Ch. 5 Review In Class Assignment
... changes into a different and usually more complex or better form ...
... changes into a different and usually more complex or better form ...
Evolution in Populations
... Gradualism: the idea that species originate through a slow, gradual change of adaptations over long periods of time Punctuated Equilibrium: the idea that species can remain stable for long periods until environmental changes cause many new species to appear. o Environmental changes lead to rapid ...
... Gradualism: the idea that species originate through a slow, gradual change of adaptations over long periods of time Punctuated Equilibrium: the idea that species can remain stable for long periods until environmental changes cause many new species to appear. o Environmental changes lead to rapid ...
UNIT 6 GUIDE
... Neanderthal — A species of hominine very closely related to our own species, Homo sapiens, that went extinct roughly 35,000 to 30,000 years ago. Genetic research shows that the DNA of people with Eurasian ancestry is partly (a few percent) Neanderthal. Though Neanderthals have sometimes been portray ...
... Neanderthal — A species of hominine very closely related to our own species, Homo sapiens, that went extinct roughly 35,000 to 30,000 years ago. Genetic research shows that the DNA of people with Eurasian ancestry is partly (a few percent) Neanderthal. Though Neanderthals have sometimes been portray ...
Mayr E. Animal species and evolution. Cambridge, MA: Harvard
... Systematics and the Origin of Species had been sold out (around 1949), I had to decide whether or not to bring out a revised edition.1 Realizing how active the field of evolutionary biology had become, I decided to prepare an entirely new work in which I would try to synthesize the entire literature ...
... Systematics and the Origin of Species had been sold out (around 1949), I had to decide whether or not to bring out a revised edition.1 Realizing how active the field of evolutionary biology had become, I decided to prepare an entirely new work in which I would try to synthesize the entire literature ...
The Nature of Science
... • Science is non-dogmatic. In science things are not accepted on faith but on evidence. ...
... • Science is non-dogmatic. In science things are not accepted on faith but on evidence. ...
Becoming Human Viewers Guide
... Read the three quotes and answer the following questions using the quotes, images and the notes you have taken as evidence. 1. “She was the ape that stood up.” 2. “Hominds such as Lucy serve as a touchstone for discussing human origins.” 3. “In some ways, homo erectus was the evolutionary parent of ...
... Read the three quotes and answer the following questions using the quotes, images and the notes you have taken as evidence. 1. “She was the ape that stood up.” 2. “Hominds such as Lucy serve as a touchstone for discussing human origins.” 3. “In some ways, homo erectus was the evolutionary parent of ...
Human Evolution
... - People who eat a hunter-gatherer-type diet have larger jaws. - People raised on the softer foods of an agricultural diet have smaller jaws. ...
... - People who eat a hunter-gatherer-type diet have larger jaws. - People raised on the softer foods of an agricultural diet have smaller jaws. ...
10. Give examples of ways in which genetic variation
... 11. Recognize that evidence drawn from geology, fossils, and comparative anatomy provides the basis of the theory of evolution. 12. Relate the extinction of species to a mismatch of adaptation and the environment. ...
... 11. Recognize that evidence drawn from geology, fossils, and comparative anatomy provides the basis of the theory of evolution. 12. Relate the extinction of species to a mismatch of adaptation and the environment. ...
Evolution
... •Many newly developed organisms remained in their old habitats and crowded older forms out of existence. •Other new organisms made their way into new surroundings, prospered, and kept adapting. Therefore, there was a steady succession of new species best suited to an environment at a particular time ...
... •Many newly developed organisms remained in their old habitats and crowded older forms out of existence. •Other new organisms made their way into new surroundings, prospered, and kept adapting. Therefore, there was a steady succession of new species best suited to an environment at a particular time ...
File - Zachary Church of Christ
... knowledge that the cruise control was set at 65 and the time of arrival was 6:00 pm, the place of departure, Zachary, there are some absolutes that can be used to calculate the time of departure ...
... knowledge that the cruise control was set at 65 and the time of arrival was 6:00 pm, the place of departure, Zachary, there are some absolutes that can be used to calculate the time of departure ...
Humanity`s Place
... the first known homo appeared. these homos were the first to have features like opposable thumbs and big brains the first homo had a 50% larger brain than the hominids, relative to their body size At this point all traces of tree climbing were gone. This homo is known as Homo ergaster and is the ...
... the first known homo appeared. these homos were the first to have features like opposable thumbs and big brains the first homo had a 50% larger brain than the hominids, relative to their body size At this point all traces of tree climbing were gone. This homo is known as Homo ergaster and is the ...
10.1 Reinforcement
... explain how such changes occur. • The theory of catastrophism states that natural disasters such as floods and volcanic eruptions have happened often during Earth’s long history. These events shaped landforms and caused species to become extinct in the process. ...
... explain how such changes occur. • The theory of catastrophism states that natural disasters such as floods and volcanic eruptions have happened often during Earth’s long history. These events shaped landforms and caused species to become extinct in the process. ...
01 - HomeworkNOW.com
... _____ 4. Darwin learned that there were resemblances between the plants and animals of South America and a. Ecuador. c. Australia. b. the Galápagos Islands. d. the English countryside. Read the question, and write your answer in the space provided. 5. What is artificial selection? __________________ ...
... _____ 4. Darwin learned that there were resemblances between the plants and animals of South America and a. Ecuador. c. Australia. b. the Galápagos Islands. d. the English countryside. Read the question, and write your answer in the space provided. 5. What is artificial selection? __________________ ...
Chapter 19 Power Point Slides
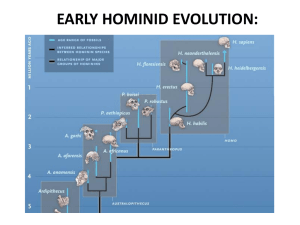
... Estimates of the dates of origin and extinction of the three main groups of hominins (green, blue, and orange). The australopithecines split into two groups about 2.5 to 2.7 million years ago. ...
... Estimates of the dates of origin and extinction of the three main groups of hominins (green, blue, and orange). The australopithecines split into two groups about 2.5 to 2.7 million years ago. ...
EARLY HOMININ EVOLUTION:
... contrast to our ancestors, that evolved as omnivores with a taste for meat massive grinding teeth and jaws ...
... contrast to our ancestors, that evolved as omnivores with a taste for meat massive grinding teeth and jaws ...
1859: Charles Darwin: The Theory of Evolution:
... (When several changes build up over a long period of time.) ...
... (When several changes build up over a long period of time.) ...
early brains
... - solve problems and create abstract ideas and images. It can also do much more. ...
... - solve problems and create abstract ideas and images. It can also do much more. ...
Evol Guided Reading
... are two types of evolution based on how long changes take to occur. 13.2 Evidence of Evolution 10. What are three sources of scientific evidence supporting evolution? _____________________________ ______________________ and _______________________________ Give ONE example: 13.3 Examples of Evolution ...
... are two types of evolution based on how long changes take to occur. 13.2 Evidence of Evolution 10. What are three sources of scientific evidence supporting evolution? _____________________________ ______________________ and _______________________________ Give ONE example: 13.3 Examples of Evolution ...
(18)Before you arrive for the Evolution lab, please
... 2. Answer these preparatory questions: What safety procedures should you be sure to follow during this lab period? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________ ...
... 2. Answer these preparatory questions: What safety procedures should you be sure to follow during this lab period? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________ ...
Chapter 6 and 9 - Wando High School
... An example of this is _________________________. 19. Structures that have no function in the organism but may have had a use in an ancestor are called _______________. Give examples of these structures. 20. Describe these 6 patterns of biological evolution: gradualism, punctuated equilibrium, diverg ...
... An example of this is _________________________. 19. Structures that have no function in the organism but may have had a use in an ancestor are called _______________. Give examples of these structures. 20. Describe these 6 patterns of biological evolution: gradualism, punctuated equilibrium, diverg ...
Review Book Topic D: Evolution - wfs
... 9. Hominid fossils consist only of bones and teeth and were preserved where dry sediments have quickly covered them and have remained undisturbed. 10. Due to the incomplete record, it is not entirely clear how the different species of hominid are related. 11. Many details of human evolutionary origi ...
... 9. Hominid fossils consist only of bones and teeth and were preserved where dry sediments have quickly covered them and have remained undisturbed. 10. Due to the incomplete record, it is not entirely clear how the different species of hominid are related. 11. Many details of human evolutionary origi ...
Discovery of human antiquity
The discovery of human antiquity was a major achievement of science in the middle of the 19th century, and the foundation of scientific paleoanthropology. The antiquity of man, human antiquity, or in simpler language the age of the human race, are names given to the series of scientific debates it involved, which with modifications continue in the 21st century. These debates have clarified and given scientific evidence, from a number of disciplines, towards solving the basic question of dating the first human being.Controversy was very active in this area in parts of the 19th century, with some dormant periods also. A key date was the 1859 re-evaluation of archaeological evidence that had been published 12 years earlier by Boucher de Perthes. It was then widely accepted, as validating the suggestion that man was much older than previously been believed, for example than the 6,000 years implied by some traditional chronologies.In 1863 T. H. Huxley argued that man was an evolved species; and in 1864 Alfred Russel Wallace combined natural selection with the issue of antiquity. The arguments from science for what was then called the ""great antiquity of man"" became convincing to most scientists, over the following decade. The separate debate on the antiquity of man had in effect merged into the larger one on evolution, being simply a chronological aspect. It has not ended as a discussion, however, since the current science of human antiquity is still in flux.