Atomic Structure
... the electrical repulsions between positively charged protons. It turns out that these forces of electrical repulsions are overcome by an attractive force between protons and neutrons called the strong nuclear force. At small distances inside a nucleus, this force is stronger than the electromagnetic ...
... the electrical repulsions between positively charged protons. It turns out that these forces of electrical repulsions are overcome by an attractive force between protons and neutrons called the strong nuclear force. At small distances inside a nucleus, this force is stronger than the electromagnetic ...
1st Six Weeks Review
... Click on “Gizmo” above the picture. Move objects onto the scale & into the cylinder & calculate the density to predict if the object will sink or float. ...
... Click on “Gizmo” above the picture. Move objects onto the scale & into the cylinder & calculate the density to predict if the object will sink or float. ...
Friday, Feb 3, 2006
... 11) Thomson passed an electric current through sealed glass tubes filled with gases The resulting glowing beam consisted of tiny negatively charged particles moving at high speed. Thomson concluded that electrons must be parts of the atoms of all elements. Millikan determined the charge and mass of ...
... 11) Thomson passed an electric current through sealed glass tubes filled with gases The resulting glowing beam consisted of tiny negatively charged particles moving at high speed. Thomson concluded that electrons must be parts of the atoms of all elements. Millikan determined the charge and mass of ...
The Atom
... Dates (some may not have dates) Important Peoples Names What they found/discovered/believed to be true The experiment they did Picture of the model they developed (if there is one) ...
... Dates (some may not have dates) Important Peoples Names What they found/discovered/believed to be true The experiment they did Picture of the model they developed (if there is one) ...
Atomic and Nuclear Physics Atomic structure
... to be less than the sum of the masses of the constituent protons and neutrons. ● Mass defect (deficit) - difference between the mass of a nucleus and the sum of the masses of its isolated nucleons ● A bound system has a lower potential energy than its constituent parts; this is what keeps the system ...
... to be less than the sum of the masses of the constituent protons and neutrons. ● Mass defect (deficit) - difference between the mass of a nucleus and the sum of the masses of its isolated nucleons ● A bound system has a lower potential energy than its constituent parts; this is what keeps the system ...
Atom Notes - mcewenscience
... • This is due to the electromagnetic force. • The electromagnetic force keeps electrons around the nucleus because they are attracted to the protons (opposites attract!) • The strong force overcomes the electromagnetic force and keeps protons in the nucleus close together. ...
... • This is due to the electromagnetic force. • The electromagnetic force keeps electrons around the nucleus because they are attracted to the protons (opposites attract!) • The strong force overcomes the electromagnetic force and keeps protons in the nucleus close together. ...
The diameter of a Ni atom is
... • Both are characterized by • Both are characterized by the their physical and chemical nature of their sub-atomic properties structure. ...
... • Both are characterized by • Both are characterized by the their physical and chemical nature of their sub-atomic properties structure. ...
Mass-Energy Equivalence - Dr. Haleys Physics Class
... Fission breaks the nucleus into two smaller pieces and often releases one or more extra neutrons. Some of the energy released by the reaction appears as gamma rays and some as kinetic energy of the smaller nuclei and the extra neutrons. ...
... Fission breaks the nucleus into two smaller pieces and often releases one or more extra neutrons. Some of the energy released by the reaction appears as gamma rays and some as kinetic energy of the smaller nuclei and the extra neutrons. ...
Mass-Energy Equivalence
... Fission breaks the nucleus into two smaller pieces and often releases one or more extra neutrons. Some of the energy released by the reaction appears as gamma rays and some as kinetic energy of the smaller nuclei and the extra neutrons. ...
... Fission breaks the nucleus into two smaller pieces and often releases one or more extra neutrons. Some of the energy released by the reaction appears as gamma rays and some as kinetic energy of the smaller nuclei and the extra neutrons. ...
Section 2A
... (protons and neutrons). A complete chemical symbol not only tells the symbol for an element, but also the information about atomic number, atomic mass and charge in a condensed fashion ...
... (protons and neutrons). A complete chemical symbol not only tells the symbol for an element, but also the information about atomic number, atomic mass and charge in a condensed fashion ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... 3-4 Changes in the Nucleus Nuclear Stability: - for elements with atomic numbers between 1 and 20, the number of neutrons to protons are about the same. - Those elements between 20 and 83 require an increasingly larger ratio of neutrons to protons. - Elements beyond 83 naturally encounter nuclear d ...
... 3-4 Changes in the Nucleus Nuclear Stability: - for elements with atomic numbers between 1 and 20, the number of neutrons to protons are about the same. - Those elements between 20 and 83 require an increasingly larger ratio of neutrons to protons. - Elements beyond 83 naturally encounter nuclear d ...
Atomic Structure
... If the number of protons changes then the identity of the element changes with it! Atomic Number (Z) – the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of that element Z = # of protons ...
... If the number of protons changes then the identity of the element changes with it! Atomic Number (Z) – the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of that element Z = # of protons ...
Nuclear Reactions - Socastee High School
... • A new isotope is created when an atom captures a neutron. • If this isotope is unstable then a neutron can convert into a proton, releasing an electron. • This is called beta decay and is a form of radioactive decay also observed on Earth. • By converting a neutron into a proton the atom has incre ...
... • A new isotope is created when an atom captures a neutron. • If this isotope is unstable then a neutron can convert into a proton, releasing an electron. • This is called beta decay and is a form of radioactive decay also observed on Earth. • By converting a neutron into a proton the atom has incre ...
Science Homework week 2
... 6. What information would you use to distinguish between atoms of different elements? The numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons. 7. Use an example to identify the smallest unit of an element. 8 a. Dalton proposed his atomic theory in 1808. Outline the theory. All matter is composed of atoms, A ...
... 6. What information would you use to distinguish between atoms of different elements? The numbers of protons, neutrons and electrons. 7. Use an example to identify the smallest unit of an element. 8 a. Dalton proposed his atomic theory in 1808. Outline the theory. All matter is composed of atoms, A ...
MORE ABOUT PROTONS, NEUTRONS AND ELECTRONS
... atoms have the same number of protons and electrons but the numbers of neutrons differ. Atoms of the same element but with different atomic masses are called ISOTOPES. Most elements have some naturally occuring isotopes including carbon, hydrogen and oxygen - which means that you have a few isoptope ...
... atoms have the same number of protons and electrons but the numbers of neutrons differ. Atoms of the same element but with different atomic masses are called ISOTOPES. Most elements have some naturally occuring isotopes including carbon, hydrogen and oxygen - which means that you have a few isoptope ...
Name - shssci
... All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-numbered ratios to form chemical compounds. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged. 14. Calculate the maximum number of electrons that can fit in the 8th ...
... All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-numbered ratios to form chemical compounds. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged. 14. Calculate the maximum number of electrons that can fit in the 8th ...
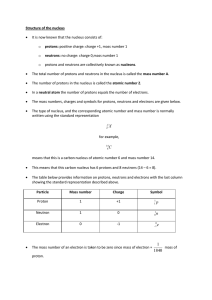
Structure of the nucleus • It is now known that the nucleus consists of
... (the equation is balanced, giving unknown daughter nucleus atomic number 88 and mass number 226. The periodic table is used to identify the element with atomic number 88 as Radon). ...
... (the equation is balanced, giving unknown daughter nucleus atomic number 88 and mass number 226. The periodic table is used to identify the element with atomic number 88 as Radon). ...
Carbon Isotopes
... The mass of an atom is mainly in the nucleus. Protons and neutrons have an approximately equal mass of one atomic mass unit. Electrons have negligible mass. Therefore, the mass of an atom is equal to the sum of the number of protons and neutrons. This number is called the atomic mass number of the a ...
... The mass of an atom is mainly in the nucleus. Protons and neutrons have an approximately equal mass of one atomic mass unit. Electrons have negligible mass. Therefore, the mass of an atom is equal to the sum of the number of protons and neutrons. This number is called the atomic mass number of the a ...
Pre-AP Chemistry
... 2 • Atomic & Molecular Structure Atomic Structure Notes #2 Section Objectives Students know how to relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its atomic number and atomic mass. (1a) Students know the nucleus of the atom is much smaller than the atom yet contains most of its mass. ...
... 2 • Atomic & Molecular Structure Atomic Structure Notes #2 Section Objectives Students know how to relate the position of an element in the periodic table to its atomic number and atomic mass. (1a) Students know the nucleus of the atom is much smaller than the atom yet contains most of its mass. ...
CHAPTER 4: ABUNDANCE AND RADIOACTIVITY OF UNSTABLE
... distribution is such that the maximum in this distribution is at an energy about one third of the maximum energy. As mentioned above, in some cases the resulting daughter nucleus is not in an excited state, so that no g radiation is emitted. This happens to be the case with the two isotopes that are ...
... distribution is such that the maximum in this distribution is at an energy about one third of the maximum energy. As mentioned above, in some cases the resulting daughter nucleus is not in an excited state, so that no g radiation is emitted. This happens to be the case with the two isotopes that are ...
Test Review: Unit 1 - Ms. Hill`s Pre
... a. Fusion: The combination of smaller molecule into larger ones. This happens on the sun. b. Fission: The splitting of large molecules into smaller radioactive daughter isotopes (“Mean Girls”) we do this in nuclear reactor and bombs! c. The big picture….both nuclear reaction result in the release of ...
... a. Fusion: The combination of smaller molecule into larger ones. This happens on the sun. b. Fission: The splitting of large molecules into smaller radioactive daughter isotopes (“Mean Girls”) we do this in nuclear reactor and bombs! c. The big picture….both nuclear reaction result in the release of ...
Introduction to the Atom
... element which have different number of neutrons which has an effect on the weight of the atom. Isotopes are identified by the mass number which is the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. An example is on the left which are all variations of the element carbon. ...
... element which have different number of neutrons which has an effect on the weight of the atom. Isotopes are identified by the mass number which is the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. An example is on the left which are all variations of the element carbon. ...