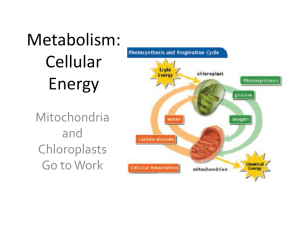
Cellular Energy
... Photosynthesis • Plants make enough glucose to be used during the night and on cloudy days when they don’t get sunlight. • The extra glucose is stored in the cells of the plant’s leaves. • When needed, the glucose travels to the mitochondria to be used in cellular respiration for the production of ...
... Photosynthesis • Plants make enough glucose to be used during the night and on cloudy days when they don’t get sunlight. • The extra glucose is stored in the cells of the plant’s leaves. • When needed, the glucose travels to the mitochondria to be used in cellular respiration for the production of ...
EATING AND EXERCISING WITH DIABETES
... Improve blood circulation around your body, reducing the risk of arterial disease, which can cause angina, heart attacks and strokes. As someone with diabetes, you do need to keep a few things in mind when exercising: ...
... Improve blood circulation around your body, reducing the risk of arterial disease, which can cause angina, heart attacks and strokes. As someone with diabetes, you do need to keep a few things in mind when exercising: ...
Helping the Student with Diabetes Succeed
... Students in the School Setting– Student’s Right to Self Manage ...
... Students in the School Setting– Student’s Right to Self Manage ...
doc Midterm 2001. Bio 201
... b) be faster at normal blood glucose concentrations than in normal people c) be proportional to the concentration of blood glucose d) be slower at normal blood glucose concentrations than in normal people e) stop 15. Which of the following statements is TRUE about equilibrium a) Keq > 1 b) Keq < 1 c ...
... b) be faster at normal blood glucose concentrations than in normal people c) be proportional to the concentration of blood glucose d) be slower at normal blood glucose concentrations than in normal people e) stop 15. Which of the following statements is TRUE about equilibrium a) Keq > 1 b) Keq < 1 c ...
Cell Respiration and Metabolism
... raise the temperature of one cubic centimeter of water from 14.5 degrees to 15.5 degrees centigrade. In an aerobic respiration one L of O2: + Carbohydrates + Proteins + Fat Therefore 1L of O2 + mixed food ...
... raise the temperature of one cubic centimeter of water from 14.5 degrees to 15.5 degrees centigrade. In an aerobic respiration one L of O2: + Carbohydrates + Proteins + Fat Therefore 1L of O2 + mixed food ...
Organ Integration and Control
... … take up glucose and store it as glycogen or convert it to fatty acids. … release glucose into the blood stream by breaking down Glycogen. … take up lactate and some amino acids (ala) and convert it into glucose. It also has the capacity to form ketone bodies from fatty acids. … degrades excess ami ...
... … take up glucose and store it as glycogen or convert it to fatty acids. … release glucose into the blood stream by breaking down Glycogen. … take up lactate and some amino acids (ala) and convert it into glucose. It also has the capacity to form ketone bodies from fatty acids. … degrades excess ami ...
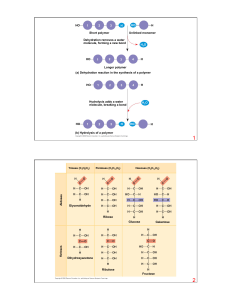
3.2 Carbohydrates, Lipids, and Proteins
... function of it, and its role in animals or plants. You may use the textbooks or computers. Ten minutes and then we will do quick presentations. 1. Glucose 2. lactose 3. glycogen 4. fructose 5. galactose 6. maltose 7. sucrose 8. starch 9. cellulose 10. ribose ...
... function of it, and its role in animals or plants. You may use the textbooks or computers. Ten minutes and then we will do quick presentations. 1. Glucose 2. lactose 3. glycogen 4. fructose 5. galactose 6. maltose 7. sucrose 8. starch 9. cellulose 10. ribose ...
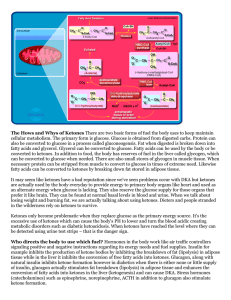
Pathology Ketone bodies are created at moderate
... cellular metabolism. The primary form is glucose. Glucose is obtained from digested carbs. Protein can also be converted to glucose in a process called gluconeogensis. Fat when digested is broken down into fatty acids and glycerol. Glycerol can be converted to glucose. Fatty acids can be used by the ...
... cellular metabolism. The primary form is glucose. Glucose is obtained from digested carbs. Protein can also be converted to glucose in a process called gluconeogensis. Fat when digested is broken down into fatty acids and glycerol. Glycerol can be converted to glucose. Fatty acids can be used by the ...
Topic 12 Homeostasis_Human Body Systems
... photosynthesis and other life activities •when plants do not keep enough water in their cells, they wilt and die stomate: a microscopic hole in a plant leaf which allows gases to enter and leave and water vapor to leave as well. Stomata is the plural of stomate. guard cells: open and close the stoma ...
... photosynthesis and other life activities •when plants do not keep enough water in their cells, they wilt and die stomate: a microscopic hole in a plant leaf which allows gases to enter and leave and water vapor to leave as well. Stomata is the plural of stomate. guard cells: open and close the stoma ...
The ATP-PCr energy system can operate with or without oxygen but
... The aerobic system, which is dependent on oxygen, is the most complex of the three energy systems. The metabolic reactions that take place in the presence of oxygen are responsible for most of the cellular energy produced by the body. However, aerobic metabolism is the slowest way to resynthesize AT ...
... The aerobic system, which is dependent on oxygen, is the most complex of the three energy systems. The metabolic reactions that take place in the presence of oxygen are responsible for most of the cellular energy produced by the body. However, aerobic metabolism is the slowest way to resynthesize AT ...
Week 4 met 2 kin 310
... 1. Describe the activation and translocation of free fatty acids into skeletal muscle that is required prior to metabolism as fuel. (do not include the regulation of translocation in your answer). 2. Describe the mobilization, circulation and uptake of free fatty acids during exercise. Why do resear ...
... 1. Describe the activation and translocation of free fatty acids into skeletal muscle that is required prior to metabolism as fuel. (do not include the regulation of translocation in your answer). 2. Describe the mobilization, circulation and uptake of free fatty acids during exercise. Why do resear ...
Doc1_5
... Glucose urine test The glucose urine test measures the amount of sugar (glucose) in a urine sample. The presence of glucose in the urine is called glycosuria or glucosuria. Glucose level can also be measured using a blood test or a cerebrospinal fluid test. This test was commonly used to test for an ...
... Glucose urine test The glucose urine test measures the amount of sugar (glucose) in a urine sample. The presence of glucose in the urine is called glycosuria or glucosuria. Glucose level can also be measured using a blood test or a cerebrospinal fluid test. This test was commonly used to test for an ...
Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... interact with one another and crystallize into a fiber; capacity to carry oxygen is greatly reduced. ...
... interact with one another and crystallize into a fiber; capacity to carry oxygen is greatly reduced. ...
Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... hemoglobin deform red blood cell into sickle shape. ...
... hemoglobin deform red blood cell into sickle shape. ...
Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... moledules, each carrying oxygen. ...
... moledules, each carrying oxygen. ...
87120_MLBIO10_LABA_CH03.indd
... Feedback mechanisms regulate the amounts of hormones released. When the levels of hormones in the blood are normal, reactions in the body take place at a normal rate and homeostasis is maintained. Sometimes, however, endocrine glands do not respond properly to feedback mechanisms. A gland might prod ...
... Feedback mechanisms regulate the amounts of hormones released. When the levels of hormones in the blood are normal, reactions in the body take place at a normal rate and homeostasis is maintained. Sometimes, however, endocrine glands do not respond properly to feedback mechanisms. A gland might prod ...
Press Release 29 May 2007 RESEARCH INVESTIGATES LINK
... study of adults in intensive care units (ICUs), which found that there were 43%1 fewer deaths and similar reductions in serious complications in adults receiving treatment to control their blood sugar levels. However it is unknown whether this form of blood sugar management will help children. ...
... study of adults in intensive care units (ICUs), which found that there were 43%1 fewer deaths and similar reductions in serious complications in adults receiving treatment to control their blood sugar levels. However it is unknown whether this form of blood sugar management will help children. ...
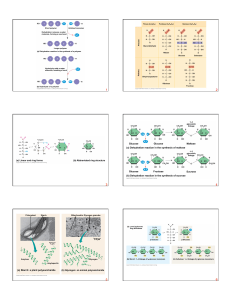
Biochem 2 Recitation #2 Spr 20152102105.pptx
... Biochem 2 Recitation #2 Glycolysis & Gluconeogenesis ...
... Biochem 2 Recitation #2 Glycolysis & Gluconeogenesis ...
Introduction Results Materials and Methods Conclusions
... From the 20 patients 12 were excluded for incomplete datasets or less than 14 days combined data. Eight patients included (6F), mean of most recent HbA1c: 7%, mean age 25.9 yrs (range 10-53) In 7 of the 8 patients observed: by leveraging those predictive models in a very basic control system, compar ...
... From the 20 patients 12 were excluded for incomplete datasets or less than 14 days combined data. Eight patients included (6F), mean of most recent HbA1c: 7%, mean age 25.9 yrs (range 10-53) In 7 of the 8 patients observed: by leveraging those predictive models in a very basic control system, compar ...
SI Powerpoint: Control of Metabolism
... Growth hormone/insulin-like growth factors Epinephrine Glucocorticoids Thyroxine Compare and contrast type I and type II diabetes mellitus with respect to: Age of onset Why blood glucose levels are high Is insulin deficient? Recommended treatment Are beta islet cells damaged? How does parathyroid ho ...
... Growth hormone/insulin-like growth factors Epinephrine Glucocorticoids Thyroxine Compare and contrast type I and type II diabetes mellitus with respect to: Age of onset Why blood glucose levels are high Is insulin deficient? Recommended treatment Are beta islet cells damaged? How does parathyroid ho ...
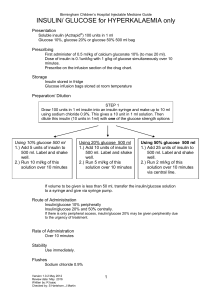
INSULIN/ GLUCOSE for HYPERKALAEMIA only
... INSULIN/ GLUCOSE for HYPERKALAEMIA only Common compatibilities at terminal Y-site IV maintenance solution containing glucose/sodium chloride. ...
... INSULIN/ GLUCOSE for HYPERKALAEMIA only Common compatibilities at terminal Y-site IV maintenance solution containing glucose/sodium chloride. ...
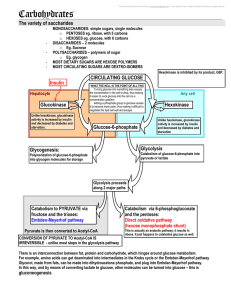
5 carbohydrates and the Krebs Cycle
... FRUCTOSE is converted to fructose-6-phosphate, analogous process to the phosphorylation of glucose; its even mediated by the same enzyme (hexokinase). The reaction of fructose phosphorylation can occur in the ABSENCE of insulin; but most of this occurs in the intestine, so it is not especially great ...
... FRUCTOSE is converted to fructose-6-phosphate, analogous process to the phosphorylation of glucose; its even mediated by the same enzyme (hexokinase). The reaction of fructose phosphorylation can occur in the ABSENCE of insulin; but most of this occurs in the intestine, so it is not especially great ...