The History and Scope of Psychology Module 1
... visual display of brain activity that detects a radioactive form of glucose while the brain performs a given task. ...
... visual display of brain activity that detects a radioactive form of glucose while the brain performs a given task. ...
The Brain - Morales Biology
... brain to the spinal cord. Center that regulates heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, swallowing, vomiting, sneezing, and coughing. ...
... brain to the spinal cord. Center that regulates heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, swallowing, vomiting, sneezing, and coughing. ...
T C N B
... in relation to stimuli presentation, task activation, or rest. Increased neuronal metabolism results in increased cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO2) and much greater increases in cerebral blood flow (CBF) to the region; this uncoupling of oxygen consumption and supply during activation causes ...
... in relation to stimuli presentation, task activation, or rest. Increased neuronal metabolism results in increased cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO2) and much greater increases in cerebral blood flow (CBF) to the region; this uncoupling of oxygen consumption and supply during activation causes ...
Correlated neuronal activity and the flow of neural information
... modulation is not likely due to the local neuronal activity, but some signal to the vascular system from remote areas. • However, the presence of connectivity between functionally related sites was shown by correlations between these low frequency oscillations in time series MRI data at resting stat ...
... modulation is not likely due to the local neuronal activity, but some signal to the vascular system from remote areas. • However, the presence of connectivity between functionally related sites was shown by correlations between these low frequency oscillations in time series MRI data at resting stat ...
CN510: Principles and Methods of Cognitive and
... Sulci and Gyri A sulcus or fissure is a groove in the brain A gyrus is a convolution (bump) in the brain What is the reason for convoluted structure of the brain? The most prominent sulci and gyri are found in almost all human brains in approximately same positions and serve as a means for separati ...
... Sulci and Gyri A sulcus or fissure is a groove in the brain A gyrus is a convolution (bump) in the brain What is the reason for convoluted structure of the brain? The most prominent sulci and gyri are found in almost all human brains in approximately same positions and serve as a means for separati ...
Regulation of rCBF by Diffusible Signals: An Analysis of Constraints
... 19901. The data suggest the following sequence of events following a brief sensory stimulus: first, 200400 ms after the onset of neural activity, highly localized oxygen delivery occurs followed 300400 ms later by an increase in blood volume. After a second or more a substantial rise in local oxyhem ...
... 19901. The data suggest the following sequence of events following a brief sensory stimulus: first, 200400 ms after the onset of neural activity, highly localized oxygen delivery occurs followed 300400 ms later by an increase in blood volume. After a second or more a substantial rise in local oxyhem ...
The brain - Epilepsy Society
... functions it is responsible for. More recent scanning techniques have shown how similar functions such as language and memory may also be located in various areas of the brain. This is particularly significant if injury or surgery affects a specific part of the brain – other areas may begin to com ...
... functions it is responsible for. More recent scanning techniques have shown how similar functions such as language and memory may also be located in various areas of the brain. This is particularly significant if injury or surgery affects a specific part of the brain – other areas may begin to com ...
The Structure of the Brain
... personality change. He became a drunk, was violent, and completely irresponsible. This led to an interest in how the brain controls behavior and personality. ...
... personality change. He became a drunk, was violent, and completely irresponsible. This led to an interest in how the brain controls behavior and personality. ...
Brain
... Clinical Observation Clinical observations have shed light on a number of brain disorders. Alterations in brain morphology due to neurological and psychiatric diseases are now being catalogued. ...
... Clinical Observation Clinical observations have shed light on a number of brain disorders. Alterations in brain morphology due to neurological and psychiatric diseases are now being catalogued. ...
(intermediate-range) elements in brain dynamics
... larger than columns, barrels and glomeruli, but they are at or below t h e lower ...
... larger than columns, barrels and glomeruli, but they are at or below t h e lower ...
PP text version
... PET scan (positron emission tomography): metabolic or chemical activity of the brain can be followed with time. Radioactive glucose or oxygen commonly used. More active brain regions use more oxygen and glucose so they give off a larger signal than the rest of the brain. Used to map areas of b ...
... PET scan (positron emission tomography): metabolic or chemical activity of the brain can be followed with time. Radioactive glucose or oxygen commonly used. More active brain regions use more oxygen and glucose so they give off a larger signal than the rest of the brain. Used to map areas of b ...
Sleep Brain Labelling
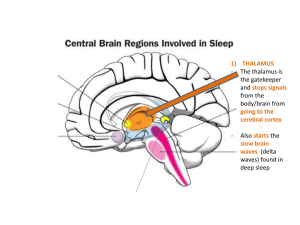
... 1) THALAMUS - The thalamus is the gatekeeper and stops signals from the body/brain from going to the cerebral cortex ...
... 1) THALAMUS - The thalamus is the gatekeeper and stops signals from the body/brain from going to the cerebral cortex ...
heledius - Society for the Advancement of Sexual Health
... greater learning and memory takes place. When an individual participates in novel and high arousal experiences, the template is at risk for being altered. High arousal experiences change the brains expectations. The brain than keeps pursuing these high arousal experiences in order to get to th ...
... greater learning and memory takes place. When an individual participates in novel and high arousal experiences, the template is at risk for being altered. High arousal experiences change the brains expectations. The brain than keeps pursuing these high arousal experiences in order to get to th ...
Topic 1
... 3. Promote public information and general education about the nature of scientific discovery and the results and implications of the latest neuroscience research. Support active and continuing discussions on ethical issues relating to the conduct and outcomes of neuroscience research. 4. Inform legi ...
... 3. Promote public information and general education about the nature of scientific discovery and the results and implications of the latest neuroscience research. Support active and continuing discussions on ethical issues relating to the conduct and outcomes of neuroscience research. 4. Inform legi ...
Work toward real-time control of a cortical neural prothesis
... Research being conducted at Arizona State University, as a part of the NIH’s Neural Prosthesis Program, is attempting to develop a cortical motor prosthesis. The goal is to design a system to record and analyze the activity of neurons in the motor cortex, and implement this to control a robotic arm. ...
... Research being conducted at Arizona State University, as a part of the NIH’s Neural Prosthesis Program, is attempting to develop a cortical motor prosthesis. The goal is to design a system to record and analyze the activity of neurons in the motor cortex, and implement this to control a robotic arm. ...
Ch 2 Physiology - Texas A&M University
... • Neurons are not directly attached but are indirectly connected by synapses. • One neuron sends an electrical signal to another neuron by releasing neurotransmitters. • Some neurons send excitatory signals (+); others send inhibitory signals (-). ch 2 ...
... • Neurons are not directly attached but are indirectly connected by synapses. • One neuron sends an electrical signal to another neuron by releasing neurotransmitters. • Some neurons send excitatory signals (+); others send inhibitory signals (-). ch 2 ...
YG013807812
... disciplines (such as pattern recognition, assistive technology development, and HCI) to maximize the use of existing knowledge and technology. 3) The boundaries between the functional components should align as much as possible with existing interface technology to facilitate comparisons between BCI ...
... disciplines (such as pattern recognition, assistive technology development, and HCI) to maximize the use of existing knowledge and technology. 3) The boundaries between the functional components should align as much as possible with existing interface technology to facilitate comparisons between BCI ...
Corpus Callosum - Psychological Associates of South Florida
... Which technique is most useful for seeing which regions of the brain are most active while a person reads a poem? A. B. C. D. ...
... Which technique is most useful for seeing which regions of the brain are most active while a person reads a poem? A. B. C. D. ...
Eagleman Ch 4. Neuroplasticity
... limb, can result in changes to the representation of the body in the brain. Sensory areas that responded to the damaged part of the body are taken over by adjacent sensory areas. Phantom limb pain is pain that seems to come from the missing body part. ...
... limb, can result in changes to the representation of the body in the brain. Sensory areas that responded to the damaged part of the body are taken over by adjacent sensory areas. Phantom limb pain is pain that seems to come from the missing body part. ...
The Brain - Wando High School
... --Dendrites: part of the neuron that receives info. from the axon. --Axons: carries messages to dendrites of another neuron. --Synapse: junction point of two or more neurons. --Vesicles: bubble-like containers of neurotransmitters; located at ends of axons. --Neurotransmitters: chemicals in the ends ...
... --Dendrites: part of the neuron that receives info. from the axon. --Axons: carries messages to dendrites of another neuron. --Synapse: junction point of two or more neurons. --Vesicles: bubble-like containers of neurotransmitters; located at ends of axons. --Neurotransmitters: chemicals in the ends ...
Chapter 2 - Neurophysiology
... Receives information from all the senses except smell The Cerebellum Extends from the rear of the brainstem “little brain” Coordinates movements, nonverbal learning and movements, judge time, alter our emotions and tell apart sounds and textures. “Our brain processes most information outside of ou ...
... Receives information from all the senses except smell The Cerebellum Extends from the rear of the brainstem “little brain” Coordinates movements, nonverbal learning and movements, judge time, alter our emotions and tell apart sounds and textures. “Our brain processes most information outside of ou ...
The Challenge of Connecting the Dots in the B.R.A.I.N.
... particles. A weather forecast requires a valid theoretical framework: a model. The model incorporates a set of rules worked out by studying interactions among particles; the actual forecast, however, is not predicted by simulating the position of every molecule. Rather, the forecast is made on the r ...
... particles. A weather forecast requires a valid theoretical framework: a model. The model incorporates a set of rules worked out by studying interactions among particles; the actual forecast, however, is not predicted by simulating the position of every molecule. Rather, the forecast is made on the r ...
Inner music and brain connectivity
... influences, the shaping of lower-level processes by more complex information. Cortical areas function as adaptive processors, being subject to attention, expectation, and perceptual task. Brain states are determined by the interactions between multiple cortical areas and the modulation of intrinsic ...
... influences, the shaping of lower-level processes by more complex information. Cortical areas function as adaptive processors, being subject to attention, expectation, and perceptual task. Brain states are determined by the interactions between multiple cortical areas and the modulation of intrinsic ...
Neuroanatomy 6-12
... • Did the CEN Outreach volunteer teach the student objectives? • Did the CEN Outreach program reach the goals of the teacher? • Did the CEN Outreach program reach it’s own goals/objectives? Resources: • http://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Homeostasis NGSS Description: MS-LS1-1 Conduct an invest ...
... • Did the CEN Outreach volunteer teach the student objectives? • Did the CEN Outreach program reach the goals of the teacher? • Did the CEN Outreach program reach it’s own goals/objectives? Resources: • http://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Homeostasis NGSS Description: MS-LS1-1 Conduct an invest ...
Functional magnetic resonance imaging

Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) is a functional neuroimaging procedure using MRI technology that measures brain activity by detecting associated changes in blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area of the brain is in use, blood flow to that region also increases.The primary form of fMRI uses the blood-oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) contrast, discovered by Seiji Ogawa. This is a type of specialized brain and body scan used to map neural activity in the brain or spinal cord of humans or other animals by imaging the change in blood flow (hemodynamic response) related to energy use by brain cells. Since the early 1990s, fMRI has come to dominate brain mapping research because it does not require people to undergo shots, surgery, or to ingest substances, or be exposed to radiation, etc. Other methods of obtaining contrast are arterial spin labeling and diffusion MRI.The procedure is similar to MRI but uses the change in magnetization between oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood as its basic measure. This measure is frequently corrupted by noise from various sources and hence statistical procedures are used to extract the underlying signal. The resulting brain activation can be presented graphically by color-coding the strength of activation across the brain or the specific region studied. The technique can localize activity to within millimeters but, using standard techniques, no better than within a window of a few seconds.fMRI is used both in the research world, and to a lesser extent, in the clinical world. It can also be combined and complemented with other measures of brain physiology such as EEG and NIRS. Newer methods which improve both spatial and time resolution are being researched, and these largely use biomarkers other than the BOLD signal. Some companies have developed commercial products such as lie detectors based on fMRI techniques, but the research is not believed to be ripe enough for widespread commercialization.