Sec 16.3 Sexual Reproduction
... ____________ gamete – is called an ____________ or ____________ ____________ gamete - is called a ____________ or ____________ ____________ occurs when a ____________penetrates the ____________and the 2 sets of chromosomes ________________to create the proper number of chromosomes, in humans = _____ ...
... ____________ gamete – is called an ____________ or ____________ ____________ gamete - is called a ____________ or ____________ ____________ occurs when a ____________penetrates the ____________and the 2 sets of chromosomes ________________to create the proper number of chromosomes, in humans = _____ ...
Multicellular Organisms Part 2 Reproduction
... actually reaching the eggs and because the unprotected fertilised eggs are often eaten by predators. Producing many eggs ensures a sufficient number of fish survive to adulthood to maintain the species. The following diagram shows the life cycle of Salmon: ...
... actually reaching the eggs and because the unprotected fertilised eggs are often eaten by predators. Producing many eggs ensures a sufficient number of fish survive to adulthood to maintain the species. The following diagram shows the life cycle of Salmon: ...
Moore 1 Timothy Moore Life Science: Unit 3, Lesson 16 22
... 17. In a plant, roots absorb water and nutrients. Those materials are then transported to other parts of the plant. What system in the human body functions in a similar way? Compare these two systems. The system that takes care of transport in the body is the cardiovascular system, also known as the ...
... 17. In a plant, roots absorb water and nutrients. Those materials are then transported to other parts of the plant. What system in the human body functions in a similar way? Compare these two systems. The system that takes care of transport in the body is the cardiovascular system, also known as the ...
Are there sex differences in sexual satisfaction?
... • Research findings that support the view that females are higher in erotic plasticity than males: ...
... • Research findings that support the view that females are higher in erotic plasticity than males: ...
Cells The Basic Unit of Life
... In binary fission, the parent cell divides equally into two daughter cells. In budding the parent cell divides unequally. The daughter cell is smaller than the parent cell. But after budding is complete, the daughter cell may grow to the size of the parent. Organisms of the kingdom Fungi, such as th ...
... In binary fission, the parent cell divides equally into two daughter cells. In budding the parent cell divides unequally. The daughter cell is smaller than the parent cell. But after budding is complete, the daughter cell may grow to the size of the parent. Organisms of the kingdom Fungi, such as th ...
Arthropods - Green Local Schools
... • Respiratory System: ▫ gills Base of each walking leg under carapace Diffusion of gases ...
... • Respiratory System: ▫ gills Base of each walking leg under carapace Diffusion of gases ...
Sexual selection
... Zahavi’s handicap theory conceived that survivors of competition with some nonheritable handicap must have extraordinary survival and adaptation skills despite the obvious maladaptation (Zahavi 1975). He argues that these males thus have superior genes that can be passed on with higher selective adv ...
... Zahavi’s handicap theory conceived that survivors of competition with some nonheritable handicap must have extraordinary survival and adaptation skills despite the obvious maladaptation (Zahavi 1975). He argues that these males thus have superior genes that can be passed on with higher selective adv ...
Chapter 10 – Sexual Techniques and Behavior
... C. one year. D. three weeks. E. three months. 12. Norplant _________. A. consists of six matchstick size capsules. D. remains effective for up to five years. B. is a contraceptive implant. E. all of the above C. releases a low continuous dosage of levonorgestrel. 13. Emergency contraception ________ ...
... C. one year. D. three weeks. E. three months. 12. Norplant _________. A. consists of six matchstick size capsules. D. remains effective for up to five years. B. is a contraceptive implant. E. all of the above C. releases a low continuous dosage of levonorgestrel. 13. Emergency contraception ________ ...
human reproduction and development what you need to know
... uterus, and provide essential materials through the placenta, and nutrition through milk for the newborn. Male Reproductive System 4.1e Human reproduction and development are influenced by factors such as gene expression, hormones, and the environment. The reproductive cycle in males is regulated by ...
... uterus, and provide essential materials through the placenta, and nutrition through milk for the newborn. Male Reproductive System 4.1e Human reproduction and development are influenced by factors such as gene expression, hormones, and the environment. The reproductive cycle in males is regulated by ...
Animals Part I - CCRI Faculty Web
... Asexual reproduction single parent gives rise to an offspring that will be genetically identical to the parent Asexual reproduction of a body part!! Fertilization /Copulation Internal fertilization External fertilization Development of a fetus Internal External ...
... Asexual reproduction single parent gives rise to an offspring that will be genetically identical to the parent Asexual reproduction of a body part!! Fertilization /Copulation Internal fertilization External fertilization Development of a fetus Internal External ...
Chapter_8
... The Centers for Disease control report that it is the third leading cause of death, behind accidents and homicide, of people aged 15 to ...
... The Centers for Disease control report that it is the third leading cause of death, behind accidents and homicide, of people aged 15 to ...
Phylum Annelida (Segmented Worms)
... • Both Asexual and Sexual Reproduction • Asexual reproduction –Budding and Fission ...
... • Both Asexual and Sexual Reproduction • Asexual reproduction –Budding and Fission ...
Chapter 9 Study Guide
... b. ___ Uses the sun’s energy to make food (photosynthesis). c. ___ Can live in extreme environments like hot springs and acidic areas. d. ___ Single-celled or simple multicellular (Ex: paramecium). e. ___ Digests food outside of body and then absorbs it. f. ___ Bacteria that live almost everywhere ( ...
... b. ___ Uses the sun’s energy to make food (photosynthesis). c. ___ Can live in extreme environments like hot springs and acidic areas. d. ___ Single-celled or simple multicellular (Ex: paramecium). e. ___ Digests food outside of body and then absorbs it. f. ___ Bacteria that live almost everywhere ( ...
Chapter 9 Study Guide
... b. ___ Uses the sun’s energy to make food (photosynthesis). c. ___ Can live in extreme environments like hot springs and acidic areas. d. ___ Single-celled or simple multicellular (Ex: paramecium). e. ___ Digests food outside of body and then absorbs it. f. ___ Bacteria that live almost everywhere ( ...
... b. ___ Uses the sun’s energy to make food (photosynthesis). c. ___ Can live in extreme environments like hot springs and acidic areas. d. ___ Single-celled or simple multicellular (Ex: paramecium). e. ___ Digests food outside of body and then absorbs it. f. ___ Bacteria that live almost everywhere ( ...
Name - cloudfront.net
... Cell that responds to water pressure in a plant to control the opening for gas exchange. Opening created in the leaves of the plant to allow for gas exchange. Is open when the plant has enough water and the sun is out for photosynthesis to take place. Will be closed at night or if the plant does not ...
... Cell that responds to water pressure in a plant to control the opening for gas exchange. Opening created in the leaves of the plant to allow for gas exchange. Is open when the plant has enough water and the sun is out for photosynthesis to take place. Will be closed at night or if the plant does not ...
File - Mr. Krueger`s Biology
... 6. CO2 used during photosynthesis is placed in the atmosphere by _______________________________ the process that produces CO2 in cells is called __________________________ 7. The CO2 is used by ___________________________________________. They take CO2 + sunlight and produce ___________+__________ ...
... 6. CO2 used during photosynthesis is placed in the atmosphere by _______________________________ the process that produces CO2 in cells is called __________________________ 7. The CO2 is used by ___________________________________________. They take CO2 + sunlight and produce ___________+__________ ...
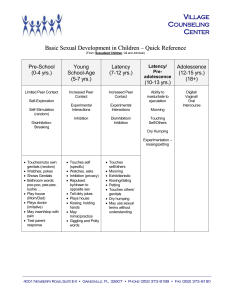
Child_Sexual_Development
... CENTER Parental Guidance: Probably one of the most critical factors in child sexual development is the level of parental guidance. Parents play an important part in instilling values about sexuality in their children. When parents view sex as dirty, inappropriate, or secretive they may set rigid and ...
... CENTER Parental Guidance: Probably one of the most critical factors in child sexual development is the level of parental guidance. Parents play an important part in instilling values about sexuality in their children. When parents view sex as dirty, inappropriate, or secretive they may set rigid and ...
CH 32 Foldable Mammals Internal content
... The mammalian circulatory system is divided into two completely separate loops with a 4-chambered heart. One loop from the lungs…the other from the body. Mammals have the most highly developed brains of any animals. A flexible backbone allows mammals to move both vertically & from side to side. ...
... The mammalian circulatory system is divided into two completely separate loops with a 4-chambered heart. One loop from the lungs…the other from the body. Mammals have the most highly developed brains of any animals. A flexible backbone allows mammals to move both vertically & from side to side. ...
spitzerhk.pps - Christian Mental Health
... He focused on a tiny region of the hypothalamus, a part of the brain that regulates body temperature, blood pressure, pulse rate & hormone production. It is also "the chief coordinator of instinct & drives," including sex drive. INAH-3 (the third interstitial nucleus of the anterior hypothalamus), n ...
... He focused on a tiny region of the hypothalamus, a part of the brain that regulates body temperature, blood pressure, pulse rate & hormone production. It is also "the chief coordinator of instinct & drives," including sex drive. INAH-3 (the third interstitial nucleus of the anterior hypothalamus), n ...
5. Reproduction and Recruitment
... Thorson, G. 1961. Length of pelagic larval life in marine bottom invertebrates as related to larval transport by ocean currents. In: Sears, M. (ed) Oceanography. American Association of Advanced Science (publ No 67), Washington D.C. pp ...
... Thorson, G. 1961. Length of pelagic larval life in marine bottom invertebrates as related to larval transport by ocean currents. In: Sears, M. (ed) Oceanography. American Association of Advanced Science (publ No 67), Washington D.C. pp ...
Redefining Sex and Marriage
... partners as sexually romantic companions rather than pragmatic partners (Frykman & Löfgren 1987). Sex within marriage was redefined as recreational rather than reproductive. With the increasing aid of contraceptive technology, childbearing within marriage was often postponed or avoided altogether. T ...
... partners as sexually romantic companions rather than pragmatic partners (Frykman & Löfgren 1987). Sex within marriage was redefined as recreational rather than reproductive. With the increasing aid of contraceptive technology, childbearing within marriage was often postponed or avoided altogether. T ...
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a form of reproduction where two morphologically distinct types of specialized reproductive cells called gametes fuse together, involving a female's large ovum (or egg) and a male's smaller sperm. Each gamete contains half the number of chromosomes of normal cells. They are created by a specialized type of cell division, which only occurs in eukaryotic cells, known as meiosis. The two gametes fuse during fertilization to produce DNA replication and the creation of a single-celled zygote which includes genetic material from both gametes. In a process called genetic recombination, genetic material (DNA) joins up so that homologous chromosome sequences are aligned with each other, and this is followed by exchange of genetic information. Two rounds of cell division then produce four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes from each original parent cell, and the same number of chromosomes as both parents, though self-fertilization can occur. For instance, in human reproduction each human cell contains 46 chromosomes, 23 pairs, except gamete cells, which only contain 23 chromosomes, so the child will have 23 chromosomes from each parent genetically recombined into 23 pairs. Cell division initiates the development of a new individual organism in multicellular organisms, including animals and plants, for the vast majority of whom this is the primary method of reproduction. A species is defined as a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms where two hybrids are capable of reproducing fertile offspring, typically using sexual reproduction, although the species problem encompasses a series of difficult related questions that often come up when biologists define the word species. The evolution of sexual reproduction is a major puzzle because asexual reproduction should be able to outcompete it as every young organism created can bear its own young. This implies that an asexual population has an intrinsic capacity to grow more rapidly with each generation. This 50% cost is a fitness disadvantage of sexual reproduction. The two-fold cost of sex includes this cost and the fact that any organism can only pass on 50% of its own genes to its offspring. One definite advantage of sexual reproduction is that it prevents the accumulation of genetic mutations.Sexual selection is a mode of natural selection in which some individuals out-reproduce others of a population because they are better at securing mates for sexual reproduction. It has been described as ""a powerful evolutionary force that does not exist in asexual populations""Prokaryotes reproduce through asexual reproduction but may display processes similar to sexual reproduction (mechanisms for lateral gene transfer such as bacterial conjugation, transformation and transduction), but they do not lead to reproduction. In prokaryotes, the initial cell has additional or transformed genetic material.