solution
... Yes, it does seem that the external balance problem of a deficit country is more severe. While the macroeconomic imbalance may be equally problematic in the long run regardless of whether it is a deficit or surplus, large external deficits involve the risk that the market will fix the problem quickl ...
... Yes, it does seem that the external balance problem of a deficit country is more severe. While the macroeconomic imbalance may be equally problematic in the long run regardless of whether it is a deficit or surplus, large external deficits involve the risk that the market will fix the problem quickl ...
1 - Solution Manual Store
... most to least liquid: dollar bill, checking account, money-market mutual fund, passbook savings account, corporate stock, gold, house. 22. M2, M1, (U.S. savings bonds are part of debt, but not part of any of the monetary aggregates), M1, ...
... most to least liquid: dollar bill, checking account, money-market mutual fund, passbook savings account, corporate stock, gold, house. 22. M2, M1, (U.S. savings bonds are part of debt, but not part of any of the monetary aggregates), M1, ...
Ass no. 3 2017
... As usual, Y is output and r is the real interest rate. Government purchases, G, are 2000. a). Find an equation relating desired national saving, s, to r and Y. b). i) What value of the real interest rate clears the goods market when Y = 10,000? Use both forms of the goods market equilibrium conditio ...
... As usual, Y is output and r is the real interest rate. Government purchases, G, are 2000. a). Find an equation relating desired national saving, s, to r and Y. b). i) What value of the real interest rate clears the goods market when Y = 10,000? Use both forms of the goods market equilibrium conditio ...
Financial Sector Reading Guide – Chapters 13, 14 and 15 Chapter
... 14. What is the money multiplier formula? Explain how it is used to find the maximum amount of new checkable deposit money that can be created by the banking system. ...
... 14. What is the money multiplier formula? Explain how it is used to find the maximum amount of new checkable deposit money that can be created by the banking system. ...
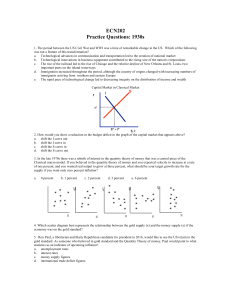
ECN202 Practice Questions: 1930s
... 9. After WWI England (UK) needed to make a decision regarding a return to the gold standard, and if they did return, they needed to set the price of the pound () in terms of gold. The basics of the problem can be seen in the table above. One of the problems was England had very high inflation rates ...
... 9. After WWI England (UK) needed to make a decision regarding a return to the gold standard, and if they did return, they needed to set the price of the pound () in terms of gold. The basics of the problem can be seen in the table above. One of the problems was England had very high inflation rates ...
ECON 1A – Macroeconomics Lecture Notes: Chapter 11
... •Barter is easy on a small scale, but is complicated in a market economy. •As money flows in the economy, it facilitates production and trade: ...
... •Barter is easy on a small scale, but is complicated in a market economy. •As money flows in the economy, it facilitates production and trade: ...
Money, Banking and Monetary Policy
... the money supply. M1 – currency, checkable deposits M2 – Near money (savings, small time deposits, MMMF) Federal Reserve Notes are token money (fiat) Checkable deposits are large component Currency held by the FED, thrift, banks are excluded ...
... the money supply. M1 – currency, checkable deposits M2 – Near money (savings, small time deposits, MMMF) Federal Reserve Notes are token money (fiat) Checkable deposits are large component Currency held by the FED, thrift, banks are excluded ...
TOTAL SPENDING = TOTAL INCOME = GDP
... bust. The government must therefore step in to keep things on an even keel. These arguments were particularly potent during and after the Great Depression of the 1930's, and were a major element giving rise to the New Deal in this country and comparable extensions of governmental intervention in oth ...
... bust. The government must therefore step in to keep things on an even keel. These arguments were particularly potent during and after the Great Depression of the 1930's, and were a major element giving rise to the New Deal in this country and comparable extensions of governmental intervention in oth ...
Homework 2, Due in class Monday August 27 at 12:10 - uc
... a. How many “spells” of unemployment occur each year in this economy? b. What percentage of the “spells” are only one month long? c. If you take all the workers unemployed each year and multiply each by the length of his or her unemployment “spell,” how many “months” of unemployment would there be i ...
... a. How many “spells” of unemployment occur each year in this economy? b. What percentage of the “spells” are only one month long? c. If you take all the workers unemployed each year and multiply each by the length of his or her unemployment “spell,” how many “months” of unemployment would there be i ...
review sheet
... will affect AD. Supply sides economics argues that decreases in taxes will increase AS. --Expansionary Fiscal Policy-- ↑government spending or ↓taxes or both → creates a budget deficit which is funded through sale of government securities. This creates an increased demand for loanable funds (loanabl ...
... will affect AD. Supply sides economics argues that decreases in taxes will increase AS. --Expansionary Fiscal Policy-- ↑government spending or ↓taxes or both → creates a budget deficit which is funded through sale of government securities. This creates an increased demand for loanable funds (loanabl ...
chapter 13 - Ken Farr (GCSU)
... When competition is present and private ownership rights are clearly defined and securely enforced by the legal system, business firms will have a strong incentive to a. innovate and develop better products and lower cost production methods. b. spend time attempting to plunder (take) the resources o ...
... When competition is present and private ownership rights are clearly defined and securely enforced by the legal system, business firms will have a strong incentive to a. innovate and develop better products and lower cost production methods. b. spend time attempting to plunder (take) the resources o ...
The relationships between currencies and gold
... the same time, failed to leave the monetary authorities sufficient room for manoeuvre. Culturally still under the influence of the gold standard, the monetary authorities were in any case little inclined to cooperate and tended to accumulate gold reserves, thereby exerting powerful deflationary pres ...
... the same time, failed to leave the monetary authorities sufficient room for manoeuvre. Culturally still under the influence of the gold standard, the monetary authorities were in any case little inclined to cooperate and tended to accumulate gold reserves, thereby exerting powerful deflationary pres ...
1 - Test banks
... most to least liquid: dollar bill, checking account, money-market mutual fund, passbook savings account, corporate stock, gold, house. 22. M2, M1, (U.S. savings bonds are part of debt, but not part of any of the monetary aggregates), M1, ...
... most to least liquid: dollar bill, checking account, money-market mutual fund, passbook savings account, corporate stock, gold, house. 22. M2, M1, (U.S. savings bonds are part of debt, but not part of any of the monetary aggregates), M1, ...
Accelerated Macro Spring 2015 Solutions to HW #4 1
... b. A financial crisis prompts households to sell off some of their stock market portfolio and deposit the proceeds into bank accounts covered by deposit insurance. Solution: As people sell their stocks and increase their deposits, the currency-deposit ratio will decline. This causes the money multip ...
... b. A financial crisis prompts households to sell off some of their stock market portfolio and deposit the proceeds into bank accounts covered by deposit insurance. Solution: As people sell their stocks and increase their deposits, the currency-deposit ratio will decline. This causes the money multip ...
Money

Money is any item or verifiable record that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services and repayment of debts in a particular country or socio-economic context, or is easily converted to such a form. The main functions of money are distinguished as: a medium of exchange; a unit of account; a store of value; and, sometimes, a standard of deferred payment. Any item or verifiable record that fulfills these functions can be considered money.Money is historically an emergent market phenomenon establishing a commodity money, but nearly all contemporary money systems are based on fiat money. Fiat money, like any check or note of debt, is without intrinsic use value as a physical commodity. It derives its value by being declared by a government to be legal tender; that is, it must be accepted as a form of payment within the boundaries of the country, for ""all debts, public and private"". Such laws in practice cause fiat money to acquire the value of any of the goods and services that it may be traded for within the nation that issues it.The money supply of a country consists of currency (banknotes and coins) and, depending on the particular definition used, one or more types of bank money (the balances held in checking accounts, savings accounts, and other types of bank accounts). Bank money, which consists only of records (mostly computerized in modern banking), forms by far the largest part of broad money in developed countries.