cyt c - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
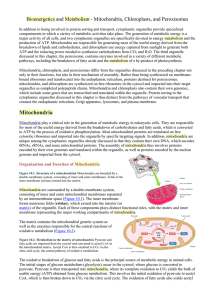
... Outer Membrane – Freely permeable to small molecules and ions. Contains porins with 10,000 dalton limit Inner membrane – Protein rich (4:1 protein:lipid). Impermeable. Contains ETR, ATP synthase, transporters. Cristae – Highly folded inner membrane structure. Increase surface area. Matrix- “cytosol ...
... Outer Membrane – Freely permeable to small molecules and ions. Contains porins with 10,000 dalton limit Inner membrane – Protein rich (4:1 protein:lipid). Impermeable. Contains ETR, ATP synthase, transporters. Cristae – Highly folded inner membrane structure. Increase surface area. Matrix- “cytosol ...
Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, and Peroxisomes
... ribosomes (23S, 16S, and 5S). Plant mitochondrial DNAs, however, also encode a third rRNA of 5S. The mitochondria of plants and protozoans also differ in importing and utilizing tRNAs encoded by the nuclear as well as the mitochondrial genome, whereas in animal mitochondria, all the tRNAs are encode ...
... ribosomes (23S, 16S, and 5S). Plant mitochondrial DNAs, however, also encode a third rRNA of 5S. The mitochondria of plants and protozoans also differ in importing and utilizing tRNAs encoded by the nuclear as well as the mitochondrial genome, whereas in animal mitochondria, all the tRNAs are encode ...
Lecture 11 Krebs Cycle Reactions
... •! During exercise the energy requirement of muscles may be more than 200 times the resting level •! Under moderate exercise muscle cells respire aerobically (in the presence of O2) •! During strenuous exercise where the energy and O2 requirements are too high that the respiratory and circulatory sy ...
... •! During exercise the energy requirement of muscles may be more than 200 times the resting level •! Under moderate exercise muscle cells respire aerobically (in the presence of O2) •! During strenuous exercise where the energy and O2 requirements are too high that the respiratory and circulatory sy ...
Document
... process: NADH + ½O2 + H+ H2O + NAD+ FADH2 + ½O2 H2O + FAD+ Go’ = -52.6 kcal/mol for NADH -36.3 kcal/mol for FADH2 How this process is coupled to the synthesis of ATP ...
... process: NADH + ½O2 + H+ H2O + NAD+ FADH2 + ½O2 H2O + FAD+ Go’ = -52.6 kcal/mol for NADH -36.3 kcal/mol for FADH2 How this process is coupled to the synthesis of ATP ...
Cellular Metabolism and Nutrition notes
... phosphate is removed and ADP (adenosine diphosphate) + a phosphate group is formed. ...
... phosphate is removed and ADP (adenosine diphosphate) + a phosphate group is formed. ...
CELLULAR RESPIRTION Powerpoint
... these electrons are carried to the electron transport chain in the form of NADH to make most of the ATP 6. Know that the entire process converts 1 molecule of glucose to 36 molecules of ATP mainly through the enzyme ATP synthase. 7. Know that oxygen is needed to accept the electrons after they have ...
... these electrons are carried to the electron transport chain in the form of NADH to make most of the ATP 6. Know that the entire process converts 1 molecule of glucose to 36 molecules of ATP mainly through the enzyme ATP synthase. 7. Know that oxygen is needed to accept the electrons after they have ...
2 ATP - HONORS BIOLOGY
... Occurs in the Matrix of the Mitochondria Everything in the Krebs Cycle happens twice because there are two pyruvates from glycolysis. 1) Pyruvate enters the mitochondria and immediately loses a CO2 and makes a NADH forming acetic acid which binds to an enzyme called Co-enzyme A. CO2 Acetic Acid + Co ...
... Occurs in the Matrix of the Mitochondria Everything in the Krebs Cycle happens twice because there are two pyruvates from glycolysis. 1) Pyruvate enters the mitochondria and immediately loses a CO2 and makes a NADH forming acetic acid which binds to an enzyme called Co-enzyme A. CO2 Acetic Acid + Co ...
Effects of Aging on Activities of Mitochondrial Electron Transport
... The aging heart is characterized by many structural, physiological and biochemical changes. Numerous studies have suggested that age-associated deterioration in heart function can be related to oxidative damage by reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced during mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. ...
... The aging heart is characterized by many structural, physiological and biochemical changes. Numerous studies have suggested that age-associated deterioration in heart function can be related to oxidative damage by reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced during mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. ...
Paracoccus denitrificans
... Glycerol – dihydroxyacetone phosphate Goes into glycolysis Fatty acid many units of acetyl CoA Goes into Krebs cycle Proteins – amino acids – proteases AA – intermediates of glycolysis, Krebs cycle ...
... Glycerol – dihydroxyacetone phosphate Goes into glycolysis Fatty acid many units of acetyl CoA Goes into Krebs cycle Proteins – amino acids – proteases AA – intermediates of glycolysis, Krebs cycle ...
Chapter 9. Cellular Respiration STAGE 1: Glycolysis
... 2. Some organisms that are exposed to oxygen, but switch to fermentation when oxygen is scarce. AP Biology ...
... 2. Some organisms that are exposed to oxygen, but switch to fermentation when oxygen is scarce. AP Biology ...
Document
... The passing of electrons through the electron transport chain causes H+ ions to build up in the intermembrane space, making it positively charged relative to the matrix. The charge difference across the membrane forces H ions through channels in enzymes known as ATP synthases. As the ATP synthases s ...
... The passing of electrons through the electron transport chain causes H+ ions to build up in the intermembrane space, making it positively charged relative to the matrix. The charge difference across the membrane forces H ions through channels in enzymes known as ATP synthases. As the ATP synthases s ...
respiration
... If it were one simple step, all the energy would be released at once and most would be released as heat or light. This would not provide the cell with the continuous supply of energy the it needs. ...
... If it were one simple step, all the energy would be released at once and most would be released as heat or light. This would not provide the cell with the continuous supply of energy the it needs. ...
Chapter 19a Oxidative Phosphorylation and
... mitochondrial membrane through the pore in the Fo complex. This movement leads to conformational changes that decrease the affinity of the F1 portion of the synthase for ATP, resulting in its release from the enzyme. 28. Mitochondrial genes: their origin and the effects of mutation Page: 739 Difficu ...
... mitochondrial membrane through the pore in the Fo complex. This movement leads to conformational changes that decrease the affinity of the F1 portion of the synthase for ATP, resulting in its release from the enzyme. 28. Mitochondrial genes: their origin and the effects of mutation Page: 739 Difficu ...
File
... • photosynthesis & cellular respiration are cyclic processes • the products of one are the reactants of the other ...
... • photosynthesis & cellular respiration are cyclic processes • the products of one are the reactants of the other ...
Cellular respiration guided notes completed
... This cycle is fast repeating…a working muscle cell recycles all of its ATP molecules about once each minute!! (that’s 10,000,000 ATP molecules spent and regenerated per second ...
... This cycle is fast repeating…a working muscle cell recycles all of its ATP molecules about once each minute!! (that’s 10,000,000 ATP molecules spent and regenerated per second ...
CELL RESPIRATION
... Directions: For each term make a flash card with the definition on one side and the term on the other side. Key Terms: metabolism anabolism catabolism reduction oxidation redox reactions adenosine triphosphate (ATP) adenosine diphosphate (ADP) adenosine monophosphate (AMP) inorganic phosphate anaero ...
... Directions: For each term make a flash card with the definition on one side and the term on the other side. Key Terms: metabolism anabolism catabolism reduction oxidation redox reactions adenosine triphosphate (ATP) adenosine diphosphate (ADP) adenosine monophosphate (AMP) inorganic phosphate anaero ...
Using Customized Nutrition to Treat
... • Many of the chemicals and heavy metals that may affect the receptors also affect the thyroid. • People with diabetes who develop hypo- or hyperthyroidism have a much harder time controlling their blood sugar. • Making sure the diabetic patient is controlling their toxic loads and are becoming good ...
... • Many of the chemicals and heavy metals that may affect the receptors also affect the thyroid. • People with diabetes who develop hypo- or hyperthyroidism have a much harder time controlling their blood sugar. • Making sure the diabetic patient is controlling their toxic loads and are becoming good ...
Cellular respiration *vs
... If you remember the word anaerobic—means w/o oxygen--fermentation is a form of anaerobic respiration. • Because there is no oxygen for use the ATP for energy is much less. This fermentation occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and produces only 2 molecules of ATP—Therefore, this is not as efficient o ...
... If you remember the word anaerobic—means w/o oxygen--fermentation is a form of anaerobic respiration. • Because there is no oxygen for use the ATP for energy is much less. This fermentation occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and produces only 2 molecules of ATP—Therefore, this is not as efficient o ...
Cellular-Respiration Student
... energy in ATP synthesis is called photosphosphorylation • In cellular respiration, it is referred to as oxidative phosphorylation, or oxidative ATP synthesis • Named because the energy used to drive ATP synthesis comes from the energy released in the ETC from a series of oxidation reactions ...
... energy in ATP synthesis is called photosphosphorylation • In cellular respiration, it is referred to as oxidative phosphorylation, or oxidative ATP synthesis • Named because the energy used to drive ATP synthesis comes from the energy released in the ETC from a series of oxidation reactions ...
Cellular respiration
... are generally not realized due to losses such as the cost of moving pyruvate (from glycolysis), phosphate, and ADP (substrates for ATP synthesis) into the mitochondria. All are actively transported using carriers that utilise the stored energy in the proton electrochemical gradient. • Pyruvate is ta ...
... are generally not realized due to losses such as the cost of moving pyruvate (from glycolysis), phosphate, and ADP (substrates for ATP synthesis) into the mitochondria. All are actively transported using carriers that utilise the stored energy in the proton electrochemical gradient. • Pyruvate is ta ...
Histidine and tyrosine phosphorylation in pea mitochondria
... kinases, lacking motifs usually found in Ser/Thr-protein kinases, but containing motifs associated with prokaryotic histidine kinases. Besides PDH and BCKDH more than 10 substrates for protein kinases have been detected in mammalian mitochondria, half of which show cAMP-dependent phosphorylation, im ...
... kinases, lacking motifs usually found in Ser/Thr-protein kinases, but containing motifs associated with prokaryotic histidine kinases. Besides PDH and BCKDH more than 10 substrates for protein kinases have been detected in mammalian mitochondria, half of which show cAMP-dependent phosphorylation, im ...
No Slide Title
... ATP, NADH, and two pyruvates are the end products of glycolysis. It’s vital to know the reactants and products for each process of cellular respiration and photosynthesis! ...
... ATP, NADH, and two pyruvates are the end products of glycolysis. It’s vital to know the reactants and products for each process of cellular respiration and photosynthesis! ...
CHE 4310 Fall 2011
... you can remember from class won’t improve your answer— just answer clearly, succinctly, and in your own words. ...
... you can remember from class won’t improve your answer— just answer clearly, succinctly, and in your own words. ...
chapter 23
... So, when the cell needs energy, pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA, and the citric acid cycle proceeds. But when the cell has sufficient energy, there is not much conversion to acetyl-CoA, and the citric acid cycle slows. ...
... So, when the cell needs energy, pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA, and the citric acid cycle proceeds. But when the cell has sufficient energy, there is not much conversion to acetyl-CoA, and the citric acid cycle slows. ...
Mitochondrion

The mitochondrion (plural mitochondria) is a double membrane-bound organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. The word mitochondrion comes from the Greek μίτος, mitos, i.e. ""thread"", and χονδρίον, chondrion, i.e. ""granule"" or ""grain-like"".Mitochondria range from 0.5 to 1.0 μm in diameter. A considerable variation can be seen in the structure and size of this organelle. Unless specifically stained, they are not visible. These structures are described as ""the powerhouse of the cell"" because they generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy. In addition to supplying cellular energy, mitochondria are involved in other tasks, such as signaling, cellular differentiation, and cell death, as well as maintaining control of the cell cycle and cell growth. Mitochondria have been implicated in several human diseases, including mitochondrial disorders, cardiac dysfunction, and heart failure. A recent University of California study including ten children diagnosed with severe autism suggests that autism may be correlated with mitochondrial defects as well.Several characteristics make mitochondria unique. The number of mitochondria in a cell can vary widely by organism, tissue, and cell type. For instance, red blood cells have no mitochondria, whereas liver cells can have more than 2000. The organelle is composed of compartments that carry out specialized functions. These compartments or regions include the outer membrane, the intermembrane space, the inner membrane, and the cristae and matrix. Mitochondrial proteins vary depending on the tissue and the species. In humans, 615 distinct types of protein have been identified from cardiac mitochondria, whereas in rats, 940 proteins have been reported. The mitochondrial proteome is thought to be dynamically regulated. Although most of a cell's DNA is contained in the cell nucleus, the mitochondrion has its own independent genome. Further, its DNA shows substantial similarity to bacterial genomes.