18 Pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA to Krebs Cycle A/P
... absence of oxygen) and in itself cause red blood cells to release oxygen more rapidly (due to its acid nature) and thus relieve the anaerobic condition. Lactic acid can induce pain and cramps due to the dual effect of high acid environment and anaerobic condition. The most recent papers have show th ...
... absence of oxygen) and in itself cause red blood cells to release oxygen more rapidly (due to its acid nature) and thus relieve the anaerobic condition. Lactic acid can induce pain and cramps due to the dual effect of high acid environment and anaerobic condition. The most recent papers have show th ...
Outline06 Metabolism - Napa Valley College
... 3. Electron Transport Chain - electron carrier proteins are located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria 3 major protein complexes (I, III, IV) cytochromes - iron-containing proteins in the E.T.C. - NADH and FADH2 donate high-energy electrons to the E.T.C. - electrons move “downhill” through E. ...
... 3. Electron Transport Chain - electron carrier proteins are located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria 3 major protein complexes (I, III, IV) cytochromes - iron-containing proteins in the E.T.C. - NADH and FADH2 donate high-energy electrons to the E.T.C. - electrons move “downhill” through E. ...
biology exam review - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... c) Golgi apparatus and nucleus d) endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and cell wall 7. Imagine that you are late for a date and you reach your friend's door out of breath because you just ran the last three blocks from the bus stop. In a lame effort to impress and to try to make your date forget ...
... c) Golgi apparatus and nucleus d) endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and cell wall 7. Imagine that you are late for a date and you reach your friend's door out of breath because you just ran the last three blocks from the bus stop. In a lame effort to impress and to try to make your date forget ...
1) Which of the following statements describes the results of this
... C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy A) C6H12O6 is oxidized and O2 is reduced. B) O2 is oxidized and H2O is reduced. C) CO2 is reduced and O2 is oxidized. D) C6H12O6is reduced and CO2 is oxidized. E) O2 is reduced and CO2 is oxidized. Answer: A ...
... C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy A) C6H12O6 is oxidized and O2 is reduced. B) O2 is oxidized and H2O is reduced. C) CO2 is reduced and O2 is oxidized. D) C6H12O6is reduced and CO2 is oxidized. E) O2 is reduced and CO2 is oxidized. Answer: A ...
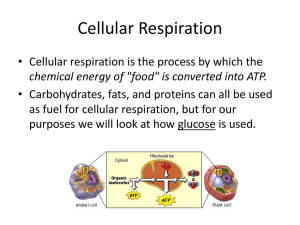
Cellular Respiration
... – The H+ that has built up in the intermembrane space wants out! It flows through a molecule called ATP synthase. As it does ATP is formed. • Each NADH that donates electrons to the chain will fuel the creation of 3 ATP. • Each FADH2 that donates elections to the chain will fuel the creation of 2 AT ...
... – The H+ that has built up in the intermembrane space wants out! It flows through a molecule called ATP synthase. As it does ATP is formed. • Each NADH that donates electrons to the chain will fuel the creation of 3 ATP. • Each FADH2 that donates elections to the chain will fuel the creation of 2 AT ...
Keigo Tanaka Chapter 9 – Cellular Respiration: Harvesting
... 6. Two hydrogens are transferred to FAD, forming FADH2 and oxidizing succinate to fumarate 7. The addition of a water molecule rearranges bonds in the substrate forming malate 8. The substrate is oxidized, reducing NAD+ to NADH and regenerating oxaloacetate so it can be used in the cycle again ...
... 6. Two hydrogens are transferred to FAD, forming FADH2 and oxidizing succinate to fumarate 7. The addition of a water molecule rearranges bonds in the substrate forming malate 8. The substrate is oxidized, reducing NAD+ to NADH and regenerating oxaloacetate so it can be used in the cycle again ...
Perspectives in Nutrition, 8th Edition
... metabolic pathways, such as glycolysis, beta-oxidation, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport system. 4. Describe the role that acetyl-CoA plays in cell metabolism. 5. Identify the conditions that lead to ketogenesis and its importance in survival during fasting. 6. Describe the process ...
... metabolic pathways, such as glycolysis, beta-oxidation, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport system. 4. Describe the role that acetyl-CoA plays in cell metabolism. 5. Identify the conditions that lead to ketogenesis and its importance in survival during fasting. 6. Describe the process ...
From Fig - Jiamusi University
... The oxidation processes of substances in organisms are known as biologic oxidation. When carbohydrate, fat, and proteins are degraded to form CO2 and water, some chemical energy is released and captured by ADP to form ATP for living processes, and part chemical energy liberated as heat to maintain b ...
... The oxidation processes of substances in organisms are known as biologic oxidation. When carbohydrate, fat, and proteins are degraded to form CO2 and water, some chemical energy is released and captured by ADP to form ATP for living processes, and part chemical energy liberated as heat to maintain b ...
BIGA 0 - SFSU Chemistry
... accomplished on time and that everyone in the group is participating. The manager will also be the only one to relay any questions the group may have to the instructor. b. Recorder: the recorder records the names and roles of the group members and the final responses for the group. c. Presenter/Spok ...
... accomplished on time and that everyone in the group is participating. The manager will also be the only one to relay any questions the group may have to the instructor. b. Recorder: the recorder records the names and roles of the group members and the final responses for the group. c. Presenter/Spok ...
Week 6 Pre-Lecture Slides
... How does diversification of metabolic output improve fitness for an organism? ...
... How does diversification of metabolic output improve fitness for an organism? ...
Chapter 3: Energy, Catalysis, and Biosynthesis
... 13-29 For each of the following sentences, fill in the blanks with the best word or phrase selected from the list below. Not all words or phrases will be used; each word or phrase may be used more than once. Oxidative phosphorylation is a process that occurs in the __________________ of mitochondria ...
... 13-29 For each of the following sentences, fill in the blanks with the best word or phrase selected from the list below. Not all words or phrases will be used; each word or phrase may be used more than once. Oxidative phosphorylation is a process that occurs in the __________________ of mitochondria ...
Free fatty acids regulate the uncoupling protein and alternative
... reducing substrates and the energy and carbon demand for biosynthesis [1,3,5], only PUMP can totally switch off chemiosmotic coupling. A puzzling question regarding the presence of these two energy-dissipating systems relates to a possible connection between their activities (shared regulation). Suc ...
... reducing substrates and the energy and carbon demand for biosynthesis [1,3,5], only PUMP can totally switch off chemiosmotic coupling. A puzzling question regarding the presence of these two energy-dissipating systems relates to a possible connection between their activities (shared regulation). Suc ...
How Cell Harvest Energy
... 23. Explain why respiration is considered exergonic. __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 24. What is the main reason energy is harvested in stages in respiration ________________________ ...
... 23. Explain why respiration is considered exergonic. __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 24. What is the main reason energy is harvested in stages in respiration ________________________ ...
Electron transport chain
... • Only 4 of 38 ATP ultimately produced by respiration of glucose are derived from substrate-level phosphorylation (2 from glycolysis and 2 from Krebs Cycle). • The vast majority of the ATP (90%) comes from the energy in the electrons carried by NADH and FADH2. • The energy in these electrons is used ...
... • Only 4 of 38 ATP ultimately produced by respiration of glucose are derived from substrate-level phosphorylation (2 from glycolysis and 2 from Krebs Cycle). • The vast majority of the ATP (90%) comes from the energy in the electrons carried by NADH and FADH2. • The energy in these electrons is used ...
10-3 Getting Energy to Make ATP
... ii. Not very efficient---only produces 2 ATP molecules from one glucose iii. There are different types of anaerobic respiration ...
... ii. Not very efficient---only produces 2 ATP molecules from one glucose iii. There are different types of anaerobic respiration ...
Exam 3
... Section 3. Problems. 4 questions 10 points each. 31. (10pts) A molecule of glucose stored in glycogen can be catabolized to two molecules of lactate under anaerobic conditions in muscle. Fill in each box with the name or structure of the intermediates along this pathway. Then indicate every step th ...
... Section 3. Problems. 4 questions 10 points each. 31. (10pts) A molecule of glucose stored in glycogen can be catabolized to two molecules of lactate under anaerobic conditions in muscle. Fill in each box with the name or structure of the intermediates along this pathway. Then indicate every step th ...
Glycogen Metabolism
... ● Ammonia secretion (5-10% of whole N turnover) in kidney tubules from glutamine (Chinese Restaurant) ● Nucleotide (pyrimidine) degradation ● Intestinal bacteria produce it from amino acids and urea Ammonia is very toxic → cerebral edema, increased cranial pressure (depletion of ATP in brain cells?) ...
... ● Ammonia secretion (5-10% of whole N turnover) in kidney tubules from glutamine (Chinese Restaurant) ● Nucleotide (pyrimidine) degradation ● Intestinal bacteria produce it from amino acids and urea Ammonia is very toxic → cerebral edema, increased cranial pressure (depletion of ATP in brain cells?) ...
Karbohidrat Metabolizması
... transport pathway in the inner mitochondrial membrane • The electrons transferred from succinate to FAD (to form FADH2) are passed directly to ubiquinone (UQ) in the electron transport pathway • Enzyme inhibited by malonate ...
... transport pathway in the inner mitochondrial membrane • The electrons transferred from succinate to FAD (to form FADH2) are passed directly to ubiquinone (UQ) in the electron transport pathway • Enzyme inhibited by malonate ...
energy & cellular respiration
... • As they do this, they pump H+ from matrix to intermembrane space ...
... • As they do this, they pump H+ from matrix to intermembrane space ...
The Organellar Genome and Metabolic Potential
... in various species (Gabaldón and Huynen 2004). Within the evolutionary ‘‘gap’’ between species with genome-containing mitochondria and species with mitosomes or hydrogenosomes (both lacking an organellar genome), the species N. ovalis provides an interesting link. Nyctotherus ovalis is an anaerobic ...
... in various species (Gabaldón and Huynen 2004). Within the evolutionary ‘‘gap’’ between species with genome-containing mitochondria and species with mitosomes or hydrogenosomes (both lacking an organellar genome), the species N. ovalis provides an interesting link. Nyctotherus ovalis is an anaerobic ...
Cellular Respiration
... cycle is a series of reactions that produce energy-storing molecules during aerobic respiration. •Electron Transport Chain During aerobic respiration, large amounts of ATP are made in an electron transport chain. ...
... cycle is a series of reactions that produce energy-storing molecules during aerobic respiration. •Electron Transport Chain During aerobic respiration, large amounts of ATP are made in an electron transport chain. ...
Mitochondrion

The mitochondrion (plural mitochondria) is a double membrane-bound organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. The word mitochondrion comes from the Greek μίτος, mitos, i.e. ""thread"", and χονδρίον, chondrion, i.e. ""granule"" or ""grain-like"".Mitochondria range from 0.5 to 1.0 μm in diameter. A considerable variation can be seen in the structure and size of this organelle. Unless specifically stained, they are not visible. These structures are described as ""the powerhouse of the cell"" because they generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy. In addition to supplying cellular energy, mitochondria are involved in other tasks, such as signaling, cellular differentiation, and cell death, as well as maintaining control of the cell cycle and cell growth. Mitochondria have been implicated in several human diseases, including mitochondrial disorders, cardiac dysfunction, and heart failure. A recent University of California study including ten children diagnosed with severe autism suggests that autism may be correlated with mitochondrial defects as well.Several characteristics make mitochondria unique. The number of mitochondria in a cell can vary widely by organism, tissue, and cell type. For instance, red blood cells have no mitochondria, whereas liver cells can have more than 2000. The organelle is composed of compartments that carry out specialized functions. These compartments or regions include the outer membrane, the intermembrane space, the inner membrane, and the cristae and matrix. Mitochondrial proteins vary depending on the tissue and the species. In humans, 615 distinct types of protein have been identified from cardiac mitochondria, whereas in rats, 940 proteins have been reported. The mitochondrial proteome is thought to be dynamically regulated. Although most of a cell's DNA is contained in the cell nucleus, the mitochondrion has its own independent genome. Further, its DNA shows substantial similarity to bacterial genomes.