Lecture 02
... observed temperature changes at smaller scales. On these scales, natural climate variability is relatively larger making it harder to distinguish changes expected due to external forcings. • Temperatures of the most extreme hot nights, cold nights and cold days are likely to have increased due to an ...
... observed temperature changes at smaller scales. On these scales, natural climate variability is relatively larger making it harder to distinguish changes expected due to external forcings. • Temperatures of the most extreme hot nights, cold nights and cold days are likely to have increased due to an ...
Decision making and climate change
... a relatively poor use of resources. Adaptive measures that build in lower emission profiles have a better cost/benefit ratio for society. • Giving mitigation measures a higher priority than adaptation, in the absence of a global legal framework, still leaves municipalities and regions vulnerable to ...
... a relatively poor use of resources. Adaptive measures that build in lower emission profiles have a better cost/benefit ratio for society. • Giving mitigation measures a higher priority than adaptation, in the absence of a global legal framework, still leaves municipalities and regions vulnerable to ...
Global emissions of greenhouse gases have been
... Source: Reproduced from Smith and others 2009. Notes: The figure shows risks from climate change, as described in 2001 (left) compared with updated data (right). Climate-change consequences are shown as bars and the increases in global mean temperature (°C) above today’s levels (0 degrees to 5 degre ...
... Source: Reproduced from Smith and others 2009. Notes: The figure shows risks from climate change, as described in 2001 (left) compared with updated data (right). Climate-change consequences are shown as bars and the increases in global mean temperature (°C) above today’s levels (0 degrees to 5 degre ...
Dealing with the impact of global warming and rising sea levels
... 1) Thermal expansion: the rising of water temperature causes it to expand and since the ocean over the past century has become warmer it has also increased in volume 2) Melting of glaciers and polar ice caps: glaciers and ice caps melt naturally each summer, in winter snow forming should balance the ...
... 1) Thermal expansion: the rising of water temperature causes it to expand and since the ocean over the past century has become warmer it has also increased in volume 2) Melting of glaciers and polar ice caps: glaciers and ice caps melt naturally each summer, in winter snow forming should balance the ...
The Dangers Caused by Climate Change for Humans’ Health
... It Relates to Global Warming Greenhouse gasses is high (quantity) in the air, so the heat is isolated in the air. Then, the air is starting to be warmer ...
... It Relates to Global Warming Greenhouse gasses is high (quantity) in the air, so the heat is isolated in the air. Then, the air is starting to be warmer ...
File
... No one was around thousands of years ago to measure temperatures so we use other indirect measurements. Some of these are Changes in species compositions Chemical analyses of ice ...
... No one was around thousands of years ago to measure temperatures so we use other indirect measurements. Some of these are Changes in species compositions Chemical analyses of ice ...
6.1 Global Warming
... • Also produced in industrial processes where fossil fuels are burned at very high temperatures ...
... • Also produced in industrial processes where fossil fuels are burned at very high temperatures ...
Lesson PowerPoint - KBS GK12 Project
... E5.4D Based on evidence of observable changes in recent history and climate change models, explain the consequences of warmer oceans (including the results of increased evaporation, shoreline and estuarine impacts, oceanic algae growth, and coral bleaching) and changing climatic zones (including the ...
... E5.4D Based on evidence of observable changes in recent history and climate change models, explain the consequences of warmer oceans (including the results of increased evaporation, shoreline and estuarine impacts, oceanic algae growth, and coral bleaching) and changing climatic zones (including the ...
Fun Facts: Climate Change
... Melting glaciers will cause the sea level to rise making coastal plains uninhabitable. Climate change will affect farming and food supply. Some animal and plant species may be forced out of their natural habitats and they may be under threat of extinction (e.g. the polar bear). ...
... Melting glaciers will cause the sea level to rise making coastal plains uninhabitable. Climate change will affect farming and food supply. Some animal and plant species may be forced out of their natural habitats and they may be under threat of extinction (e.g. the polar bear). ...
Aim: SWBAT explain how feedback loops may contribute to climate
... harder for them to exercise. They exercise less, so they gain more weight, making it even harder for them to exercise. Repeat. ...
... harder for them to exercise. They exercise less, so they gain more weight, making it even harder for them to exercise. Repeat. ...
Climate Change in VERMONT - Vermont Agency of Natural
... Weather - the short term state of the atmosphere at a specific time and place, including the temperature, humidity, cloud coverage, precipitation, wind, etc. Climate - the long-term “average weather” pattern of an area, including temperature, precipitation, and wind. ...
... Weather - the short term state of the atmosphere at a specific time and place, including the temperature, humidity, cloud coverage, precipitation, wind, etc. Climate - the long-term “average weather” pattern of an area, including temperature, precipitation, and wind. ...
ATM306-Section4 - University at Albany Atmospheric Sciences
... environment, living things, and society, we need to reduce greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere • Scale of the negative consequences depends on how much carbon accumulates in the atmosphere over time • To keep temperatures below a 2°C temperature rise, we need to act quickly and make sign ...
... environment, living things, and society, we need to reduce greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere • Scale of the negative consequences depends on how much carbon accumulates in the atmosphere over time • To keep temperatures below a 2°C temperature rise, we need to act quickly and make sign ...
inter alia
... effective global response to climate change. (4) The third object of this Act is: (a) if Australia is a party to a comprehensive international agreement that is capable of stabilising atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases at around 450 parts per million of carbon dioxide equivalence or lowe ...
... effective global response to climate change. (4) The third object of this Act is: (a) if Australia is a party to a comprehensive international agreement that is capable of stabilising atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases at around 450 parts per million of carbon dioxide equivalence or lowe ...
Duka_Castillo_The effects of climate change on New York City
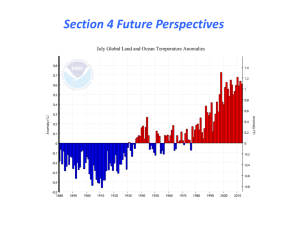
... impression that is made by the effects of climate change and all of its factors, on the increased frequency of extreme weather. Although we wanted data to be as accurate and conceivable as possible, we studied data sets within the past five years: specifically the year 2008 until 2012. Through our f ...
... impression that is made by the effects of climate change and all of its factors, on the increased frequency of extreme weather. Although we wanted data to be as accurate and conceivable as possible, we studied data sets within the past five years: specifically the year 2008 until 2012. Through our f ...
Global Climate Change?
... Global Climate Change: How do you measure “change” in a meaningful way? Global Climate Change Increasing Weather Volatility Has Real Impacts (economic and public health) ...
... Global Climate Change: How do you measure “change” in a meaningful way? Global Climate Change Increasing Weather Volatility Has Real Impacts (economic and public health) ...
Climate Health Impact introductory presentation
... Global warming is the increase in the average temperature of the Earth's near-surface air and oceans since the mid-20th century, and its projected continuation. Global surface temperature increased 0.74 ± 0.18°C during the 100 years ending in 2005 due to an enhanced greenhouse effect. Climate model ...
... Global warming is the increase in the average temperature of the Earth's near-surface air and oceans since the mid-20th century, and its projected continuation. Global surface temperature increased 0.74 ± 0.18°C during the 100 years ending in 2005 due to an enhanced greenhouse effect. Climate model ...
Global Warming Is Unequivocal
... Air holds more water vapor at higher temperatures A basic physical law tells us that the water holding capacity of the atmosphere goes up at about 4% per degree Fahrenheit increase in temperature. Observations show that this is happening at the surface and in lower atmosphere: 1.0F since 1970 over ...
... Air holds more water vapor at higher temperatures A basic physical law tells us that the water holding capacity of the atmosphere goes up at about 4% per degree Fahrenheit increase in temperature. Observations show that this is happening at the surface and in lower atmosphere: 1.0F since 1970 over ...
Slide 1
... • Radiation effect of greenhouse gases: warming. • Observed change of mean: air temperature, ocean temperature, melting of arctic sea ice, Greenland ice sheet, snow and glaciers, rising of ...
... • Radiation effect of greenhouse gases: warming. • Observed change of mean: air temperature, ocean temperature, melting of arctic sea ice, Greenland ice sheet, snow and glaciers, rising of ...
ClimateChange
... i.e., temperature increases by 0.2°C (0.3°F) for a radiative forcing of 1 W m-2 But this is for a system in equilibrium ...
... i.e., temperature increases by 0.2°C (0.3°F) for a radiative forcing of 1 W m-2 But this is for a system in equilibrium ...
Observed Changes to the Climate and their Causes Some human
... • more precipitation falls as rain rather than snow, especially in the fall and spring. • snow melt occurs faster and sooner in the spring • snow pack is therefore less as summer arrives • soil moisture is less, and recycling is less • global warming means more drying and heat stress • the risk of d ...
... • more precipitation falls as rain rather than snow, especially in the fall and spring. • snow melt occurs faster and sooner in the spring • snow pack is therefore less as summer arrives • soil moisture is less, and recycling is less • global warming means more drying and heat stress • the risk of d ...
THINK GLOBAL, WORK LOCAL
... mathematical models which are integrated on the most powerful supercomputers and used to understand the history and future evolution of the Earth’s climate. The evidence shows unequivocally that the climate is warming, mostly because of increasing emissions of carbon dioxide, methane and other green ...
... mathematical models which are integrated on the most powerful supercomputers and used to understand the history and future evolution of the Earth’s climate. The evidence shows unequivocally that the climate is warming, mostly because of increasing emissions of carbon dioxide, methane and other green ...
ClimateChangePowerpo..
... melts, it makes a fizzing sound called "Bergie Seltzer." This sound is made when compressed air bubbles trapped in the iceberg pop. ...
... melts, it makes a fizzing sound called "Bergie Seltzer." This sound is made when compressed air bubbles trapped in the iceberg pop. ...
Global warming
Global warming and climate change are terms for the observed century-scale rise in the average temperature of the Earth's climate system and its related effects.Multiple lines of scientific evidence show that the climate system is warming. Although the increase of near-surface atmospheric temperature is the measure of global warming often reported in the popular press, most of the additional energy stored in the climate system since 1970 has gone into ocean warming. The remainder has melted ice, and warmed the continents and atmosphere. Many of the observed changes since the 1950s are unprecedented over decades to millennia.Scientific understanding of global warming is increasing. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reported in 2014 that scientists were more than 95% certain that most of global warming is caused by increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases and other human (anthropogenic) activities. Climate model projections summarized in the report indicated that during the 21st century the global surface temperature is likely to rise a further 0.3 to 1.7 °C (0.5 to 3.1 °F) for their lowest emissions scenario using stringent mitigation and 2.6 to 4.8 °C (4.7 to 8.6 °F) for their highest. These findings have been recognized by the national science academies of the major industrialized nations.Future climate change and associated impacts will differ from region to region around the globe. Anticipated effects include warming global temperature, rising sea levels, changing precipitation, and expansion of deserts in the subtropics. Warming is expected to be greatest in the Arctic, with the continuing retreat of glaciers, permafrost and sea ice. Other likely changes include more frequent extreme weather events including heat waves, droughts, heavy rainfall, and heavy snowfall; ocean acidification; and species extinctions due to shifting temperature regimes. Effects significant to humans include the threat to food security from decreasing crop yields and the abandonment of populated areas due to flooding.Possible societal responses to global warming include mitigation by emissions reduction, adaptation to its effects, building systems resilient to its effects, and possible future climate engineering. Most countries are parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC),whose ultimate objective is to prevent dangerous anthropogenic climate change. The UNFCCC have adopted a range of policies designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and to assist in adaptation to global warming. Parties to the UNFCCC have agreed that deep cuts in emissions are required, and that future global warming should be limited to below 2.0 °C (3.6 °F) relative to the pre-industrial level.