Carbohydrate Metabolism-1
... Glycogenesis is the formation of glycogen from glucose. • Glycogen is synthesized depending on the demand for glucose and ATP (energy). If both are present in relatively high amounts, then the excess of insulin promotes the glucose conversion into glycogen for storage in liver and muscle cells. In t ...
... Glycogenesis is the formation of glycogen from glucose. • Glycogen is synthesized depending on the demand for glucose and ATP (energy). If both are present in relatively high amounts, then the excess of insulin promotes the glucose conversion into glycogen for storage in liver and muscle cells. In t ...
Organic Compounds
... • Hydrophobic (held together by non-polar covalent bonds) • Contains MORE energy-rich C-H bonds than carbs • Types include: neutral fats, phospholipids, steroids, carotenoids, waxes – Neutral fats: most abundant type of lipid 3 Fatty Acids + glycerol • Simplest lipid = fatty acid ...
... • Hydrophobic (held together by non-polar covalent bonds) • Contains MORE energy-rich C-H bonds than carbs • Types include: neutral fats, phospholipids, steroids, carotenoids, waxes – Neutral fats: most abundant type of lipid 3 Fatty Acids + glycerol • Simplest lipid = fatty acid ...
Discovering Macromolecular Interactions
... The quality of the sample that is used for IP applications critically depends on the right lysis buffer, which stabilizes native protein conformation, inhibits enzymatic activity, minimizes antibody binding site denaturation and maximizes the release of proteins from the cells or tissue. The lysis b ...
... The quality of the sample that is used for IP applications critically depends on the right lysis buffer, which stabilizes native protein conformation, inhibits enzymatic activity, minimizes antibody binding site denaturation and maximizes the release of proteins from the cells or tissue. The lysis b ...
Metabolism
... It is a series of protein/prosthetic group carriers that pass electrons from one to the other. Electrons are donated to the ETS by NADH and FADH2 As a pair of electrons is passed from carrier to carrier, energy is released and is used to form ATP At the end of the electron transport chain, oxyge ...
... It is a series of protein/prosthetic group carriers that pass electrons from one to the other. Electrons are donated to the ETS by NADH and FADH2 As a pair of electrons is passed from carrier to carrier, energy is released and is used to form ATP At the end of the electron transport chain, oxyge ...
STUDY GUIDE: GLYCOLYSIS, FERMENTATION AND ANAEROBIC
... 2. Explain how the molecular reactions of cellular respiration transform the chemical bond energy of krebs cycle substrates into the more readily available bond energy of ATP. Include in your discussion the structure of the mitochondrion and show how it is important to the reactions of the Krebs cyc ...
... 2. Explain how the molecular reactions of cellular respiration transform the chemical bond energy of krebs cycle substrates into the more readily available bond energy of ATP. Include in your discussion the structure of the mitochondrion and show how it is important to the reactions of the Krebs cyc ...
7 CellRespiration
... part. Where in a prokaryotic cell is each process performed? Where in a eukaryotic cell is each process performed? 5. Describe the process of glycolysis with regards to the starting molecule, ending molecule(s), and the other reactants used and products produced. How many carbons are in the product ...
... part. Where in a prokaryotic cell is each process performed? Where in a eukaryotic cell is each process performed? 5. Describe the process of glycolysis with regards to the starting molecule, ending molecule(s), and the other reactants used and products produced. How many carbons are in the product ...
Fe-S
... The glyoxylate cycle results in the net conversion of two acetyl-CoA to succinate instead of 4 CO2 in citric acid cycle. ...
... The glyoxylate cycle results in the net conversion of two acetyl-CoA to succinate instead of 4 CO2 in citric acid cycle. ...
Biochemistry of Cells
... Proteins as Enzymes • Many proteins act as biological catalysts or enzymes Thousands of different enzymes exist in the body Enzymes control the rate of chemical reactions by weakening bonds, thus lowering the amount of activation energy needed for the reaction ...
... Proteins as Enzymes • Many proteins act as biological catalysts or enzymes Thousands of different enzymes exist in the body Enzymes control the rate of chemical reactions by weakening bonds, thus lowering the amount of activation energy needed for the reaction ...
Biochemistry Metabolic pathways - Limes-Institut-Bonn
... polysaccharides and lipids are broken down into their component building blocks. Stage 2: The building blocks are degraded into the common product, generally the acetyl groups of acetyl-CoA. ...
... polysaccharides and lipids are broken down into their component building blocks. Stage 2: The building blocks are degraded into the common product, generally the acetyl groups of acetyl-CoA. ...
Bio-201-chapter-5-MEC
... linkages can’t hydrolyze linkages in cellulose • Cellulose in human food passes through the digestive tract as insoluble fiber • Some microbes use enzymes to digest cellulose • Many herbivores, from cows to termites, have symbiotic relationships with these microbes ...
... linkages can’t hydrolyze linkages in cellulose • Cellulose in human food passes through the digestive tract as insoluble fiber • Some microbes use enzymes to digest cellulose • Many herbivores, from cows to termites, have symbiotic relationships with these microbes ...
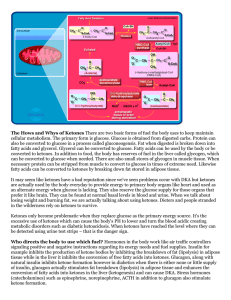
Pathology Ketone bodies are created at moderate
... can be converted to glucose when needed. There are also small stores of glycogen in muscle tissue. When necessary protein can be stripped from muscle to convert to glucose in times of extreme need. Likewise fatty acids can be converted to ketones by breaking down fat stored in adipose tissue. It may ...
... can be converted to glucose when needed. There are also small stores of glycogen in muscle tissue. When necessary protein can be stripped from muscle to convert to glucose in times of extreme need. Likewise fatty acids can be converted to ketones by breaking down fat stored in adipose tissue. It may ...
Chapter 9 – Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... One catabolic process is called fermentation which is a partial oxidation of organic molecules, and it occurs without oxygen. Aerobic respiration is the complete oxidation of organic compounds, like sugar, with the participation of oxygen in the process. Food provides the “fuel” for the cells, and m ...
... One catabolic process is called fermentation which is a partial oxidation of organic molecules, and it occurs without oxygen. Aerobic respiration is the complete oxidation of organic compounds, like sugar, with the participation of oxygen in the process. Food provides the “fuel” for the cells, and m ...
Cell Respiration Take Home Test 1. When cells break down food
... a. is released all at once. b. is released entirely as body heat into the environment. c. is temporarily stored in ATP molecules while some is released as body heat. d. causes excitation of electrons in chlorophyll molecules. 2. The process of aerobic cellular respiration a. is performed only by org ...
... a. is released all at once. b. is released entirely as body heat into the environment. c. is temporarily stored in ATP molecules while some is released as body heat. d. causes excitation of electrons in chlorophyll molecules. 2. The process of aerobic cellular respiration a. is performed only by org ...
Communication, Homeostasis
... An organic substance that can be used for respiration Carbohydrates is the primary respiratory substrate Protein would be regarded as the respiratory substrate that is only used if no others are available = Last resort!!! This is because protein is extremely valuable as most of human body is ...
... An organic substance that can be used for respiration Carbohydrates is the primary respiratory substrate Protein would be regarded as the respiratory substrate that is only used if no others are available = Last resort!!! This is because protein is extremely valuable as most of human body is ...
Blood glucose homeostasis
... promoted by glucokinase which has a lower affinity than hexokinase. • The activity of glucokinase increases with high blood glucose levels and the liver removes glucose from the portal blood after a meal. • After uptake and phosphorylation, excess glucose is stored in the liver as glycogen. ...
... promoted by glucokinase which has a lower affinity than hexokinase. • The activity of glucokinase increases with high blood glucose levels and the liver removes glucose from the portal blood after a meal. • After uptake and phosphorylation, excess glucose is stored in the liver as glycogen. ...
cell respiration notes ap - Wesleyan
... INNER MEMBRANE (CRISTAE) –contains Electron transport proteins MATRIX- contains enzymes for KREBS CYCLE INTERMEMBRANE SPACE- between cristae and outer membrane Place where H+ ions accumulate during ETC GLYCOLYSIS “Glykos”= sweet; “lysis”=split apart GLUCOSE → 2 PYRUVATE Occurs in cytosol Requires 2 ...
... INNER MEMBRANE (CRISTAE) –contains Electron transport proteins MATRIX- contains enzymes for KREBS CYCLE INTERMEMBRANE SPACE- between cristae and outer membrane Place where H+ ions accumulate during ETC GLYCOLYSIS “Glykos”= sweet; “lysis”=split apart GLUCOSE → 2 PYRUVATE Occurs in cytosol Requires 2 ...
Chapter 26 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... • Carbohydrates are rapidly oxidized, RDA greater than any other nutrient (175 g/day) • Dietary sources: – monosaccharides = glucose, galactose and fructose • liver converts galactose and fructose to glucose – outside hepatic portal system, only blood sugar is glucose – normal blood sugar concentrat ...
... • Carbohydrates are rapidly oxidized, RDA greater than any other nutrient (175 g/day) • Dietary sources: – monosaccharides = glucose, galactose and fructose • liver converts galactose and fructose to glucose – outside hepatic portal system, only blood sugar is glucose – normal blood sugar concentrat ...
Bioenergetics
... Metabolic pathways are chains of reactions facilitated by enzymes in which the product of one reaction becomes the substrate for the next o Rate limiting enzymes are generally present at the start of a metabolic pathway and control the rate at which reactions occur In the case of ATP production, l ...
... Metabolic pathways are chains of reactions facilitated by enzymes in which the product of one reaction becomes the substrate for the next o Rate limiting enzymes are generally present at the start of a metabolic pathway and control the rate at which reactions occur In the case of ATP production, l ...
BIOLOGY EOC QUESTIONS BIOCHEMISTRY
... 7. Which best describes how enzymes function in the body? A. Enzymes are converted in products by the reaction they catalyze. B. Enzymes lower the activation energy of reactions. C. One enzyme can catalyze many different reactions. D. An enzyme is used once and then destroyed by the cell ...
... 7. Which best describes how enzymes function in the body? A. Enzymes are converted in products by the reaction they catalyze. B. Enzymes lower the activation energy of reactions. C. One enzyme can catalyze many different reactions. D. An enzyme is used once and then destroyed by the cell ...
Post-translational Modifications and Their
... of this modification is very fast. Therefore specific detection of phosphorylated peptides using phosphatase inhibitors are indispensable to identify phosphorylation. Acetylation and deacetylation in N-terminal and K-residue are suggested as rival to phosphorylation (Kouzarides, 2000). Recent identi ...
... of this modification is very fast. Therefore specific detection of phosphorylated peptides using phosphatase inhibitors are indispensable to identify phosphorylation. Acetylation and deacetylation in N-terminal and K-residue are suggested as rival to phosphorylation (Kouzarides, 2000). Recent identi ...
food proteins
... Availability of plant based proteins is currently limited; even though plant based proteins cause less environmental load than animal proteins. VTT has developed technology to recover plant proteins into multifunctional ingredients by using novel dry fractionation technology. For example oat is an e ...
... Availability of plant based proteins is currently limited; even though plant based proteins cause less environmental load than animal proteins. VTT has developed technology to recover plant proteins into multifunctional ingredients by using novel dry fractionation technology. For example oat is an e ...
Cellular Respiration
... No electron acceptor at the end of ETC NADH accumulates, NAD+ depleted Krebs & glycolysis stop w/o NAD+ No ATP production (will cause cell death) ...
... No electron acceptor at the end of ETC NADH accumulates, NAD+ depleted Krebs & glycolysis stop w/o NAD+ No ATP production (will cause cell death) ...
Phosphorylation

Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation and its counterpart, dephosphorylation, turn many protein enzymes on and off, thereby altering their function and activity. Protein phosphorylation is one type of post-translational modification.Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes. Its prominent role in biochemistry is the subject of a very large body of research (as of March 2015, the Medline database returns over 240,000 articles on the subject, largely on protein phosphorylation).