Chemistry: Matter and Change
... Types of Radiation (cont.) • Gamma rays are high-energy electromagnetic radiation. • Gamma rays (short wavelength) are photons, which are high-energy • Gamma rays have no mass or charge so the emission of gamma rays does not change the atomic number or mass number of a nucleus. • Gamma rays almost ...
... Types of Radiation (cont.) • Gamma rays are high-energy electromagnetic radiation. • Gamma rays (short wavelength) are photons, which are high-energy • Gamma rays have no mass or charge so the emission of gamma rays does not change the atomic number or mass number of a nucleus. • Gamma rays almost ...
Match the person / institution with the concept / discovery
... containing positive protons and neutral neutrons. The behavior of each electron is described in terms of probabilities that are used to identify a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron of that energy. b. Negative electrons are found outside a small, dense, massi ...
... containing positive protons and neutral neutrons. The behavior of each electron is described in terms of probabilities that are used to identify a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron of that energy. b. Negative electrons are found outside a small, dense, massi ...
Notes
... • Every element wants to have a full outer orbit – then they are stable – so… • if an element has it’s 1st orbit full and stable – it will have 2 valence e• if an element has it’s 2nd , or 3rd orbit full and stable – it will have 8 valence e- (we call that a Stable octet) • Everything wants to bind ...
... • Every element wants to have a full outer orbit – then they are stable – so… • if an element has it’s 1st orbit full and stable – it will have 2 valence e• if an element has it’s 2nd , or 3rd orbit full and stable – it will have 8 valence e- (we call that a Stable octet) • Everything wants to bind ...
Atomic Theory - Portland Public Schools
... disintegrate releasing either an alpha particle or a beta particle as well as some high energy gamma radiation. ...
... disintegrate releasing either an alpha particle or a beta particle as well as some high energy gamma radiation. ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... All nuclear decay is accompanied by a release of energy. Alpha and beta particles have ...
... All nuclear decay is accompanied by a release of energy. Alpha and beta particles have ...
File
... Daltons atomic theory was based on the following hypotheses : 1. Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other ele ...
... Daltons atomic theory was based on the following hypotheses : 1. Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other ele ...
Notes: Nuclear Chemistry
... Infrared is the region of the electromagnetic spectrum that extends from the visible region to about one millimeter (in wavelength). Infrared waves include thermal radiation. For example, burning charcoal may not give off light, but it does emit infrared radiation which is felt as heat. Infrared ra ...
... Infrared is the region of the electromagnetic spectrum that extends from the visible region to about one millimeter (in wavelength). Infrared waves include thermal radiation. For example, burning charcoal may not give off light, but it does emit infrared radiation which is felt as heat. Infrared ra ...
What is an atomic number and an atomic mass?
... If you know the atomic number of an element, you also know the number of electrons in an atom of that element - they are both the same. They are the same because an atom has neither a positive nor a negative charge. It is neutral. In order for an atom to be neutral, the positive charges of the proto ...
... If you know the atomic number of an element, you also know the number of electrons in an atom of that element - they are both the same. They are the same because an atom has neither a positive nor a negative charge. It is neutral. In order for an atom to be neutral, the positive charges of the proto ...
nuclear decays, radioactivity, and reactions
... A is sum of protons and neutrons, Z is number of protons also called atomic number, the principle number that defines the place of an element in the periodic table, X is called parent nucleus for example and Y is called daughter nucleus ...
... A is sum of protons and neutrons, Z is number of protons also called atomic number, the principle number that defines the place of an element in the periodic table, X is called parent nucleus for example and Y is called daughter nucleus ...
Homework #1 Atoms
... in whole-number ratios. 3. Chemical reactions occur when _____________ are separated, joined, or rearranged. ...
... in whole-number ratios. 3. Chemical reactions occur when _____________ are separated, joined, or rearranged. ...
Protons + Neutrons
... Hydrogen – 1 (has one particle in the nucleus *the one particle in the nucleus is a proton Hydrogen – 2 (has 2 particles in the nucleus) *Subtract the atomic number from the new atomic mass to get the new number of neutrons) Hydrogen – 3 (has three particles in the nucleus) *Only one particle ...
... Hydrogen – 1 (has one particle in the nucleus *the one particle in the nucleus is a proton Hydrogen – 2 (has 2 particles in the nucleus) *Subtract the atomic number from the new atomic mass to get the new number of neutrons) Hydrogen – 3 (has three particles in the nucleus) *Only one particle ...
Atomic structure - Central High School
... • Because the radiation forced protons out of the atoms, the radiation was made of heavy particles! Neutrons have mass! ...
... • Because the radiation forced protons out of the atoms, the radiation was made of heavy particles! Neutrons have mass! ...
Topic 2 Part 1 Slides - Coral Gables Senior High
... Isotopes are different atoms of the same element with different mass numbers; i.e. different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus. Isotopes have the same chemical properties (they react in exactly the same way), but have different physical properties, such as different melting points, boiling points, ...
... Isotopes are different atoms of the same element with different mass numbers; i.e. different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus. Isotopes have the same chemical properties (they react in exactly the same way), but have different physical properties, such as different melting points, boiling points, ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... • Dalton’s atomic theory states that all atoms of a given element are identical. This is mostly true • Atoms of the same element can differ in the number of neutrons • most elements have two or more isotopes • Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons (and therefore d ...
... • Dalton’s atomic theory states that all atoms of a given element are identical. This is mostly true • Atoms of the same element can differ in the number of neutrons • most elements have two or more isotopes • Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons (and therefore d ...
nuclear fission
... very radioactive product which they thought was a nucleus of a very heavy element, formed when the neutrons joined onto the uranium nucleus. However, when they analysed the products they found not elements heavier than uranium but two about half the mass number of the original uranium, a solution th ...
... very radioactive product which they thought was a nucleus of a very heavy element, formed when the neutrons joined onto the uranium nucleus. However, when they analysed the products they found not elements heavier than uranium but two about half the mass number of the original uranium, a solution th ...
Chapter 4 Quiz ____ 1. The Greek philosopher Democritus coined
... ____ 2. Which of the following is NOT part of John Dalton’s atomic theory? a. All elements are composed of atoms. b. All atoms of the same element have the same mass. c. Atoms contain subatomic particles. d. A compound contains atoms of more than one element. ____ 3. Rutherford’s gold foil experimen ...
... ____ 2. Which of the following is NOT part of John Dalton’s atomic theory? a. All elements are composed of atoms. b. All atoms of the same element have the same mass. c. Atoms contain subatomic particles. d. A compound contains atoms of more than one element. ____ 3. Rutherford’s gold foil experimen ...
Atom
... The next important development came in 1914 when Danish physicist Niels Bohr revised the model again. It had been known for some time that the light given out when atoms were heated always had specific amounts of energy, but no one had been able to explain this. Bohr suggested that the electrons mus ...
... The next important development came in 1914 when Danish physicist Niels Bohr revised the model again. It had been known for some time that the light given out when atoms were heated always had specific amounts of energy, but no one had been able to explain this. Bohr suggested that the electrons mus ...
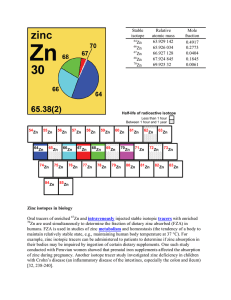
Zinc isotopes in biology Oral tracers of enriched Zn and
... anthropogenic – resulting from human activity. [return] atomic number (Z) – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. atomic weight (relative mean atomic mass) – the sum of the products of the relative atomic mass and the mole fraction of each stable and long-lived radioactive isotope of that ...
... anthropogenic – resulting from human activity. [return] atomic number (Z) – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. atomic weight (relative mean atomic mass) – the sum of the products of the relative atomic mass and the mole fraction of each stable and long-lived radioactive isotope of that ...
ATOMIC MODEL
... · Cathode Rays are a stream of very small and very light particles emitted the cathode. · These particles are negatively charged, since they travel from the Cathode () toward the Anode (+), and they are repelled by the negative plate of an electric field. · These particles are present in any fo ...
... · Cathode Rays are a stream of very small and very light particles emitted the cathode. · These particles are negatively charged, since they travel from the Cathode () toward the Anode (+), and they are repelled by the negative plate of an electric field. · These particles are present in any fo ...
Lecture Notes Chapter 4-The Structure of the Atom
... radioactive (high energy) particles. Radioactivity is caused by a proton to neutron ratio. The greater the difference between the p+ and no, the more unstable. An unstable atom will emit energy until a more stable form is reached. This is called radioactive decay. ...
... radioactive (high energy) particles. Radioactivity is caused by a proton to neutron ratio. The greater the difference between the p+ and no, the more unstable. An unstable atom will emit energy until a more stable form is reached. This is called radioactive decay. ...
Practice_Final_B
... 7. You have exactly 4 resistors: one 3 , one 4 , one 5 , and one 6 . How can you combine these to make a 2 resistor? (The symbol stands for "ohm".) A) Connect the 3 resistor in parallel with the 4 resistor. B) Connect the 3 resistor in series with the 5 resistor. C) Connect all four resistors in par ...
... 7. You have exactly 4 resistors: one 3 , one 4 , one 5 , and one 6 . How can you combine these to make a 2 resistor? (The symbol stands for "ohm".) A) Connect the 3 resistor in parallel with the 4 resistor. B) Connect the 3 resistor in series with the 5 resistor. C) Connect all four resistors in par ...
Physical Science
... of the same element must have the same number of protons but can have a different number of neutrons. These atoms are known as isotopes. ...
... of the same element must have the same number of protons but can have a different number of neutrons. These atoms are known as isotopes. ...