Chapter Nine
... 7. Name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the eukaryotic cell where each stage occurs. 8. Describe how the carbon skeleton of glucose changes as it proceeds through glycolysis. 9. Explain why ATP is required for the preparatory steps of glycolysis. 10. Identify where s ...
... 7. Name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the eukaryotic cell where each stage occurs. 8. Describe how the carbon skeleton of glucose changes as it proceeds through glycolysis. 9. Explain why ATP is required for the preparatory steps of glycolysis. 10. Identify where s ...
File
... 7. Name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the eukaryotic cell where each stage occurs. 8. Describe how the carbon skeleton of glucose changes as it proceeds through glycolysis. 9. Explain why ATP is required for the preparatory steps of glycolysis. 10. Identify where s ...
... 7. Name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the eukaryotic cell where each stage occurs. 8. Describe how the carbon skeleton of glucose changes as it proceeds through glycolysis. 9. Explain why ATP is required for the preparatory steps of glycolysis. 10. Identify where s ...
chapter 9
... 7. Name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the eukaryotic cell where each stage occurs. 8. Describe how the carbon skeleton of glucose changes as it proceeds through glycolysis. 9. Explain why ATP is required for the preparatory steps of glycolysis. 10. Identify where s ...
... 7. Name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the eukaryotic cell where each stage occurs. 8. Describe how the carbon skeleton of glucose changes as it proceeds through glycolysis. 9. Explain why ATP is required for the preparatory steps of glycolysis. 10. Identify where s ...
Dear Notetaker:
... - Stable 4 hour of glucagon infusion can deplete a liver of glycogen Effects of Glucagon on Carbohydrate metabolism - Induce gluconeogenesis in liver - Start converting amino acids into glucose ...
... - Stable 4 hour of glucagon infusion can deplete a liver of glycogen Effects of Glucagon on Carbohydrate metabolism - Induce gluconeogenesis in liver - Start converting amino acids into glucose ...
18 Pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA to Krebs Cycle A/P
... energy macromolecules (such as sugar, lipid, and protein). Pyruvate can be converted to lactic acid in bacteria and man when oxygen is in short supply or not available. The build up of lactic acid causes some interesting effects. 1.) Lactic acid build up is a way to temporarily store a high-energy h ...
... energy macromolecules (such as sugar, lipid, and protein). Pyruvate can be converted to lactic acid in bacteria and man when oxygen is in short supply or not available. The build up of lactic acid causes some interesting effects. 1.) Lactic acid build up is a way to temporarily store a high-energy h ...
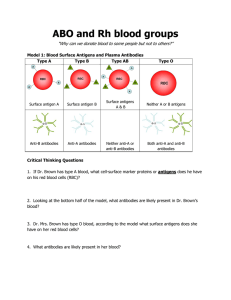
ABO and Rh blood groups
... 7. What reaction occurs between the donor's red blood cells and the recipient's opposing antibodies? a. What process follows agglutination? 8. Blood mis-matches can result in a condition called Acute Hemolytic Reaction. What are the symptoms of this reaction? ...
... 7. What reaction occurs between the donor's red blood cells and the recipient's opposing antibodies? a. What process follows agglutination? 8. Blood mis-matches can result in a condition called Acute Hemolytic Reaction. What are the symptoms of this reaction? ...
Camp 1
... • The biosynthesis of other di-, oligo-, and polysaccharides also uses this common activation step to form an appropriate UDP derivative. ...
... • The biosynthesis of other di-, oligo-, and polysaccharides also uses this common activation step to form an appropriate UDP derivative. ...
BIOLOGY 1 WORKSHEET II
... Compare and contrast the differences in cellular respiration when oxygen is readily available and when oxygen becomes limited in supply. Include differences in ATP production, electron transport, and waste products. Also describe the locations where the chemical pathways occur. O2 Available (Normal ...
... Compare and contrast the differences in cellular respiration when oxygen is readily available and when oxygen becomes limited in supply. Include differences in ATP production, electron transport, and waste products. Also describe the locations where the chemical pathways occur. O2 Available (Normal ...
9/2/08 Transcript I - UAB School of Optometry
... Today we will study glucose as an example of how are carbohydrates are metabolized. Slide #1- Glycolysis The Embden-Meyerhof (Warburg) Pathway: All cells can carry out this primitive anaerobic pathway, even red blood cells which do not have a nucleus or mitochrondria Anaerobic pathway- does not ...
... Today we will study glucose as an example of how are carbohydrates are metabolized. Slide #1- Glycolysis The Embden-Meyerhof (Warburg) Pathway: All cells can carry out this primitive anaerobic pathway, even red blood cells which do not have a nucleus or mitochrondria Anaerobic pathway- does not ...
Metabolic Pathways and Energy Production
... Is the primary energy source for the brain, skeletal muscle, and red blood cells. Deficiency can impair the brain and nervous system. Copyright © 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Is the primary energy source for the brain, skeletal muscle, and red blood cells. Deficiency can impair the brain and nervous system. Copyright © 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Hexose MonoPhosphate (HMP) shunt pathway
... drug reduction, and as a cofactor for some non-synthetic enzymatic reactions. In addition, HMP is used for the production of ribose for nucleotide and nucleic acid synthesis. The hexose monophosphate pathway also allows the entry of some carbohydrates into the glycolytic ...
... drug reduction, and as a cofactor for some non-synthetic enzymatic reactions. In addition, HMP is used for the production of ribose for nucleotide and nucleic acid synthesis. The hexose monophosphate pathway also allows the entry of some carbohydrates into the glycolytic ...
Hexose MonoPhosphate (HMP) shunt pathway
... drug reduction, and as a cofactor for some non-synthetic enzymatic reactions. In addition, HMP is used for the production of ribose for nucleotide and nucleic acid synthesis. The hexose monophosphate pathway also allows the entry of some carbohydrates into the glycolytic ...
... drug reduction, and as a cofactor for some non-synthetic enzymatic reactions. In addition, HMP is used for the production of ribose for nucleotide and nucleic acid synthesis. The hexose monophosphate pathway also allows the entry of some carbohydrates into the glycolytic ...
Chapter 7 Carbohydrates: Nomenclature Monosaccharides
... mixture of the two contains more beta than alpha. Note we most commonly find glucose and other aldohexoses in the pyranose ring form, while fructose, a keto hexose, is found in the furanose ring form, and ribose, an aldopentose, is found in the furanose ring form. The free sugars can exist as a mixt ...
... mixture of the two contains more beta than alpha. Note we most commonly find glucose and other aldohexoses in the pyranose ring form, while fructose, a keto hexose, is found in the furanose ring form, and ribose, an aldopentose, is found in the furanose ring form. The free sugars can exist as a mixt ...
Lecture 3
... – Mostly in liver – Lactate and pyruvate (usu. In the form of alanine) and glycerol can be used by the liver to produce glucose ...
... – Mostly in liver – Lactate and pyruvate (usu. In the form of alanine) and glycerol can be used by the liver to produce glucose ...
Cellular Respiration
... Cellular Respiration The process by which glucose molecules are broken down to release energy is cellular respiration. It is a series of chemical reactions that produces ATP. Most cellular processes use ATP for energy. ...
... Cellular Respiration The process by which glucose molecules are broken down to release energy is cellular respiration. It is a series of chemical reactions that produces ATP. Most cellular processes use ATP for energy. ...
U4L22 exercise - University of Sydney
... – Fatty acids substitute for glucose as a fuel – Fatty acids prevent glucose from being ...
... – Fatty acids substitute for glucose as a fuel – Fatty acids prevent glucose from being ...
Chapter 14 Glycolysis and the catabolism of hexoses
... Lactose intolerance come from the disappearance of lactase activity from the intestinal epithelial. When the undigested lactose hit the large intestine bacteria convert it to toxic product that cause cramps and its presence increases the osmolality So more water is retained. C. Other monosaccharides ...
... Lactose intolerance come from the disappearance of lactase activity from the intestinal epithelial. When the undigested lactose hit the large intestine bacteria convert it to toxic product that cause cramps and its presence increases the osmolality So more water is retained. C. Other monosaccharides ...
Forensic Serology Chapter 12
... A-B-O blood types: When a gene is made of two similar genes, they are said to be homozygous. Examples include AA or BB. If the gene is made up of two different genes, it is said to be heterozygous. An example would be AB. A and B genes are dominant, while O genes are recessive. A pair of A-B- ...
... A-B-O blood types: When a gene is made of two similar genes, they are said to be homozygous. Examples include AA or BB. If the gene is made up of two different genes, it is said to be heterozygous. An example would be AB. A and B genes are dominant, while O genes are recessive. A pair of A-B- ...
The Glucose Tolerance Test as a Laboratory Tool with
... Premise: The oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is vital for the characterization of metabolic syndrome, the natural progression from prediabetes to Type 2 diabetes, and characterization of the metabolic actions of cardiovascular and metabolic drugs. Although the OGTT is seldom used as a diagnostic ...
... Premise: The oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) is vital for the characterization of metabolic syndrome, the natural progression from prediabetes to Type 2 diabetes, and characterization of the metabolic actions of cardiovascular and metabolic drugs. Although the OGTT is seldom used as a diagnostic ...
Clozaril Monitoring Education Sheet
... CLOZARIL® / CLOZAPINE MONITORING “In clinical trials, Clozaril use was associated with a 1%-2% incidence of agranulocytosis, a potentially fatal blood disorder which, if caught early, can be reversed. Mandatory monitoring of WBC and ANC blood levels and drug dispensing as per requirements, provide a ...
... CLOZARIL® / CLOZAPINE MONITORING “In clinical trials, Clozaril use was associated with a 1%-2% incidence of agranulocytosis, a potentially fatal blood disorder which, if caught early, can be reversed. Mandatory monitoring of WBC and ANC blood levels and drug dispensing as per requirements, provide a ...
Energy Metabolism - Rajarata University of Sri Lanka
... inhaled through the lungs. When oxygen is limiting, aerobic oxidation is affected and energy production is inhibited. In the case of a stroke, brain function fails as a result of non availability of energy for its maintenance and functioning3. The hydrogen extracted from dietary constituents is tran ...
... inhaled through the lungs. When oxygen is limiting, aerobic oxidation is affected and energy production is inhibited. In the case of a stroke, brain function fails as a result of non availability of energy for its maintenance and functioning3. The hydrogen extracted from dietary constituents is tran ...
NME2.28: fat and carbohydrate metabolism in the
... Non-hormonal control of fatty acid synthesis is through: o Citrate – activates acetyl-CoA carboxylase promoting fatty acid synthesis o Fatty acids – inhibit PDH and acetyl-CoA carboxylase restricting fatty acid synthesis o NADH – inhibits PDH restricting fatty acid synthesis ...
... Non-hormonal control of fatty acid synthesis is through: o Citrate – activates acetyl-CoA carboxylase promoting fatty acid synthesis o Fatty acids – inhibit PDH and acetyl-CoA carboxylase restricting fatty acid synthesis o NADH – inhibits PDH restricting fatty acid synthesis ...
Body`s Transport System
... vessels branch into smaller ones. Eventually blood flows through tiny capillaries that are in close contact with the air that comes into the lungs. ...
... vessels branch into smaller ones. Eventually blood flows through tiny capillaries that are in close contact with the air that comes into the lungs. ...
MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY Lectures 35-36 Chp. 26
... eyes (sclera) experienced by Erin Galway, occurs when plasma becomes supersaturated with bilirubin (>2 to 2.5 mg/dL), and the excess diffuses into tissues. ...
... eyes (sclera) experienced by Erin Galway, occurs when plasma becomes supersaturated with bilirubin (>2 to 2.5 mg/dL), and the excess diffuses into tissues. ...