circulatory routes - OCPS TeacherPress
... – Arteries: thinner walls, less elastic tissue, larger diameter (resistance?) – Deoxygenated blood (CO2 rich) to lungs and oxygen-rich back to heart – Pulmonary trunk, pulmonary arteries/veins ...
... – Arteries: thinner walls, less elastic tissue, larger diameter (resistance?) – Deoxygenated blood (CO2 rich) to lungs and oxygen-rich back to heart – Pulmonary trunk, pulmonary arteries/veins ...
PowerPoint to accompany
... • changes in fluid concentration • changes in electrolyte concentration • amount of adipose tissue ...
... • changes in fluid concentration • changes in electrolyte concentration • amount of adipose tissue ...
Filter Paper Blood Spots
... Important: Blood tests are analyzed every Thursday and results are reported on Fridays. Please place the filter paper into the mailbox by Sunday so that it arrives by Wednesday. All tests that arrive after Wednesday afternoon will not be reported until the following Friday. Blood spots should b ...
... Important: Blood tests are analyzed every Thursday and results are reported on Fridays. Please place the filter paper into the mailbox by Sunday so that it arrives by Wednesday. All tests that arrive after Wednesday afternoon will not be reported until the following Friday. Blood spots should b ...
acetyl-CoA
... GLUCONEOGENESIS The liver maintains glucose levels in blood during fasting through either glycogenolysis or gluconeogenesis. These pathways are promoted by glucagon and epinephrine and inhibited by insulin. In fasting, glycogen reserves drop dramatically in the first 12 hours, during which time gluc ...
... GLUCONEOGENESIS The liver maintains glucose levels in blood during fasting through either glycogenolysis or gluconeogenesis. These pathways are promoted by glucagon and epinephrine and inhibited by insulin. In fasting, glycogen reserves drop dramatically in the first 12 hours, during which time gluc ...
File
... In mammals, some tissues depend almost completely on glucose for their metabolic energy. Glucose from the blood is the sole or major fuel source for: • Human brain and nervous system - Brain requires 120 g/day, more than half that is stored as glycogen in muscles and liver. ...
... In mammals, some tissues depend almost completely on glucose for their metabolic energy. Glucose from the blood is the sole or major fuel source for: • Human brain and nervous system - Brain requires 120 g/day, more than half that is stored as glycogen in muscles and liver. ...
Carborie - Valensnutrition.com
... Sprinkle and stir in desired amount of Valens Carborie® into pre-mixed or prepared foods such as mashed potatoes, soups, gravies, yogurt or oatmeal. Used enclosed spoon to add recommended amount of glucose polymer based on the nutritional information and individual patients calories requirements. On ...
... Sprinkle and stir in desired amount of Valens Carborie® into pre-mixed or prepared foods such as mashed potatoes, soups, gravies, yogurt or oatmeal. Used enclosed spoon to add recommended amount of glucose polymer based on the nutritional information and individual patients calories requirements. On ...
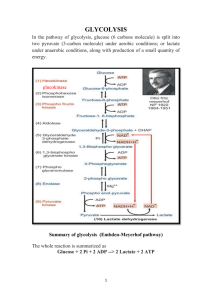
Summary of glycolysis (Embden
... availability of co-enzymes inside a cell is limited. Therefore, this step becomes a bottleneck in the whole reaction sequence. For smooth operation of the pathway, the NADH is to be reconverted to NAD+ by oxidative phosphorylation which needs oxygen. However, during exercise, there is lack of oxygen ...
... availability of co-enzymes inside a cell is limited. Therefore, this step becomes a bottleneck in the whole reaction sequence. For smooth operation of the pathway, the NADH is to be reconverted to NAD+ by oxidative phosphorylation which needs oxygen. However, during exercise, there is lack of oxygen ...
ch 8 diagnostic review
... you need ASAP – don’t wait until the night before an assessment or the last few days of the marking period when it is too late to effect a positive change. ...
... you need ASAP – don’t wait until the night before an assessment or the last few days of the marking period when it is too late to effect a positive change. ...
Dr. Tessa King, a veterinarian at Pilchuck Veterinary Hospital
... pancreatic enzymes and a T4 (thyroid level). A CBC evaluates the number of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets, along with the concentration of red blood cells (hematocrit or PCV) and hemoglobin levels. Abnormal changes on a CBC could include anemia (low red blood-cell count), leukocyto ...
... pancreatic enzymes and a T4 (thyroid level). A CBC evaluates the number of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets, along with the concentration of red blood cells (hematocrit or PCV) and hemoglobin levels. Abnormal changes on a CBC could include anemia (low red blood-cell count), leukocyto ...
Transport of molecules into a bacterial cell
... The vitamin CoA is way bigger than the organic acids acted on by the enzymes. CoA serves as a handle; an acid attaches to it, chemistry is done on the acid. Acids (e.g. acetate, succinate) attach to this –SH group here. ...
... The vitamin CoA is way bigger than the organic acids acted on by the enzymes. CoA serves as a handle; an acid attaches to it, chemistry is done on the acid. Acids (e.g. acetate, succinate) attach to this –SH group here. ...
Lecture 7: Metabolic Regulation - University of California, Berkeley
... Regulation of Glucose Homeostasis under Normal Conditions Regulation vs. Control. These are two terms for specific situations. Metabolic regulation — maintaining [metabolite]; homeostasis. Metabolic control — in response to stimulus the output through the metabolic pathway is altered “Fight or Fligh ...
... Regulation of Glucose Homeostasis under Normal Conditions Regulation vs. Control. These are two terms for specific situations. Metabolic regulation — maintaining [metabolite]; homeostasis. Metabolic control — in response to stimulus the output through the metabolic pathway is altered “Fight or Fligh ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism: Glycolysis
... The initial materials can come directly from the chloroplast, from stored starch in an amyloplast, or from imported sucrose. The activation of fructose and glucose requires ATP. ...
... The initial materials can come directly from the chloroplast, from stored starch in an amyloplast, or from imported sucrose. The activation of fructose and glucose requires ATP. ...
Exam 4, 2015 - Biochemistry at CSU, Stanislaus
... 14. (24 points) Describe how liver cells are controlled so that glycolysis and gluconeogenesis do not occur simultaneously in the liver. Give specific details about the regulation by insulin and glucagon. Give specific details about the reactions that are regulated. What enzyme, how is it regulated? ...
... 14. (24 points) Describe how liver cells are controlled so that glycolysis and gluconeogenesis do not occur simultaneously in the liver. Give specific details about the regulation by insulin and glucagon. Give specific details about the reactions that are regulated. What enzyme, how is it regulated? ...
24.t Glycolysis
... comes from inorganic phosphate ions present in the cytoplasm, so no ATP is expended here. In fact, I,3-bisphosphoglycerateis itself a high-energy compound-a mixed anhydride of a carboxylic acid and phosphoric acid (see Sec.23.7) that can transfer its newphosphoryl group to ADP (The phosphorylation o ...
... comes from inorganic phosphate ions present in the cytoplasm, so no ATP is expended here. In fact, I,3-bisphosphoglycerateis itself a high-energy compound-a mixed anhydride of a carboxylic acid and phosphoric acid (see Sec.23.7) that can transfer its newphosphoryl group to ADP (The phosphorylation o ...
ROSE CRYSTA-70(Rose Petal Extract)
... vegetables are necessary. ROSE POLYPHENOL relieves that exertion. ROSE POLYPHENOL can control blood glucose level, and it keeps blood glucose level low after eating. It also derives to keep insulin level low, to suppress producing fats from sugars. It is reported that ROSE POLYPHENOL inhibits lipase ...
... vegetables are necessary. ROSE POLYPHENOL relieves that exertion. ROSE POLYPHENOL can control blood glucose level, and it keeps blood glucose level low after eating. It also derives to keep insulin level low, to suppress producing fats from sugars. It is reported that ROSE POLYPHENOL inhibits lipase ...
glycolysis4bio
... that make a little bit of ATP from the partial breakdown of sugar into energy. • Organisms usually choose one of two paths after glycolysis: Fermentation or Aerobic Respiration. ...
... that make a little bit of ATP from the partial breakdown of sugar into energy. • Organisms usually choose one of two paths after glycolysis: Fermentation or Aerobic Respiration. ...
Metabolism III
... • Glucose is synthesized from glycerol, amino acids and lactate in gluconeogenesis • Pentose phosphate pathway produces NADPH and ribose 5-phosphate • Photosynthetic organisms absorb and direct solar energy through electron transport chains to synthesize ATP and NADPH. These high-energy products are ...
... • Glucose is synthesized from glycerol, amino acids and lactate in gluconeogenesis • Pentose phosphate pathway produces NADPH and ribose 5-phosphate • Photosynthetic organisms absorb and direct solar energy through electron transport chains to synthesize ATP and NADPH. These high-energy products are ...
Regulation of carbohydrate metabolism
... Her decrease in Fe-S centers is impairing the transfer of electrons in the electron transport chain. She is not producing as much H2O in the electron transport chain, leading to dehydration, which has resulted in fatigue. Iron forms a chelate with NADH and FAD(2H) that is necessary for them to donat ...
... Her decrease in Fe-S centers is impairing the transfer of electrons in the electron transport chain. She is not producing as much H2O in the electron transport chain, leading to dehydration, which has resulted in fatigue. Iron forms a chelate with NADH and FAD(2H) that is necessary for them to donat ...
Summary of lesson
... Q10. The simulation refers to oxidative phosphorylation, which is similar to respiration in that both require which molecule? A. Oxygen B. H20 C. CO2 D. Light Q11. FADH2 can be converted into how many ATPs? A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D. 3 Q12. NADH can be converted into how many ATP molecules? A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D. ...
... Q10. The simulation refers to oxidative phosphorylation, which is similar to respiration in that both require which molecule? A. Oxygen B. H20 C. CO2 D. Light Q11. FADH2 can be converted into how many ATPs? A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D. 3 Q12. NADH can be converted into how many ATP molecules? A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D. ...
Blood Groups - Ms. Cole`s Science Center
... • Why is it important for people in a hospital to get the right blood type when they need if for a transfusion? ...
... • Why is it important for people in a hospital to get the right blood type when they need if for a transfusion? ...
Bio Energy Blood Sugar Patch : Bio Energy Patch
... not get time to take the medicines regularly without fail. Fortunately there is a simple and easy method to maintain your blood sugar at normal ranges without taking any medicines. Use new bio energy blood sugar patches which monitor blood sugar levels!! If you are thinking of getting a bio energy b ...
... not get time to take the medicines regularly without fail. Fortunately there is a simple and easy method to maintain your blood sugar at normal ranges without taking any medicines. Use new bio energy blood sugar patches which monitor blood sugar levels!! If you are thinking of getting a bio energy b ...
Endocrinology 2007
... levels- but this approach increases the risk of hypoglycemic attacks c. it is acceptable today to add another treatment PO like sulfonylurea to patient with DM 1 who are overweight. d. daily follow up after sugar levels in the blood ( 3-6 times a day) e. insulin analogues have improved significantly ...
... levels- but this approach increases the risk of hypoglycemic attacks c. it is acceptable today to add another treatment PO like sulfonylurea to patient with DM 1 who are overweight. d. daily follow up after sugar levels in the blood ( 3-6 times a day) e. insulin analogues have improved significantly ...
word
... Note: In determining whether a patient specimen has a minimal likelihood that pathogens are present, an element of professional judgment is required to determine if a substance is exempt under this paragraph. That judgment should be based on the known medical history, symptoms and individual circums ...
... Note: In determining whether a patient specimen has a minimal likelihood that pathogens are present, an element of professional judgment is required to determine if a substance is exempt under this paragraph. That judgment should be based on the known medical history, symptoms and individual circums ...
Chapter 25
... – absorption of simple sugars (glucose, fructose & galactose) • In liver – fructose & galactose transformed into glucose – storage of glycogen (also in muscle) • In body cells --functions of glucose – oxidized to produce energy – conversion into something else – storage energy as triglyceride in fat ...
... – absorption of simple sugars (glucose, fructose & galactose) • In liver – fructose & galactose transformed into glucose – storage of glycogen (also in muscle) • In body cells --functions of glucose – oxidized to produce energy – conversion into something else – storage energy as triglyceride in fat ...