Document
... In the process of respiration, energy stored in organic food molecules is transferred to the molecule Adenosine Triphosphate ATP. ATP in turn supplies the energy for metabolic processes in the cell. Synthesizing ATP uses a series of linked oxidation and reduction reaction. 8.1.1 Oxidation and Reduct ...
... In the process of respiration, energy stored in organic food molecules is transferred to the molecule Adenosine Triphosphate ATP. ATP in turn supplies the energy for metabolic processes in the cell. Synthesizing ATP uses a series of linked oxidation and reduction reaction. 8.1.1 Oxidation and Reduct ...
Recap: structure of ATP
... • This is catalysed by dehydrogenase enzymes • Co-enzymes are required to activate the oxidation reactions in respiration – Hydrogen atoms becomes attached to co enzymes e.g. NAD ...
... • This is catalysed by dehydrogenase enzymes • Co-enzymes are required to activate the oxidation reactions in respiration – Hydrogen atoms becomes attached to co enzymes e.g. NAD ...
Cellular Energetics
... • As NADH and FADH2 are oxidized, H+ inside the mitochondrial matrix is transported to the intermembrane space. This creates a proton-motive force and H+ moves back across the membrane thru ATP synthase and ATP is produced ...
... • As NADH and FADH2 are oxidized, H+ inside the mitochondrial matrix is transported to the intermembrane space. This creates a proton-motive force and H+ moves back across the membrane thru ATP synthase and ATP is produced ...
Note 4.1 - Cellular Respiration
... The mitochondrion is a membrane bound organelle, and is the power house of the cell, producing ATP. There are four steps to cellular respiration. Three of the four occur in the mitochondrion (pyruvate oxidation, citric acid cycle, and electron transport) and one in the cytosol (glycolysis). The mito ...
... The mitochondrion is a membrane bound organelle, and is the power house of the cell, producing ATP. There are four steps to cellular respiration. Three of the four occur in the mitochondrion (pyruvate oxidation, citric acid cycle, and electron transport) and one in the cytosol (glycolysis). The mito ...
SfRBM UAB 2017 Regional Redox Symposium, Abstract/Poster
... Moderate Exercise Training Attenuates Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Damage by Activating Nrf2-Signaling Identification of human lung epithelial metabolic responses to acute PAH exposure The novel RT-SQuARED-M method reveals the direct relationship between mitochondrial dynamics and redox potentia ...
... Moderate Exercise Training Attenuates Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Damage by Activating Nrf2-Signaling Identification of human lung epithelial metabolic responses to acute PAH exposure The novel RT-SQuARED-M method reveals the direct relationship between mitochondrial dynamics and redox potentia ...
160 GLUCOSE DECREASES DURING AMINO ACID
... proteinlmin in spite of the decreased incorporation seen in the mitochondria, suggesting that externally added ATP stimulates the phosphorylation of adenosine and release of nucleotides into the medium. The amount of adenosine associated with the mitochondria was constant from 0 to 10 min of incubat ...
... proteinlmin in spite of the decreased incorporation seen in the mitochondria, suggesting that externally added ATP stimulates the phosphorylation of adenosine and release of nucleotides into the medium. The amount of adenosine associated with the mitochondria was constant from 0 to 10 min of incubat ...
Cellular Respiration
... it as glucose. That glucose must be transformed into energy the cell can use, specifically ATP. This takes place in the mitochondria of cells. ...
... it as glucose. That glucose must be transformed into energy the cell can use, specifically ATP. This takes place in the mitochondria of cells. ...
View Newsletter - Bristlecone Behavioral Health
... distress, which turns on ancient pathways of cellular preservation. This archaic pathway of survival reverts the cell away from respiration with oxygen and over to sugar fermentation. In addition, the retrograde signal has a cascading effect within the cell’s nucleus… it triggers an overexpression o ...
... distress, which turns on ancient pathways of cellular preservation. This archaic pathway of survival reverts the cell away from respiration with oxygen and over to sugar fermentation. In addition, the retrograde signal has a cascading effect within the cell’s nucleus… it triggers an overexpression o ...
Welcome to the basics lecture on cellular respiration
... Now, let’s look at the side road of fermentation. This is a two‐step process that includes glycolysis, as we have seen already, and then a reversing of the reaction where the electrons that were removed from pyruvate are put right back onto it. The resulting molecule in mammals is lactate. We m ...
... Now, let’s look at the side road of fermentation. This is a two‐step process that includes glycolysis, as we have seen already, and then a reversing of the reaction where the electrons that were removed from pyruvate are put right back onto it. The resulting molecule in mammals is lactate. We m ...
Respiration
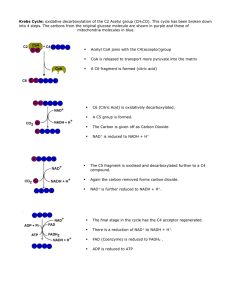
... enters the cycle and it is oxidized into 2 CO2 • The following are generated in the ...
... enters the cycle and it is oxidized into 2 CO2 • The following are generated in the ...
Name 1 Bio 451 12th November, 1999 EXAM III This
... ___ Required for the translocation of ALA synthase to the cytosol ...
... ___ Required for the translocation of ALA synthase to the cytosol ...
BIOL 303 Cell Biology Test preparation questionnaire # 1
... 111. What pathway of anaerobic metabolism is capable of maintaining the level of cellular NAD+? 112. What is the name and structure of the organelle where aerobic respiration takes place? 113. Describe the biochemical reaction that connects glycolysis to the TCA cycle. 114. Name and describe the thr ...
... 111. What pathway of anaerobic metabolism is capable of maintaining the level of cellular NAD+? 112. What is the name and structure of the organelle where aerobic respiration takes place? 113. Describe the biochemical reaction that connects glycolysis to the TCA cycle. 114. Name and describe the thr ...
Matrix: Citric Acid Cycle and Pyruvate Oxidation Mitochondrion A
... NADH donates electrons to Complex I (NADH Dehydrogenase) The poison cyanide prevents transfer of electrons to oxygen ...
... NADH donates electrons to Complex I (NADH Dehydrogenase) The poison cyanide prevents transfer of electrons to oxygen ...
Biology Chp 7 Notes
... 1. Glycolysis: Organic compounds are broken down into 3 carbon “Pyruvic Acid” a. ATP and NADH are made b. It is anaerobic 2. Aerobic Respiration: oxygen is used to break down pyruvic acid and make ATP c. Fermentation: glycolysis and anaerobic pathways occur when oxygen is not available d. Many of th ...
... 1. Glycolysis: Organic compounds are broken down into 3 carbon “Pyruvic Acid” a. ATP and NADH are made b. It is anaerobic 2. Aerobic Respiration: oxygen is used to break down pyruvic acid and make ATP c. Fermentation: glycolysis and anaerobic pathways occur when oxygen is not available d. Many of th ...
Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
... Before multiplexing, validation studies were conducted to show that LATE-PCR could amplify and sequence single copy mtDNA (Figures 4 and 5). Multiplexing was then conducted using the 12 primer sets (Figures 6-9). ...
... Before multiplexing, validation studies were conducted to show that LATE-PCR could amplify and sequence single copy mtDNA (Figures 4 and 5). Multiplexing was then conducted using the 12 primer sets (Figures 6-9). ...
Metabolism PPT File
... • Plays an important role during extreme physical exercise. • When not enough oxygen getting to muscle cells that need it. • anaerobic respiration supplies the extra energy needed. • But.... What results is a build up of lactic acid in your muscles = pain & fatigue. ...
... • Plays an important role during extreme physical exercise. • When not enough oxygen getting to muscle cells that need it. • anaerobic respiration supplies the extra energy needed. • But.... What results is a build up of lactic acid in your muscles = pain & fatigue. ...
Cellular Respiration NOTES
... NAD+ (so more glycolysis can still occur) and to take care of the pyruvate, organisms will convert the pyruvate into either: lactic acid (as we humans do) or into carbon dioxide and alcohol (like bacteria and yeasts). Note that fermentation does not result in any more ATP, so the only ATP is the 2 g ...
... NAD+ (so more glycolysis can still occur) and to take care of the pyruvate, organisms will convert the pyruvate into either: lactic acid (as we humans do) or into carbon dioxide and alcohol (like bacteria and yeasts). Note that fermentation does not result in any more ATP, so the only ATP is the 2 g ...
4 - Clark College
... • Describe what substrates enter and what products exit the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation when oxygen is available to the cell. • Name the coenzymes of the citric acid cycle and their role in metabolism. • Identify where in the cell the reactions of the citric acid cycle and oxidat ...
... • Describe what substrates enter and what products exit the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation when oxygen is available to the cell. • Name the coenzymes of the citric acid cycle and their role in metabolism. • Identify where in the cell the reactions of the citric acid cycle and oxidat ...
Review for Final Summer 2008
... o 4 levels of structure nucleic acid o Structure: 5Carbon sugar attached to nitrogen containing base and phosphate group o DNA vs. RNA (know structures) o ATP NADH NADPH FADH2 are nucleic acids ...
... o 4 levels of structure nucleic acid o Structure: 5Carbon sugar attached to nitrogen containing base and phosphate group o DNA vs. RNA (know structures) o ATP NADH NADPH FADH2 are nucleic acids ...
Bio150 Practice Exam 2 Name
... The light-dependent reactions produce water as a by-product; the light-independent reactions produce carbon dioxide as a waste product. e. The products of the light-dependent reactions are ADP, NADP+, and O2; the products of the light-independent reactions are ATP, NADPH, and sugar. Bonus Questions: ...
... The light-dependent reactions produce water as a by-product; the light-independent reactions produce carbon dioxide as a waste product. e. The products of the light-dependent reactions are ADP, NADP+, and O2; the products of the light-independent reactions are ATP, NADPH, and sugar. Bonus Questions: ...
Document
... Glucose (6C) is split into two pyruvate (3C) molecules. (aka pyruvic acid) does not require oxygen energy harvested/glucose: 2 ATP (via substrate-level phosphorylation) 2 NADH (actively transported into mitochondria of eukaryotic cells for use by the electron transport chain) 1st half: activates glu ...
... Glucose (6C) is split into two pyruvate (3C) molecules. (aka pyruvic acid) does not require oxygen energy harvested/glucose: 2 ATP (via substrate-level phosphorylation) 2 NADH (actively transported into mitochondria of eukaryotic cells for use by the electron transport chain) 1st half: activates glu ...
Bio 20-Cellular Respiration Assignment Part A
... 7. Glycolysis takes place in the ____________ of the cells a. Mitochondrial matrix b. Mitochondrial cristae c. Nucleus d. Cytoplasm 8. The carbon containing compounds formed at the end of glycolysis are two molecules of: a. Citric acid b. Carbon dioxide c. Pyruvate d. Lactic acid 9. Muscle fatigue ...
... 7. Glycolysis takes place in the ____________ of the cells a. Mitochondrial matrix b. Mitochondrial cristae c. Nucleus d. Cytoplasm 8. The carbon containing compounds formed at the end of glycolysis are two molecules of: a. Citric acid b. Carbon dioxide c. Pyruvate d. Lactic acid 9. Muscle fatigue ...
Metabolic Minimap article
... all (the first, of course, being photosynthesis), but its fairly obvious title has been the subject of much thought. The object has been to interrelate three pathways in which energy generated by respiration is coupled to the synthesis of ATP from ADP and phosphate. The formation of ATP is the end p ...
... all (the first, of course, being photosynthesis), but its fairly obvious title has been the subject of much thought. The object has been to interrelate three pathways in which energy generated by respiration is coupled to the synthesis of ATP from ADP and phosphate. The formation of ATP is the end p ...
Mitochondrion

The mitochondrion (plural mitochondria) is a double membrane-bound organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. The word mitochondrion comes from the Greek μίτος, mitos, i.e. ""thread"", and χονδρίον, chondrion, i.e. ""granule"" or ""grain-like"".Mitochondria range from 0.5 to 1.0 μm in diameter. A considerable variation can be seen in the structure and size of this organelle. Unless specifically stained, they are not visible. These structures are described as ""the powerhouse of the cell"" because they generate most of the cell's supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), used as a source of chemical energy. In addition to supplying cellular energy, mitochondria are involved in other tasks, such as signaling, cellular differentiation, and cell death, as well as maintaining control of the cell cycle and cell growth. Mitochondria have been implicated in several human diseases, including mitochondrial disorders, cardiac dysfunction, and heart failure. A recent University of California study including ten children diagnosed with severe autism suggests that autism may be correlated with mitochondrial defects as well.Several characteristics make mitochondria unique. The number of mitochondria in a cell can vary widely by organism, tissue, and cell type. For instance, red blood cells have no mitochondria, whereas liver cells can have more than 2000. The organelle is composed of compartments that carry out specialized functions. These compartments or regions include the outer membrane, the intermembrane space, the inner membrane, and the cristae and matrix. Mitochondrial proteins vary depending on the tissue and the species. In humans, 615 distinct types of protein have been identified from cardiac mitochondria, whereas in rats, 940 proteins have been reported. The mitochondrial proteome is thought to be dynamically regulated. Although most of a cell's DNA is contained in the cell nucleus, the mitochondrion has its own independent genome. Further, its DNA shows substantial similarity to bacterial genomes.