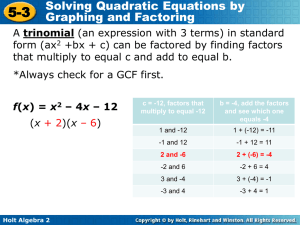
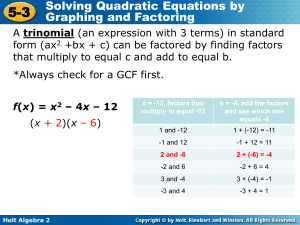
Trinomials when signs are the same
... - factor out what’s in common in both terms (13v) - write what you factored outside the parentheses ...
... - factor out what’s in common in both terms (13v) - write what you factored outside the parentheses ...
Transcendence Degree and Noether Normalization
... Reversing the roles of {x i } and {y j } in the lemma, you see that any two finite transcendence bases have the same cardinality. The lemma also implies that if one transcendence base is finite then so is any other. P By the hypothesis on {y j }, x satisfies some non-trivial polynomial P(y j , ...
... Reversing the roles of {x i } and {y j } in the lemma, you see that any two finite transcendence bases have the same cardinality. The lemma also implies that if one transcendence base is finite then so is any other. P By the hypothesis on {y j }, x satisfies some non-trivial polynomial P(y j , ...
Lecture notes for Section 5.5
... Big Idea: Polynomials are the most important topic in algebra because any equation that can be written using addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, integer powers, or roots (which are rational powers) can be solved by converting the equation into a polynomial equation. Looking at the patte ...
... Big Idea: Polynomials are the most important topic in algebra because any equation that can be written using addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, integer powers, or roots (which are rational powers) can be solved by converting the equation into a polynomial equation. Looking at the patte ...
Factorization
In mathematics, factorization (also factorisation in some forms of British English) or factoring is the decomposition of an object (for example, a number, a polynomial, or a matrix) into a product of other objects, or factors, which when multiplied together give the original. For example, the number 15 factors into primes as 3 × 5, and the polynomial x2 − 4 factors as (x − 2)(x + 2). In all cases, a product of simpler objects is obtained.The aim of factoring is usually to reduce something to “basic building blocks”, such as numbers to prime numbers, or polynomials to irreducible polynomials. Factoring integers is covered by the fundamental theorem of arithmetic and factoring polynomials by the fundamental theorem of algebra. Viète's formulas relate the coefficients of a polynomial to its roots.The opposite of polynomial factorization is expansion, the multiplying together of polynomial factors to an “expanded” polynomial, written as just a sum of terms.Integer factorization for large integers appears to be a difficult problem. There is no known method to carry it out quickly. Its complexity is the basis of the assumed security of some public key cryptography algorithms, such as RSA.A matrix can also be factorized into a product of matrices of special types, for an application in which that form is convenient. One major example of this uses an orthogonal or unitary matrix, and a triangular matrix. There are different types: QR decomposition, LQ, QL, RQ, RZ.Another example is the factorization of a function as the composition of other functions having certain properties; for example, every function can be viewed as the composition of a surjective function with an injective function. This situation is generalized by factorization systems.