Protein and proteome analytics
... One- or two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with subsequent sensitive staining of the proteins Scanning of the gels with subsequent evaluation and ...
... One- or two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with subsequent sensitive staining of the proteins Scanning of the gels with subsequent evaluation and ...
CRYSTAL 24 Abstract Submission Form
... and in inflammation and therefore have great potential for medical application. Several hundreds of these genes have been identified in this collaborative work using microarray experiments. This set of genes – many of which encode novel proteins of unknown structure and function – has been targetted ...
... and in inflammation and therefore have great potential for medical application. Several hundreds of these genes have been identified in this collaborative work using microarray experiments. This set of genes – many of which encode novel proteins of unknown structure and function – has been targetted ...
Mass Spectrometers - Porto Conte Ricerche
... accurate information on the structure and molecular weight of biomolecules such as peptides, proteins, oligonucleotides and carbohydrates, as well as synthetic polymers. Furthermore, through the PMF (Peptide MassFingerprinting) technique, it enables ultra-fast identification of the proteins separate ...
... accurate information on the structure and molecular weight of biomolecules such as peptides, proteins, oligonucleotides and carbohydrates, as well as synthetic polymers. Furthermore, through the PMF (Peptide MassFingerprinting) technique, it enables ultra-fast identification of the proteins separate ...
Isolation of proteins
... forms: cationic (red), neutral (green) and anionic (blue) -under acidic conditions, the dye is predominantly in the protonated cationic form (red) -when the dye binds to proteins, it is converted to a stable form (blue) -it is this blue form that is detected at 595 nm to quantify the concentration o ...
... forms: cationic (red), neutral (green) and anionic (blue) -under acidic conditions, the dye is predominantly in the protonated cationic form (red) -when the dye binds to proteins, it is converted to a stable form (blue) -it is this blue form that is detected at 595 nm to quantify the concentration o ...
Explanation of Scaffold`s Display Options - Proteome Software
... question. This number is the number of assigned spectra for this protein divided by the total spectra in the sample (as seen in the Load Data View). Assigned spectra: This is the number of spectra which Protein Prophet assigns to the protein in question.The peptides represented by these spectra may ...
... question. This number is the number of assigned spectra for this protein divided by the total spectra in the sample (as seen in the Load Data View). Assigned spectra: This is the number of spectra which Protein Prophet assigns to the protein in question.The peptides represented by these spectra may ...
Let`s Get Pumped Up about Proteins!!!
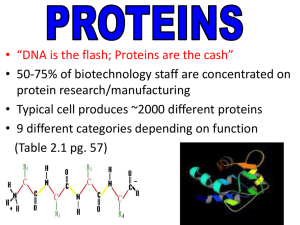
... • Typical cell produces ~2000 different proteins • 9 different categories depending on function (Table 2.1 pg. 57) ...
... • Typical cell produces ~2000 different proteins • 9 different categories depending on function (Table 2.1 pg. 57) ...
Biological Building Blocks Andrew Rylaarsdam
... how they fold and bind metals. Peptides are miniature proteins which are often used by the body as pheromones and signaling molecules. Studying peptides is also important because they can serve as a model system for the binding pockets which exist in much larger proteins. Proteins are an essential p ...
... how they fold and bind metals. Peptides are miniature proteins which are often used by the body as pheromones and signaling molecules. Studying peptides is also important because they can serve as a model system for the binding pockets which exist in much larger proteins. Proteins are an essential p ...
Proteomics
... • Most proteins interact with more than one other protein in the cell. • Many proteins may have multiple tasks in a cell. ...
... • Most proteins interact with more than one other protein in the cell. • Many proteins may have multiple tasks in a cell. ...
Chapter 5 Separations: I) Based on Charge or pI A) Electrophoresis
... a peptide and result in the cleavage of this amino acid from the chain as a phenylthiohydantoin (PTH) derivative. The PTH derivative can then be identified by chromatographic techniques by its retention time compared to standards. Advantages: This can be fully automated. Disadvantages: 1) Must have ...
... a peptide and result in the cleavage of this amino acid from the chain as a phenylthiohydantoin (PTH) derivative. The PTH derivative can then be identified by chromatographic techniques by its retention time compared to standards. Advantages: This can be fully automated. Disadvantages: 1) Must have ...
File
... • These interactions may include hydrogen bonds, disulphide bridges, ionic interactions, polar associations, etc. • The affinity or repulsion of side chains will affect the overall shape of the polypeptide chain and are determined by the position of specific amino acids within a sequence. ...
... • These interactions may include hydrogen bonds, disulphide bridges, ionic interactions, polar associations, etc. • The affinity or repulsion of side chains will affect the overall shape of the polypeptide chain and are determined by the position of specific amino acids within a sequence. ...
Proteins
... 6. Label the type of bond used to make proteins. 7. Draw arrows to identify these bonds in your model 8. Label the N-terminus and C-terminus 9. Put SQUARES around the R groups 10. Use your amino acid chart to identify & label the type of R group (non-polar, polar, charge basic, charged acidic, etc) ...
... 6. Label the type of bond used to make proteins. 7. Draw arrows to identify these bonds in your model 8. Label the N-terminus and C-terminus 9. Put SQUARES around the R groups 10. Use your amino acid chart to identify & label the type of R group (non-polar, polar, charge basic, charged acidic, etc) ...
Chapter 20 Amino acids and proteins
... 2. Given an amino acid, classify it as non-polar, polar, acidic, or basic. 3. Given an amino acid, determine if it is a D or L- amino acid. 4. Draw the Fischer projections of amino acids. 20.3 amino acids as acids and bases 1. Draw the ionic form of an amino acid at the pH above the pI, at the pI an ...
... 2. Given an amino acid, classify it as non-polar, polar, acidic, or basic. 3. Given an amino acid, determine if it is a D or L- amino acid. 4. Draw the Fischer projections of amino acids. 20.3 amino acids as acids and bases 1. Draw the ionic form of an amino acid at the pH above the pI, at the pI an ...
Proteins
... Mass Spectrometry for Proteins 1. ESI-Ion Trap Sample in solution, lower mass limit. 2. MALDI-TOF ...
... Mass Spectrometry for Proteins 1. ESI-Ion Trap Sample in solution, lower mass limit. 2. MALDI-TOF ...
Proteomics – 2D gels - Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Now that the proteins have been separated by isoelectic point, they can be analyzed based on their mass. Proteins are separated by mass using Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate. SDS acts as a detergent to uncoil the protein and give it a negative charge, since the proteins have zero charge after the isoelectic ...
... Now that the proteins have been separated by isoelectic point, they can be analyzed based on their mass. Proteins are separated by mass using Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate. SDS acts as a detergent to uncoil the protein and give it a negative charge, since the proteins have zero charge after the isoelectic ...
Protein Aggregation in High-Protein Caramel
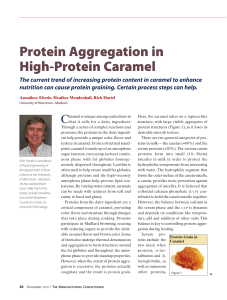
... Here, the caramel takes on a tapioca-like structure, with large visible aggregates of protein structures (Figure 1), as it loses its desirable smooth texture. There are two general categories of proteins in milk — the caseins (≈80%) and the serum proteins (≈20%). The various casein proteins form int ...
... Here, the caramel takes on a tapioca-like structure, with large visible aggregates of protein structures (Figure 1), as it loses its desirable smooth texture. There are two general categories of proteins in milk — the caseins (≈80%) and the serum proteins (≈20%). The various casein proteins form int ...
protein Synthesis
... 1. Protein synthesis is2. The set of instructions in a cell is called? 3. DNA has the information to make what? 4. What do proteins do? What do enzymes do? 5. Where is DNA located? What are genes? 6. What units are proteins made from? Where are proteins synthesized? 7. How does the DNA information g ...
... 1. Protein synthesis is2. The set of instructions in a cell is called? 3. DNA has the information to make what? 4. What do proteins do? What do enzymes do? 5. Where is DNA located? What are genes? 6. What units are proteins made from? Where are proteins synthesized? 7. How does the DNA information g ...
Lecture 1
... Protein 3 contains a prosthetic group. The secondary structure of protein 3 is all a-helix. These proteins have both secondary and tertiary structure. ...
... Protein 3 contains a prosthetic group. The secondary structure of protein 3 is all a-helix. These proteins have both secondary and tertiary structure. ...
Determination of Proteins
... membrane proteins which are hydrophobic •Absorption maxima in the ultraviolet region •Proteins are charged molecules, but the charge depend on the pH of the buffer. •Move under an electric field and can be separated by electrophoresis ...
... membrane proteins which are hydrophobic •Absorption maxima in the ultraviolet region •Proteins are charged molecules, but the charge depend on the pH of the buffer. •Move under an electric field and can be separated by electrophoresis ...
2016 N1 Week 4
... Warm UP Identify the following properties as either a carbohydrate or a lipid: 1. Does not dissolve in water. 2. The monomer is monosaccharide. 3. This molecule is not a true polymer. 4. The ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is 2:1. 5. Identify the following as a carb or lipid. B A ...
... Warm UP Identify the following properties as either a carbohydrate or a lipid: 1. Does not dissolve in water. 2. The monomer is monosaccharide. 3. This molecule is not a true polymer. 4. The ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is 2:1. 5. Identify the following as a carb or lipid. B A ...
Hemagglutinin Protein (HA1 Subunit) (His Tag)
... Western Australia/1756/1983(H15N2)) hemagglutinin (ABB90704.1) (ABB90704.1) (Met1-Arg349), termed as HA1, was expressed with a Cterminal polyhistidine tag. ...
... Western Australia/1756/1983(H15N2)) hemagglutinin (ABB90704.1) (ABB90704.1) (Met1-Arg349), termed as HA1, was expressed with a Cterminal polyhistidine tag. ...
051507
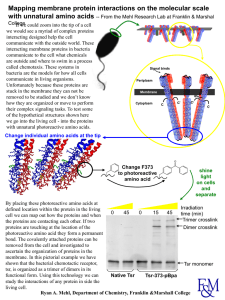
... pKa/pI – Side chains may have different pKas • pKa affected by charges on amino/carboxyl groups • pKa may be affected by interactions with other side chains in the larger molecule ...
... pKa/pI – Side chains may have different pKas • pKa affected by charges on amino/carboxyl groups • pKa may be affected by interactions with other side chains in the larger molecule ...
information. - Magellan BioScience
... motifs that can be identified to have new activity. These can be discovered as new leads for drug or other research. From these leads a smaller peptide can be made or changes in the sequence can be studied to increase the activity. Considering 3 amino acids as a motif (similar to an antigenic determ ...
... motifs that can be identified to have new activity. These can be discovered as new leads for drug or other research. From these leads a smaller peptide can be made or changes in the sequence can be studied to increase the activity. Considering 3 amino acids as a motif (similar to an antigenic determ ...
Hot Topics in Protein Medicinal Chemistry
... David Tirrell, California Institute of Technology “Non-Canonical Amino Acids as Tools for Protein Medicinal Chemistry” ...
... David Tirrell, California Institute of Technology “Non-Canonical Amino Acids as Tools for Protein Medicinal Chemistry” ...
Protein mass spectrometry

Protein mass spectrometry refers to the application of mass spectrometry to the study of proteins. Mass spectrometry is an important emerging method for the characterization of proteins. The two primary methods for ionization of whole proteins are electrospray ionization (ESI) and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI). In keeping with the performance and mass range of available mass spectrometers, two approaches are used for characterizing proteins. In the first, intact proteins are ionized by either of the two techniques described above, and then introduced to a mass analyzer. This approach is referred to as ""top-down"" strategy of protein analysis. In the second, proteins are enzymatically digested into smaller peptides using a protease such as trypsin. Subsequently these peptides are introduced into the mass spectrometer and identified by peptide mass fingerprinting or tandem mass spectrometry. Hence, this latter approach (also called ""bottom-up"" proteomics) uses identification at the peptide level to infer the existence of proteins.Whole protein mass analysis is primarily conducted using either time-of-flight (TOF) MS, or Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance (FT-ICR). These two types of instrument are preferable here because of their wide mass range, and in the case of FT-ICR, its high mass accuracy. Mass analysis of proteolytic peptides is a much more popular method of protein characterization, as cheaper instrument designs can be used for characterization. Additionally, sample preparation is easier once whole proteins have been digested into smaller peptide fragments. The most widely used instrument for peptide mass analysis are the MALDI time-of-flight instruments as they permit the acquisition of peptide mass fingerprints (PMFs) at high pace (1 PMF can be analyzed in approx. 10 sec). Multiple stage quadrupole-time-of-flight and the quadrupole ion trap also find use in this application.