bonds and are therefore very soluble in a polar solvent such as water. They do not completely dissociate to for ...
Alberta Chemistry 20-30 Sample CAB Questions - McGraw
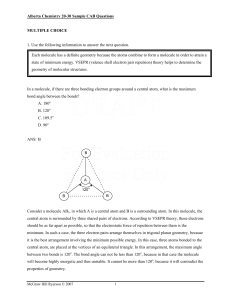
... Consider a molecule AB3, in which A is a central atom and B is a surrounding atom. In this molecule, the central atom is surrounded by three shared pairs of electrons. According to VSEPR theory, these electrons should be as far apart as possible, so that the electrostatic force of repulsion between ...
... Consider a molecule AB3, in which A is a central atom and B is a surrounding atom. In this molecule, the central atom is surrounded by three shared pairs of electrons. According to VSEPR theory, these electrons should be as far apart as possible, so that the electrostatic force of repulsion between ...
Liquid–liquid extraction

Liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) consists in transferring one (or more) solute(s) contained in a feed solution to another immiscible liquid (solvent). The solvent that is enriched in solute(s) is called extract. The feed solution that is depleted in solute(s) is called raffinate.Liquid–liquid extraction also known as solvent extraction and partitioning, is a method to separate compounds based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids, usually water and an organic solvent. It is an extraction of a substance from one liquid into another liquid phase. Liquid–liquid extraction is a basic technique in chemical laboratories, where it is performed using a variety of apparatus, from separatory funnels to countercurrent distribution equipment. This type of process is commonly performed after a chemical reaction as part of the work-up.The term partitioning is commonly used to refer to the underlying chemical and physical processes involved in liquid–liquid extraction, but on another reading may be fully synonymous with it. The term solvent extraction can also refer to the separation of a substance from a mixture by preferentially dissolving that substance in a suitable solvent. In that case, a soluble compound is separated from an insoluble compound or a complex matrix.Solvent extraction is used in nuclear reprocessing, ore processing, the production of fine organic compounds, the processing of perfumes, the production of vegetable oils and biodiesel, and other industries.Liquid–liquid extraction is possible in non-aqueous systems: In a system consisting of a molten metal in contact with molten salts, metals can be extracted from one phase to the other. This is related to a mercury electrode where a metal can be reduced, the metal will often then dissolve in the mercury to form an amalgam that modifies its electrochemistry greatly. For example, it is possible for sodium cations to be reduced at a mercury cathode to form sodium amalgam, while at an inert electrode (such as platinum) the sodium cations are not reduced. Instead, water is reduced to hydrogen. A detergent or fine solid can be used to stabilize an emulsion, or third phase.