Project synopsis on
... method to record electrical activity of the brain. It is typically noninvasive, with the electrodes placed along the scalp, although invasive electrodes are sometimes used in specific applications. EEG measures voltage fluctuations resulting from ionic current within the neurons of the brain. In cli ...
... method to record electrical activity of the brain. It is typically noninvasive, with the electrodes placed along the scalp, although invasive electrodes are sometimes used in specific applications. EEG measures voltage fluctuations resulting from ionic current within the neurons of the brain. In cli ...
Project Self-Discovery
... Neurotransmitters released by axon across synaptic gap (cleft) to neighboring neuron’s dendrite ...
... Neurotransmitters released by axon across synaptic gap (cleft) to neighboring neuron’s dendrite ...
7.2 Student Notes
... Brain obtains energy using _____________________________________, which pass rapidly from the blood to the brain cells. ______________________________ helps to make ATP within the brain. CHO storage in the brain __________________________, so the supply of glucose must be continuous. ...
... Brain obtains energy using _____________________________________, which pass rapidly from the blood to the brain cells. ______________________________ helps to make ATP within the brain. CHO storage in the brain __________________________, so the supply of glucose must be continuous. ...
Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of
... E) thresholds. 11. Reuptake refers to the A) movement of neurotransmitter molecules across a synaptic gap. B) release of hormones into the bloodstream. C) inflow of positively charged ions through an axon membrane. D) reabsorption of excess neurotransmitter molecules by a sending neuron. E) the endi ...
... E) thresholds. 11. Reuptake refers to the A) movement of neurotransmitter molecules across a synaptic gap. B) release of hormones into the bloodstream. C) inflow of positively charged ions through an axon membrane. D) reabsorption of excess neurotransmitter molecules by a sending neuron. E) the endi ...
Toxic Leukoencephalopathy
... • The left MRI scan shows a malignant brain tumor before radiation; after radiation (right), the tumor is smaller but the white matter is damaged ...
... • The left MRI scan shows a malignant brain tumor before radiation; after radiation (right), the tumor is smaller but the white matter is damaged ...
psychology - Eagan High School
... The brain has no pain, because there are no nerves that register pain within the brain itself, neurosurgeons can probe the brain while a patient is conscious. They can then use feedback from the patient to identify important regions, such as those used for speech. The brain has the largest area of u ...
... The brain has no pain, because there are no nerves that register pain within the brain itself, neurosurgeons can probe the brain while a patient is conscious. They can then use feedback from the patient to identify important regions, such as those used for speech. The brain has the largest area of u ...
What We Can and What We Can`t Do with fMRI
... At any given time, the active regions of a discharging neuron’s membranes are considered to act as a current sink, whereas the inactive ones act as a current source for the active regions (Logothetis, 2008). The linear superposition of currents from all sinks and sources forms the extracellular fiel ...
... At any given time, the active regions of a discharging neuron’s membranes are considered to act as a current sink, whereas the inactive ones act as a current source for the active regions (Logothetis, 2008). The linear superposition of currents from all sinks and sources forms the extracellular fiel ...
Lecture
... first scanning method to give FUNCTIONAL information on the brain measures the emission of positrons from the brain after a small amount of radioactive isotopes, or tracers, have been injected into the blood stream. A common example is a glucose-relative with embedded fluor-18. With this molecule, t ...
... first scanning method to give FUNCTIONAL information on the brain measures the emission of positrons from the brain after a small amount of radioactive isotopes, or tracers, have been injected into the blood stream. A common example is a glucose-relative with embedded fluor-18. With this molecule, t ...
Harnessing Plasticity to Reset Dysfunctional Neurons
... circuits were laid down and their functions assigned, little change was possible. This notion is no longer tenable. The brain has a lifelong inherent ability to change and adapt: individual neurons and neural circuits can change their “job descriptions” and their allegiance in response to demands. T ...
... circuits were laid down and their functions assigned, little change was possible. This notion is no longer tenable. The brain has a lifelong inherent ability to change and adapt: individual neurons and neural circuits can change their “job descriptions” and their allegiance in response to demands. T ...
Chapter 3 Practice Test
... Which part of your brain receives information that you are moving your legs? a. amygdala b. sensory cortex c. hypothalamus d. motor cortex e. Broca's area The capacity of one brain area to take over the functions of another damaged brain area is known as brain a. tomography. b. aphasia. c. phrenolog ...
... Which part of your brain receives information that you are moving your legs? a. amygdala b. sensory cortex c. hypothalamus d. motor cortex e. Broca's area The capacity of one brain area to take over the functions of another damaged brain area is known as brain a. tomography. b. aphasia. c. phrenolog ...
Brain
... 2. Despite the specialization, no brain area performs only one function. 3. The brain represents the world in maps. 4. All incoming sensory information goes through a switchboard first. ...
... 2. Despite the specialization, no brain area performs only one function. 3. The brain represents the world in maps. 4. All incoming sensory information goes through a switchboard first. ...
Chapters 1,2,3 - UCSD Cognitive Science
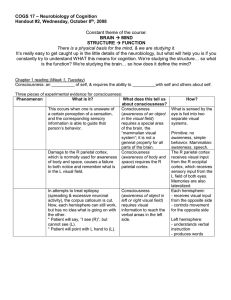
... Consciousness: an __________ of self, & requires the ability to __________with self and others about self. Three pieces of experimental evidence for consciousness: Phenomenon What is it? What does this tell us about consciousness? This occurs when one is unaware of Consciousness a certain perception ...
... Consciousness: an __________ of self, & requires the ability to __________with self and others about self. Three pieces of experimental evidence for consciousness: Phenomenon What is it? What does this tell us about consciousness? This occurs when one is unaware of Consciousness a certain perception ...
The nervous system
... brain by many blood vessels. These vessels are found on the surface of the brain and deep within the brain. The blood vessels (and nerves) enter the brain through holes in the skull called foramina . ...
... brain by many blood vessels. These vessels are found on the surface of the brain and deep within the brain. The blood vessels (and nerves) enter the brain through holes in the skull called foramina . ...
Cognitive Neuroscience
... • EEG • Recording of electrical activity in the brain, which appears as waves of various widths and heights ...
... • EEG • Recording of electrical activity in the brain, which appears as waves of various widths and heights ...
PSY550 Research and Ingestion
... • transmission electron microscope – A microscope that passes a focused beam of electrons through thin slices of tissues to reveal extremely small details. • scanning electron microscope – A microscope that provides three-dimensional information about the shape of the surface of a small object by sc ...
... • transmission electron microscope – A microscope that passes a focused beam of electrons through thin slices of tissues to reveal extremely small details. • scanning electron microscope – A microscope that provides three-dimensional information about the shape of the surface of a small object by sc ...
Brain matters in multiple sclerosis
... An axon: This carries information from this neuron to other neurons ...
... An axon: This carries information from this neuron to other neurons ...
Introduction to Cognitive Development 2012
... By looking at the slide with structures that are visible in the cut you can determine where the brain was cut: right between the eyes or between the eye and the ear. We need to cut the brain in different places because the brain is 3-D and we can’t see all brain structures if we always cut right bet ...
... By looking at the slide with structures that are visible in the cut you can determine where the brain was cut: right between the eyes or between the eye and the ear. We need to cut the brain in different places because the brain is 3-D and we can’t see all brain structures if we always cut right bet ...
Chapter 3 Section 2 - 6th
... Accidents- study how the brain is connected to psychological functions Electrical Stimulation of the brain- Jose Delgado used electrical stimulation of the brain to show how a bull would change its behavioral patterns. James Olds and Peter Milner used rats to push levers, which sent electrodes into ...
... Accidents- study how the brain is connected to psychological functions Electrical Stimulation of the brain- Jose Delgado used electrical stimulation of the brain to show how a bull would change its behavioral patterns. James Olds and Peter Milner used rats to push levers, which sent electrodes into ...
Evolutionary Psychology: Understanding Human Nature
... Temporal lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. - Motor Cortex: an area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. - Somatosensory cortex: area at the front ...
... Temporal lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear. - Motor Cortex: an area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. - Somatosensory cortex: area at the front ...
Psyc 001 Week 6
... A technique with a device that uses the interaction between radio waves and a strong magnetic field to produce images of slices of the interior of the body ...
... A technique with a device that uses the interaction between radio waves and a strong magnetic field to produce images of slices of the interior of the body ...
HW CH 5 PSY 2513 Submit your answers on canvas
... is the first part of the brain to stop growing. c. is less sensitive to environmental influences than other parts of the brain. d. fully develops during the third trimester of pregnancy. ...
... is the first part of the brain to stop growing. c. is less sensitive to environmental influences than other parts of the brain. d. fully develops during the third trimester of pregnancy. ...
Ch 2 Cognition & the Brain
... (1) What are the building blocks of the brain? (2) How do they work? (3) How are things in the environment, such as faces, trees, or houses, represented in the brain? (4) How is the brain organized? (5) What methods do we have to study the link between neurobiology and human behavior? ...
... (1) What are the building blocks of the brain? (2) How do they work? (3) How are things in the environment, such as faces, trees, or houses, represented in the brain? (4) How is the brain organized? (5) What methods do we have to study the link between neurobiology and human behavior? ...
Axia College Material Appendix B Structures of the Nervous System
... Structures of the Nervous System This activity will increase your understanding of the different structures of the nervous system and brain. During the Web activity, you will view a variety of structures of the brain and nervous system and label each with the appropriate term. You will use this docu ...
... Structures of the Nervous System This activity will increase your understanding of the different structures of the nervous system and brain. During the Web activity, you will view a variety of structures of the brain and nervous system and label each with the appropriate term. You will use this docu ...
Functional magnetic resonance imaging

Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) is a functional neuroimaging procedure using MRI technology that measures brain activity by detecting associated changes in blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area of the brain is in use, blood flow to that region also increases.The primary form of fMRI uses the blood-oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) contrast, discovered by Seiji Ogawa. This is a type of specialized brain and body scan used to map neural activity in the brain or spinal cord of humans or other animals by imaging the change in blood flow (hemodynamic response) related to energy use by brain cells. Since the early 1990s, fMRI has come to dominate brain mapping research because it does not require people to undergo shots, surgery, or to ingest substances, or be exposed to radiation, etc. Other methods of obtaining contrast are arterial spin labeling and diffusion MRI.The procedure is similar to MRI but uses the change in magnetization between oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood as its basic measure. This measure is frequently corrupted by noise from various sources and hence statistical procedures are used to extract the underlying signal. The resulting brain activation can be presented graphically by color-coding the strength of activation across the brain or the specific region studied. The technique can localize activity to within millimeters but, using standard techniques, no better than within a window of a few seconds.fMRI is used both in the research world, and to a lesser extent, in the clinical world. It can also be combined and complemented with other measures of brain physiology such as EEG and NIRS. Newer methods which improve both spatial and time resolution are being researched, and these largely use biomarkers other than the BOLD signal. Some companies have developed commercial products such as lie detectors based on fMRI techniques, but the research is not believed to be ripe enough for widespread commercialization.