NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES INFLATION AND GROWTH Stanley Fischer Working Paper No. 1235
... In his work with Duncan Foley (1970 and 1971), Sidrauski was able both to use a more sophisticated definition of monetary policy and to take a step away ...
... In his work with Duncan Foley (1970 and 1971), Sidrauski was able both to use a more sophisticated definition of monetary policy and to take a step away ...
Money, Banking, and the Financial System
... 21) By designating Federal Reserve currency as legal tender, the federal government A) has ensured that Federal Reserve currency will serve as money. B) has guaranteed that Federal Reserve currency may be exchanged for an equivalent amount of gold or silver. C) has mandated that Federal Reserve curr ...
... 21) By designating Federal Reserve currency as legal tender, the federal government A) has ensured that Federal Reserve currency will serve as money. B) has guaranteed that Federal Reserve currency may be exchanged for an equivalent amount of gold or silver. C) has mandated that Federal Reserve curr ...
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from... of Economic Research Volume Title: The International Transmission of Inflation
... a systematic way the effects of O M 0 and FXO. None of them are either satisfactory or complete.2 The specific questions that are asked in this study are: (1) What are the dynamic effects (i.e. not only the impact effects, but also the short-run and long-run effects) of O M 0 and FXO on major macroe ...
... a systematic way the effects of O M 0 and FXO. None of them are either satisfactory or complete.2 The specific questions that are asked in this study are: (1) What are the dynamic effects (i.e. not only the impact effects, but also the short-run and long-run effects) of O M 0 and FXO on major macroe ...
Keynes, Keynesians and Contemporary Monetary Theory and Policy
... Thus Keynes employs Marshallian tools to present in plain English the view of an economy that fluctuates, as a consequence of a volatile marginal efficiency of capital, about a level of economic activity too low to sustain full employment because the rate of interest is too high. There is a str ...
... Thus Keynes employs Marshallian tools to present in plain English the view of an economy that fluctuates, as a consequence of a volatile marginal efficiency of capital, about a level of economic activity too low to sustain full employment because the rate of interest is too high. There is a str ...
Ecs1028 (1) - gimmenotes
... serve as a unit of account. Money is only the most convenient unit of account. Money as a store of value In any society there is a need to hold wealth or surplus production in some form or another. The most common form of holding wealth is money, since it can always be exchanged for other goods or s ...
... serve as a unit of account. Money is only the most convenient unit of account. Money as a store of value In any society there is a need to hold wealth or surplus production in some form or another. The most common form of holding wealth is money, since it can always be exchanged for other goods or s ...
Nr. 34 The Precarious Fiscal Foundations of EMU (PDF: 158.6
... place both in foreign and domestic currency, fluctuations in the country’s fiscal status are magnified, because it is the ratio of domestic debt to the primary surplus after dollar interest is subtracted that determines the price level. Foreign currency borrowing therefore acts as leverage in the FT ...
... place both in foreign and domestic currency, fluctuations in the country’s fiscal status are magnified, because it is the ratio of domestic debt to the primary surplus after dollar interest is subtracted that determines the price level. Foreign currency borrowing therefore acts as leverage in the FT ...
Lecture 11: Real Business Cycles - personal.kent.edu
... growth rate of real GDP rises when technology advances quickly and falls when it advances slowly, and, when productivity falls, the growth rate of real GDP turns negative, the actual sign of a business downturn. Warning required by the Economist-General: This idea of a real business cycle is relat ...
... growth rate of real GDP rises when technology advances quickly and falls when it advances slowly, and, when productivity falls, the growth rate of real GDP turns negative, the actual sign of a business downturn. Warning required by the Economist-General: This idea of a real business cycle is relat ...
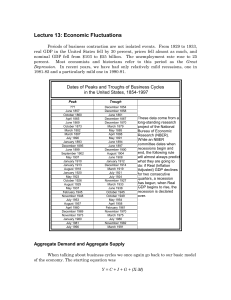
Lecture 13
... And, adjusting for the price level, Real Aggregate Demand = Y = MV/P If we want to see the slope of the aggregate demand curve, the second equation is more convenient. Holding both the money supply and velocity constant, aggregate demand curve is a downward sloping function of price. The higher the ...
... And, adjusting for the price level, Real Aggregate Demand = Y = MV/P If we want to see the slope of the aggregate demand curve, the second equation is more convenient. Holding both the money supply and velocity constant, aggregate demand curve is a downward sloping function of price. The higher the ...