3. What is the empirical formula of a compound that is
... 5. How many grams of NaCl are made if 1.36 × 1024 formula units of NaNO2 react in the presence of excess hydrochloric acid? ...
... 5. How many grams of NaCl are made if 1.36 × 1024 formula units of NaNO2 react in the presence of excess hydrochloric acid? ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... These reactions will be further discussed in Chapter 8 2. Neutralization: The most important reaction of acids and bases is called neutralization. In these reactions an acid combines with a base to form a salt and water. For example: ...
... These reactions will be further discussed in Chapter 8 2. Neutralization: The most important reaction of acids and bases is called neutralization. In these reactions an acid combines with a base to form a salt and water. For example: ...
Topic 4 Chemistry of the Elements of the Main Group
... groups: Metals, Metalloids and non-Metals Non-metals are not electrical conductors, they are characterised by a high electronegativity value (over 2). The valence electrons of non-metals are strongly attracted to their positively charged nucleus and are not available to conduct electricity. Metals ...
... groups: Metals, Metalloids and non-Metals Non-metals are not electrical conductors, they are characterised by a high electronegativity value (over 2). The valence electrons of non-metals are strongly attracted to their positively charged nucleus and are not available to conduct electricity. Metals ...
SMU: Transferring as a Chemistry Major
... Gen’l Physics with lab I UC Breadth Course UC Breadth Course Elective or minor course 1 hour PE Course ...
... Gen’l Physics with lab I UC Breadth Course UC Breadth Course Elective or minor course 1 hour PE Course ...
Section 1 The Nature of Chemical Reactions
... • The law of definite proportions states that a compound always contains the same elements in the same proportions, regardless of how the compound is made or how much of the compound is formed. • Because the law of definite proportions holds true for all chemical substances in all reactions, mole ra ...
... • The law of definite proportions states that a compound always contains the same elements in the same proportions, regardless of how the compound is made or how much of the compound is formed. • Because the law of definite proportions holds true for all chemical substances in all reactions, mole ra ...
Chapter 4 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
... three-dimensional arrangements of atoms, and so we have added several questions that will be more challenging for most students. This chapter lays the foundation for later elaboration of roles of molecular structure in various life processes. Several form/function questions assess student understand ...
... three-dimensional arrangements of atoms, and so we have added several questions that will be more challenging for most students. This chapter lays the foundation for later elaboration of roles of molecular structure in various life processes. Several form/function questions assess student understand ...
ert207 analytical chemistry
... 1) What is it (Qualitative) –identification of elements, ions or compound 2) How much is it (Quantitative) ...
... 1) What is it (Qualitative) –identification of elements, ions or compound 2) How much is it (Quantitative) ...
File
... Increases across a period; increases down a group. b. Increases across a period; decreases down a group. c. Decreases across a period; increases down a group. d. Decreases across a period; decreases down a group. ...
... Increases across a period; increases down a group. b. Increases across a period; decreases down a group. c. Decreases across a period; increases down a group. d. Decreases across a period; decreases down a group. ...
Stereochemistry - Kantipur Engineering College
... enantiomers and diastereomers. The students should understand basic concepts like chirality, plane polarized light, specific rotation, stereocenters, maximum number of stereoisomers related to the number of chiral centers, racemic mixture, meso compound, and ways to separate enantiomers from their r ...
... enantiomers and diastereomers. The students should understand basic concepts like chirality, plane polarized light, specific rotation, stereocenters, maximum number of stereoisomers related to the number of chiral centers, racemic mixture, meso compound, and ways to separate enantiomers from their r ...
aq - Wikispaces
... • Do the sheet “uncertainty” • The sheet will be corrected in class. • Procedures for an in-class exercise • Make sure your first and last name are on the sheet. • Complete as much of the sheet as you can in the time allotted. Use a pencil or dark colour pen. • When the time is up, follow the teache ...
... • Do the sheet “uncertainty” • The sheet will be corrected in class. • Procedures for an in-class exercise • Make sure your first and last name are on the sheet. • Complete as much of the sheet as you can in the time allotted. Use a pencil or dark colour pen. • When the time is up, follow the teache ...
Chem 11 Notes Booklet (pdf version)
... Notice that the water molecule can only be made by joining together two hydrogen atoms (symbol = H) with one oxygen atom (symbol = O). The formula for water will be H2O. Note: If there is no number after a symbol in a formula, assume it is a one. Example: CaO means Ca1O1 In summary, pure substan ...
... Notice that the water molecule can only be made by joining together two hydrogen atoms (symbol = H) with one oxygen atom (symbol = O). The formula for water will be H2O. Note: If there is no number after a symbol in a formula, assume it is a one. Example: CaO means Ca1O1 In summary, pure substan ...
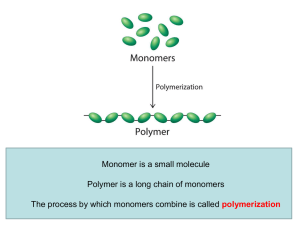
Linear Polymer
... A pendant group on a polymer is a small group of atoms (even a small chain sometimes) that hangs off of the main chain (that is, the backbone of the polymer). ...
... A pendant group on a polymer is a small group of atoms (even a small chain sometimes) that hangs off of the main chain (that is, the backbone of the polymer). ...
Design and Analysis of Chain and Network Structures from Organic
... Two different clusters were examined as building blocks in this study: a difunctional cluster, [W6O25H(AsR)2]5(R ) C6H4-4-NH2), and a tetrafunctional cluster, [Mo12O46(AsR)4]4- (R ) C6H4-4-NH3+). The former is isostructural with the previously reported phenyl derivative17 and similar to the molybden ...
... Two different clusters were examined as building blocks in this study: a difunctional cluster, [W6O25H(AsR)2]5(R ) C6H4-4-NH2), and a tetrafunctional cluster, [Mo12O46(AsR)4]4- (R ) C6H4-4-NH3+). The former is isostructural with the previously reported phenyl derivative17 and similar to the molybden ...
Objective (Local, State, National – College Board)
... weak acids and bases. Arrhenius definitions are based on these observations. Bronsted Lowry theory can be introduced by considering things that are known to be acids but are not aqueous solutions. The “accounting system” of naming acids, bases conjugate acids and conjugate bases should be mastered i ...
... weak acids and bases. Arrhenius definitions are based on these observations. Bronsted Lowry theory can be introduced by considering things that are known to be acids but are not aqueous solutions. The “accounting system” of naming acids, bases conjugate acids and conjugate bases should be mastered i ...
Balancing Reaction Equations Oxidation State Reduction
... step. Be sure the equation is balanced for both atoms and charge. • Write the net ionic equation by removing the spectators. Reduce coefficients to lowest terms. Be sure the equation is balanced for both atoms and charge. ...
... step. Be sure the equation is balanced for both atoms and charge. • Write the net ionic equation by removing the spectators. Reduce coefficients to lowest terms. Be sure the equation is balanced for both atoms and charge. ...
CHEM230P1_06_2014_Y_P1
... The pressure in the container is now increased by decreasing the volume of the container. Explain how the composition of A and B will change during this process and also state whether the equilibrium constant, KP, will increase, decrease or stay the same. ...
... The pressure in the container is now increased by decreasing the volume of the container. Explain how the composition of A and B will change during this process and also state whether the equilibrium constant, KP, will increase, decrease or stay the same. ...
The Copper Cycle
... and excess hydronium ions (H3O+) remain from the nitric acid used. 2nd Beaker: Adding NaOH(aq) to the blue solution results in the OH– ions neutralizing the H3O+ ions to form water: H3O+(aq) + OH–(aq) → 2 H2O(l). The Na+ ions and resulting water molecules are not shown. 3rd and 4th Beakers: Once all ...
... and excess hydronium ions (H3O+) remain from the nitric acid used. 2nd Beaker: Adding NaOH(aq) to the blue solution results in the OH– ions neutralizing the H3O+ ions to form water: H3O+(aq) + OH–(aq) → 2 H2O(l). The Na+ ions and resulting water molecules are not shown. 3rd and 4th Beakers: Once all ...
Final Review 2
... 76) Hydrates are defined as: a) compounds with water molecules attached to them. b) compounds that have had their water molecules removed c) compounds that have been heated to high temperatures d) none of these answers is correct. 77) Why do two nonmetals generally form covalent bonds with one anot ...
... 76) Hydrates are defined as: a) compounds with water molecules attached to them. b) compounds that have had their water molecules removed c) compounds that have been heated to high temperatures d) none of these answers is correct. 77) Why do two nonmetals generally form covalent bonds with one anot ...
6.02 × 1023 molecules = 1 mole
... One of the most well-known numbers in the study of chemistry is number of units in a mole. The number of units in a mole is called Avogadro’s number (named after the Italian physicist). The mole is defined as the number of atoms in 12.0 grams of 12C. As you can tell from the equality below, the mole ...
... One of the most well-known numbers in the study of chemistry is number of units in a mole. The number of units in a mole is called Avogadro’s number (named after the Italian physicist). The mole is defined as the number of atoms in 12.0 grams of 12C. As you can tell from the equality below, the mole ...
Eperimental studies of V.Ostwald and J.van Hoff
... process (patent 1902), used in the manufacture of nitric acid, although the basic chemistry had been patented some 64 years earlier by Kuhlmann, when it was probably of only academic interest due to the lack of a significant source of ammonia. That may have still been the state of affairs in 1902, a ...
... process (patent 1902), used in the manufacture of nitric acid, although the basic chemistry had been patented some 64 years earlier by Kuhlmann, when it was probably of only academic interest due to the lack of a significant source of ammonia. That may have still been the state of affairs in 1902, a ...
Chemistry 21A: Survey of General and Organic Chemistry
... 8. discuss the factors which affect the rate of reactions and apply Le Chatelier's Principle to equilibria. 9. state the properties and definitions of acids and bases and interpret elementary acid-base equilibria, including buffer systems. 10. describe the bonding and geometry of carbon compounds in ...
... 8. discuss the factors which affect the rate of reactions and apply Le Chatelier's Principle to equilibria. 9. state the properties and definitions of acids and bases and interpret elementary acid-base equilibria, including buffer systems. 10. describe the bonding and geometry of carbon compounds in ...
Chemistry
... matter is also addressed by physics, but while physics takes a more general and fundamental approach, chemistry is more specialized, being concerned with the composition, behavior (or reaction), structure, and properties of matter, as well as the changes it undergoes during chemical reactions.[2] It ...
... matter is also addressed by physics, but while physics takes a more general and fundamental approach, chemistry is more specialized, being concerned with the composition, behavior (or reaction), structure, and properties of matter, as well as the changes it undergoes during chemical reactions.[2] It ...
chemical reaction
... • How to Balance an Equation To balance an equation, you must use coefficients. A coefficient is a number that is placed in front of a chemical symbol or formula. • For an equation to be balanced, all atoms must be counted. So, you multiply the subscript of each element in a formula by the formula’s ...
... • How to Balance an Equation To balance an equation, you must use coefficients. A coefficient is a number that is placed in front of a chemical symbol or formula. • For an equation to be balanced, all atoms must be counted. So, you multiply the subscript of each element in a formula by the formula’s ...
getting started 3.1 hydrocarbons
... 3. In general, polar molecules have higher boiling points than less polar molecules because polar molecules have stronger intermolecular attractions that require more energy (higher temperatures) to overcome. Very large nonpolar molecules are affected by London dispersion forces that may cause their ...
... 3. In general, polar molecules have higher boiling points than less polar molecules because polar molecules have stronger intermolecular attractions that require more energy (higher temperatures) to overcome. Very large nonpolar molecules are affected by London dispersion forces that may cause their ...
2009 U. S. NATIONAL CHEMISTRY OLYMPIAD
... b. Account for the fact that standard enthalpies of formation of compounds at 25˚C may be either positive or negative. c. Explain why all elements and compounds have positive S˚ values at 25˚C. d. Give an example of a chemical species that does not have a positive S˚ value at 25 ˚C and explain why i ...
... b. Account for the fact that standard enthalpies of formation of compounds at 25˚C may be either positive or negative. c. Explain why all elements and compounds have positive S˚ values at 25˚C. d. Give an example of a chemical species that does not have a positive S˚ value at 25 ˚C and explain why i ...
Organic chemistry

Organic chemistry is a chemistry subdiscipline involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. Study of structure includes many physical and chemical methods to determine the chemical composition and the chemical constitution of organic compounds and materials. Study of properties includes both physical properties and chemical properties, and uses similar methods as well as methods to evaluate chemical reactivity, with the aim to understand the behavior of the organic matter in its pure form (when possible), but also in solutions, mixtures, and fabricated forms. The study of organic reactions includes probing their scope through use in preparation of target compounds (e.g., natural products, drugs, polymers, etc.) by chemical synthesis, as well as the focused study of the reactivities of individual organic molecules, both in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study.The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry include hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen), as well as myriad compositions based always on carbon, but also containing other elements, especially oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus (these, included in many organic chemicals in biology) and the radiostable elements of the halogens.In the modern era, the range extends further into the periodic table, with main group elements, including:Group 1 and 2 organometallic compounds, i.e., involving alkali (e.g., lithium, sodium, and potassium) or alkaline earth metals (e.g., magnesium)Metalloids (e.g., boron and silicon) or other metals (e.g., aluminium and tin)In addition, much modern research focuses on organic chemistry involving further organometallics, including the lanthanides, but especially the transition metals; (e.g., zinc, copper, palladium, nickel, cobalt, titanium and chromium)Finally, organic compounds form the basis of all earthly life and constitute a significant part of human endeavors in chemistry. The bonding patterns open to carbon, with its valence of four—formal single, double, and triple bonds, as well as various structures with delocalized electrons—make the array of organic compounds structurally diverse, and their range of applications enormous. They either form the basis of, or are important constituents of, many commercial products including pharmaceuticals; petrochemicals and products made from them (including lubricants, solvents, etc.); plastics; fuels and explosives; etc. As indicated, the study of organic chemistry overlaps with organometallic chemistry and biochemistry, but also with medicinal chemistry, polymer chemistry, as well as many aspects of materials science.