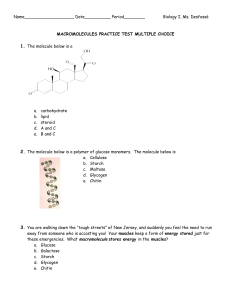
macromolecules practice test multiple choice
... Proteins are made up of chains of Monosaccharides Nucleotides Amino acids Fatty acids Steroids ...
... Proteins are made up of chains of Monosaccharides Nucleotides Amino acids Fatty acids Steroids ...
CHAPTER 8 CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... 5. Glucose is high-energy molecule; CO2 and H2O are low-energy molecules; process is exergonic and releases energy. 6. Electrons are removed from substrates and received by oxygen which combines with H+ to become water. 7. Glucose is oxidized and O2 is reduced. 8. The buildup of ATP is an endergonic ...
... 5. Glucose is high-energy molecule; CO2 and H2O are low-energy molecules; process is exergonic and releases energy. 6. Electrons are removed from substrates and received by oxygen which combines with H+ to become water. 7. Glucose is oxidized and O2 is reduced. 8. The buildup of ATP is an endergonic ...
Trafficking of phosphatidylinositol by phosphatidylinositol transfer
... proteins that were able to bind and transport phospholipids, in particular PtdIns and PtdCho (phosphatidylcholine). The first mammalian PITP was purified from bovine brain [1] and its sequence was determined in 1989 [2]. It encoded a protein of 271 amino acids, which showed no sequence similarity wi ...
... proteins that were able to bind and transport phospholipids, in particular PtdIns and PtdCho (phosphatidylcholine). The first mammalian PITP was purified from bovine brain [1] and its sequence was determined in 1989 [2]. It encoded a protein of 271 amino acids, which showed no sequence similarity wi ...
Histone H3 phosphorylation is required for the initiation, but not
... telophase (Gurley et al., 1978; Paulson and Taylor, 1982; Hendzel et al., 1997). In Tetrahymena, H3 phosphorylation occurs only in the mitotic micronucleus; H3 is not phosphorylated in the macronucleus, which divides amitotically without obvious chromosome condensation (Allis and Gorovsky, 1981). Wh ...
... telophase (Gurley et al., 1978; Paulson and Taylor, 1982; Hendzel et al., 1997). In Tetrahymena, H3 phosphorylation occurs only in the mitotic micronucleus; H3 is not phosphorylated in the macronucleus, which divides amitotically without obvious chromosome condensation (Allis and Gorovsky, 1981). Wh ...
Chapter_02_4E - Ironbark (xtelco)
... Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain, resulting in the formation of H2O, CO2, and 38-39 molecules of ATP • Fat oxidation involves β-oxidation of free fatty acids, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain to produce more ATP than carbohydrate • The maximum rate of ATP formation from ...
... Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain, resulting in the formation of H2O, CO2, and 38-39 molecules of ATP • Fat oxidation involves β-oxidation of free fatty acids, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain to produce more ATP than carbohydrate • The maximum rate of ATP formation from ...
In Vitro Bioassays Technical Sheet
... and efficacy of biopharmaceutical products, and also for the confirmation of biocomparability of innovator and biosimilar product. In turn, these assays must be reliable, standardized, and relevant to reflect the product’s mode of action. This sheet reviews assays which would be most appropriate to ...
... and efficacy of biopharmaceutical products, and also for the confirmation of biocomparability of innovator and biosimilar product. In turn, these assays must be reliable, standardized, and relevant to reflect the product’s mode of action. This sheet reviews assays which would be most appropriate to ...
Notes - Biological Molecules
... than negative feedback. Indeed, in Biology 12, there is only ONE specific example of positive feedback that you must know, and that is the positive feedback loop that occurs during LABOUR (childbirth) involving the hormone OXYTOCIN. Oxytocin is made in the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pi ...
... than negative feedback. Indeed, in Biology 12, there is only ONE specific example of positive feedback that you must know, and that is the positive feedback loop that occurs during LABOUR (childbirth) involving the hormone OXYTOCIN. Oxytocin is made in the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pi ...
as a PDF
... 5) Conclusions..........................................................................................9 6) References...........................................................................................10 ABSTRACT : Glucose is a simple sugar with a varied chemistry. It is an essential molecu ...
... 5) Conclusions..........................................................................................9 6) References...........................................................................................10 ABSTRACT : Glucose is a simple sugar with a varied chemistry. It is an essential molecu ...
Abscisic Acid–Induced Transcription Is Mediated by
... have the ability to mediate ABA signals, because transcription from a chimeric promoter containing GAL4 binding sites becomes ABA inducible in the presence of a GAL4 DNA binding domain–TRAB1 fusion protein (Hobo et al., 1999b). ABI5 is an Arabidopsis bZIP factor homologous with TRAB1 (Finkelstein an ...
... have the ability to mediate ABA signals, because transcription from a chimeric promoter containing GAL4 binding sites becomes ABA inducible in the presence of a GAL4 DNA binding domain–TRAB1 fusion protein (Hobo et al., 1999b). ABI5 is an Arabidopsis bZIP factor homologous with TRAB1 (Finkelstein an ...
Macronutrient Metabolism in Exercise and Training
... – CNS used blood glucose as energy (central fatigue) – Increased fat metabolism – Fat provides energy at a slower rate ...
... – CNS used blood glucose as energy (central fatigue) – Increased fat metabolism – Fat provides energy at a slower rate ...
GLYCOLYSIS AND GLUCONEOGENESIS
... enzyme, which normally uses phosphate and makes 1,3-disphosphoglycerate, is fooled by the arsenate and makes the arsenate ester instead. With the phosphate ester, the next enzyme in glycolysis makes an ATP from the 1,3-diphosphoglycerate. The arsenate analog of 1,3-disphosphoglycerate is chemically ...
... enzyme, which normally uses phosphate and makes 1,3-disphosphoglycerate, is fooled by the arsenate and makes the arsenate ester instead. With the phosphate ester, the next enzyme in glycolysis makes an ATP from the 1,3-diphosphoglycerate. The arsenate analog of 1,3-disphosphoglycerate is chemically ...
IL-5 Receptor-mediated Tyrosine Phosphorylation of SH2
... which activates Sos protein, a Ras nucleotide-exchange protein (22). Ras has been shown to work downstream of tyrosine kinases in the growth signaling pathway (23-25). p95 ray (26) and p75 Hsl (27), which are expressed specifically in hematopoietic cells and have SH2 and/or SH3 domains, were recentl ...
... which activates Sos protein, a Ras nucleotide-exchange protein (22). Ras has been shown to work downstream of tyrosine kinases in the growth signaling pathway (23-25). p95 ray (26) and p75 Hsl (27), which are expressed specifically in hematopoietic cells and have SH2 and/or SH3 domains, were recentl ...
Answers to end of chapter questions
... reaction that releases energy? (C) Exergonic 11. What term is used to denote the energy difference between the substrates of an enzymatic reaction and the transition state? (B) DG‡ 12. Which one of the following statements is incorrect? (A) An enzyme changes the DG values for substrates and ...
... reaction that releases energy? (C) Exergonic 11. What term is used to denote the energy difference between the substrates of an enzymatic reaction and the transition state? (B) DG‡ 12. Which one of the following statements is incorrect? (A) An enzyme changes the DG values for substrates and ...
fMRI: Biological Basis and Experiment Design
... Continued debate about whether (approximately) stoichiometric coupling indicates that glucose uptake is driven by glutamate cycling Continued debate about compartmentalization of oxidative and non-oxidative metabolism in neurons and glia ...
... Continued debate about whether (approximately) stoichiometric coupling indicates that glucose uptake is driven by glutamate cycling Continued debate about compartmentalization of oxidative and non-oxidative metabolism in neurons and glia ...
9700/04 - StudyGuide.PK
... (a) Describe the importance of ATP in cells, giving two examples of processes in which it is used. ...
... (a) Describe the importance of ATP in cells, giving two examples of processes in which it is used. ...
Biosynthesis of glucose – gluconeogenesis
... The amounts and activities of the distinctive enzymes of each pathway are controlled. The rate of glycolysis is determined by the concentration of glucose. ...
... The amounts and activities of the distinctive enzymes of each pathway are controlled. The rate of glycolysis is determined by the concentration of glucose. ...
Blood Glucose
... • It is a tyrosine kinase i.e. functions as an enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to tyrosine residues on intracellular target proteins. • Binding of insulin to the alpha subunits causes the beta subunits to phosphorylate themselves (autophosphorylation), thus activating the catalytic a ...
... • It is a tyrosine kinase i.e. functions as an enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to tyrosine residues on intracellular target proteins. • Binding of insulin to the alpha subunits causes the beta subunits to phosphorylate themselves (autophosphorylation), thus activating the catalytic a ...
Gluconeogenesis
... 1. Pyruvate carboxylase catalyses the irreversible ATP-driven formation of oxaloacetate from pyruvate and CO2. This enzyme found in the mitochondria of the liver and kidney but not of muscle. 2. PEP carboxykinase (PEPCK) concerts oxaloacetate to PEP that uses GTP as a phosphorylating agent. ...
... 1. Pyruvate carboxylase catalyses the irreversible ATP-driven formation of oxaloacetate from pyruvate and CO2. This enzyme found in the mitochondria of the liver and kidney but not of muscle. 2. PEP carboxykinase (PEPCK) concerts oxaloacetate to PEP that uses GTP as a phosphorylating agent. ...
electron transport chain
... • electrons are conducted laterally through the membrane from one ETC complex to the next, each time donating some of their energy to "pump" H+ ions. • Finally the de-energized electrons are combined with hydrogen ions and oxygen to produce water in the matrix • This reaction is catalyzed by cytochr ...
... • electrons are conducted laterally through the membrane from one ETC complex to the next, each time donating some of their energy to "pump" H+ ions. • Finally the de-energized electrons are combined with hydrogen ions and oxygen to produce water in the matrix • This reaction is catalyzed by cytochr ...
Cellular Respiration
... Unit: Linking Cell Structures to Function Read the passage below. Then answer the questions that follow. ...
... Unit: Linking Cell Structures to Function Read the passage below. Then answer the questions that follow. ...
Metabolism: Introduction
... The diffusion of ions across a membrane build up of proton gradient just so H+ could flow through ATP synthase enzyme to build ATP ...
... The diffusion of ions across a membrane build up of proton gradient just so H+ could flow through ATP synthase enzyme to build ATP ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).