NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... normally strong enough to hold the protons and neutrons together. However, sometimes the force of repulsion due to the protons having the same charge overcomes the strong nuclear force and the atom breaks apart. ...
... normally strong enough to hold the protons and neutrons together. However, sometimes the force of repulsion due to the protons having the same charge overcomes the strong nuclear force and the atom breaks apart. ...
Alpha Beta Fission Fusion
... a T½ of five days. Bi215, by comparison, undergoes decay to Po215 with a T½ of 7.6 minutes, and Bi208 undergoes yet another mode of radioactive decay (called electron capture) with a T½ of 368,000 years! Stimulated Nuclear Reactions While many elements undergo radioactive decay naturally, nuclear ...
... a T½ of five days. Bi215, by comparison, undergoes decay to Po215 with a T½ of 7.6 minutes, and Bi208 undergoes yet another mode of radioactive decay (called electron capture) with a T½ of 368,000 years! Stimulated Nuclear Reactions While many elements undergo radioactive decay naturally, nuclear ...
CHEM 1211K Test I MULTIPLE CHOICE. (3 points each) 1
... the same mass and mass is spread essentially uniformly throughout the atom E) mass is spread essentially uniformly throughout the atom 20) Cathode rays are deflected away from a negatively charged plate because __________. A) they are negatively charged particles B) they are not particles C) they ar ...
... the same mass and mass is spread essentially uniformly throughout the atom E) mass is spread essentially uniformly throughout the atom 20) Cathode rays are deflected away from a negatively charged plate because __________. A) they are negatively charged particles B) they are not particles C) they ar ...
Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter Date:
... 1. We have discovered that atoms can be broken down into subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons - We have also learned that quantum particles exist: quarks, leptons, positrons etc. 2. Atoms of an element are not always identical. Some elements have atoms with different masses. These a ...
... 1. We have discovered that atoms can be broken down into subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons - We have also learned that quantum particles exist: quarks, leptons, positrons etc. 2. Atoms of an element are not always identical. Some elements have atoms with different masses. These a ...
1.1 to 1.4
... describe how substances react with each other in a chemical reaction to form a new substance with different properties • example: reactive and inert (unreactive) Note: proof of a chemical reaction could be a change in 5 colour, energy, state or odour. ...
... describe how substances react with each other in a chemical reaction to form a new substance with different properties • example: reactive and inert (unreactive) Note: proof of a chemical reaction could be a change in 5 colour, energy, state or odour. ...
Test 2 Review Test 2 Review (15-16)_2
... (14) ____________ Which column from above contains the alkaline earth metals? (15) ____________ Which column from above contains the Noble Gases? (16) ____________ Which column from above contains the most reactive non-metals? (17) ____________ Which column from above contains VERY non-reactive elem ...
... (14) ____________ Which column from above contains the alkaline earth metals? (15) ____________ Which column from above contains the Noble Gases? (16) ____________ Which column from above contains the most reactive non-metals? (17) ____________ Which column from above contains VERY non-reactive elem ...
atomic mass - ImlerBiology
... The atomic number tells you the number of protons The atomic mass is equal to the number of protons + the average number of neutrons In some atoms, called isotopes there are more or less neutrons. Isotopes usually have slightly different properties than their parent atoms. ...
... The atomic number tells you the number of protons The atomic mass is equal to the number of protons + the average number of neutrons In some atoms, called isotopes there are more or less neutrons. Isotopes usually have slightly different properties than their parent atoms. ...
Nuclear - chemmybear.com
... (d) Nuclear fusion requires large amounts of energy (a) 94Pu 2 + 92U and to get started, whereas nuclear fission can ocCopyright 1970 to 2001 by Educational Testing Service, Princeton, NJ 08541. All rights reserved. For face-to-face teaching purposes, classroom teachers are permitted to reprodu ...
... (d) Nuclear fusion requires large amounts of energy (a) 94Pu 2 + 92U and to get started, whereas nuclear fission can ocCopyright 1970 to 2001 by Educational Testing Service, Princeton, NJ 08541. All rights reserved. For face-to-face teaching purposes, classroom teachers are permitted to reprodu ...
Periodic Table ppt
... The number of Protons in atom is also the Atomic number, so therefore the Atomic number also represents the amount of Protons in the nucleus of that Atom. ...
... The number of Protons in atom is also the Atomic number, so therefore the Atomic number also represents the amount of Protons in the nucleus of that Atom. ...
21J 2011 The Polywell Nuclear Reactor Website July 4, 2011
... atom, and giving the rest of the atom a net positive electrical charge. Neutrons can cause already existing chemicals in air, water or other nearby materials to become unstable and radioactive. As these unstable forms of natural materials return to their normal stable state, they also can release io ...
... atom, and giving the rest of the atom a net positive electrical charge. Neutrons can cause already existing chemicals in air, water or other nearby materials to become unstable and radioactive. As these unstable forms of natural materials return to their normal stable state, they also can release io ...
Early Atomic Theorists
... isotopes of an element Change in the number of protons results in a new atom Change in the number of electrons results in an ion (+ or – charge) Change in the number of neutrons results in an isotope ...
... isotopes of an element Change in the number of protons results in a new atom Change in the number of electrons results in an ion (+ or – charge) Change in the number of neutrons results in an isotope ...
Identify which of the three subatomic particles (p+, n, e–): is the
... ‘neutrons’ and ‘electrons’. An atom is a thing made up from protons neutrons and electrons. The center of an atom contains the nucleus witch inside contains protons ( P+) neutrons (N). the outside of the attom is a cloud that is created by electrons forming a cloud around the nucleus by moving quick ...
... ‘neutrons’ and ‘electrons’. An atom is a thing made up from protons neutrons and electrons. The center of an atom contains the nucleus witch inside contains protons ( P+) neutrons (N). the outside of the attom is a cloud that is created by electrons forming a cloud around the nucleus by moving quick ...
History of Modern Atomic Theory-2012
... 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties. 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. 4. Atoms of different elements can combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form chemical compoun ...
... 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties. 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. 4. Atoms of different elements can combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form chemical compoun ...
Practice problems for chapter 1, 2 and 3 1) A small amount of salt
... D) elemental copper E) milk 3) For which of the following can the composition vary? A) pure substance B) element C) both homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures D) homogeneous mixture E) heterogeneous mixture 4) An element cannot __________. 5) Homogeneous mixtures are also known as __________. 6) In ...
... D) elemental copper E) milk 3) For which of the following can the composition vary? A) pure substance B) element C) both homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures D) homogeneous mixture E) heterogeneous mixture 4) An element cannot __________. 5) Homogeneous mixtures are also known as __________. 6) In ...
Slide 1
... • Mass number is used to describe the nuclear content of one isotope (usually the most abundant) of an element. • Atomic mass is the weighted average of all of the isotopes of an element. • Atomic masses on the periodic table are not whole numbers because they contain the mass numbers all of the is ...
... • Mass number is used to describe the nuclear content of one isotope (usually the most abundant) of an element. • Atomic mass is the weighted average of all of the isotopes of an element. • Atomic masses on the periodic table are not whole numbers because they contain the mass numbers all of the is ...
Review: theory vs law the atomic theory contributions of early scientists
... Neutral Inside the Neutron Heavy (similar to nucleus protons) Oct 711:36 AM ...
... Neutral Inside the Neutron Heavy (similar to nucleus protons) Oct 711:36 AM ...
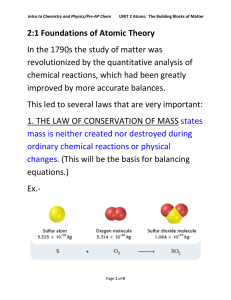
2:1 Foundations of Atomic Theory In the 1790s the study of matter
... Ex.- Silver [Ag] has an atomic number of 47. This means that a silver atom has 47 protons, and since all atoms are neutral, 47 electrons. ...
... Ex.- Silver [Ag] has an atomic number of 47. This means that a silver atom has 47 protons, and since all atoms are neutral, 47 electrons. ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.