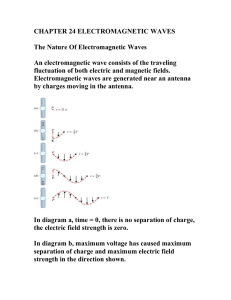
Electromagnetic Waves
... • Glass is transparent: its natural freqs are higher, in the ultraviolet range. So glass is not transparent to ultraviolet. But is transparent to lower freqs i.e. visible spectrum. • What happens in this off-resonance case? Atoms are forced into vibration but at less amplitude, so don’t hold on to t ...
... • Glass is transparent: its natural freqs are higher, in the ultraviolet range. So glass is not transparent to ultraviolet. But is transparent to lower freqs i.e. visible spectrum. • What happens in this off-resonance case? Atoms are forced into vibration but at less amplitude, so don’t hold on to t ...
Introduction to the physics of light
... then a changing electric field should make a magnetic field. • A consequence of this is that changing electric and magnetic fields should trigger each other and these changing fields should move at a speed equal to the speed of light. • Maxwell also said that light is an electromagnetic wave. ...
... then a changing electric field should make a magnetic field. • A consequence of this is that changing electric and magnetic fields should trigger each other and these changing fields should move at a speed equal to the speed of light. • Maxwell also said that light is an electromagnetic wave. ...
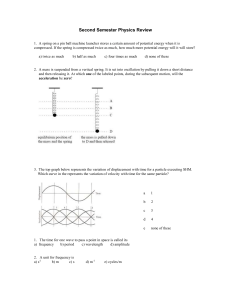
Second Semester Final Practice
... 64. The principle reason voltage is induced in the loops of a generator coil is that the.. a) loops are rotating, changing the amount of magnetic field within the loops. b) size of the loops is changing c) the magnet’s strength is changing d) magnet is rotating e) all the above 65. Yellow light is s ...
... 64. The principle reason voltage is induced in the loops of a generator coil is that the.. a) loops are rotating, changing the amount of magnetic field within the loops. b) size of the loops is changing c) the magnet’s strength is changing d) magnet is rotating e) all the above 65. Yellow light is s ...
class1_BK - Center for Detectors
... • Earth’s atmosphere – transparent to some uv, all visible, some infrared. But is (thankfully) opaque to high uv. - the small amount of uv that does get through causes dangerous sunburn. - clouds are semi-transparent to uv, so can still get sunburnt on a cloudy day. ...
... • Earth’s atmosphere – transparent to some uv, all visible, some infrared. But is (thankfully) opaque to high uv. - the small amount of uv that does get through causes dangerous sunburn. - clouds are semi-transparent to uv, so can still get sunburnt on a cloudy day. ...
Joseph John Thomson - SCIENCE
... In their first experiment, he investigated whether the negative charges could be separated from the cathode rays by means of magnetism. Thompson concluded that the negative charge is inseparable from the rays. ...
... In their first experiment, he investigated whether the negative charges could be separated from the cathode rays by means of magnetism. Thompson concluded that the negative charge is inseparable from the rays. ...
3. Maxwell`s Equations, Light Waves, Power, and Photons
... Light is not only a wave, but also a particle. Photographs taken in dimmer light look grainier. Very very dim ...
... Light is not only a wave, but also a particle. Photographs taken in dimmer light look grainier. Very very dim ...
Part V
... Light is not only a wave, but also a particle. Photographs taken in dimmer light look grainier. Very very dim ...
... Light is not only a wave, but also a particle. Photographs taken in dimmer light look grainier. Very very dim ...
Technological Sciences for the Operating Room Physics for the
... does not include study of the forces that caused motion ...
... does not include study of the forces that caused motion ...
Practice - UF Physics
... 15. A light ray traveling in the horizontal direction is incident onto a prism as shown in the figure. At what angle relative to horizontal does the light ray emerge from the second face of the shown prism if the prism has an index of refraction of 1.5 and is surrounded by air? The cross section of ...
... 15. A light ray traveling in the horizontal direction is incident onto a prism as shown in the figure. At what angle relative to horizontal does the light ray emerge from the second face of the shown prism if the prism has an index of refraction of 1.5 and is surrounded by air? The cross section of ...
Electromagnetic Waves - Galileo and Einstein
... Light goes out between teeth of rotating wheel, reflects off distant mirror, by the time it gets back, a tooth may be blocking its path, depending on wheel speed: at certain speeds, the observer sees nothing. Knowing the wheel rotation rate, the speed of light can be figured out. (1849) (720 teeth!) ...
... Light goes out between teeth of rotating wheel, reflects off distant mirror, by the time it gets back, a tooth may be blocking its path, depending on wheel speed: at certain speeds, the observer sees nothing. Knowing the wheel rotation rate, the speed of light can be figured out. (1849) (720 teeth!) ...
NA 2nd Semester Review Regular Physics No Ans
... 9. If you know the wavelength of any form of electromagnetic radiation, you can determine its frequency because a. all wavelengths travel at the same speed. b. the speed of light varies for each form. c. wavelength and frequency are equal. d. the speed of light increases as wavelength increases. ...
... 9. If you know the wavelength of any form of electromagnetic radiation, you can determine its frequency because a. all wavelengths travel at the same speed. b. the speed of light varies for each form. c. wavelength and frequency are equal. d. the speed of light increases as wavelength increases. ...
PPT - LSU Physics & Astronomy
... Radiation Pressure Waves not only carry energy but also momentum. The effect is very small (we don’t ordinarily feel pressure from light). If light is completely absorbed during an interval Δt, the momentum Transferred Δp is given by Du and twice as much if reflected. Dp = Newton’s law: ...
... Radiation Pressure Waves not only carry energy but also momentum. The effect is very small (we don’t ordinarily feel pressure from light). If light is completely absorbed during an interval Δt, the momentum Transferred Δp is given by Du and twice as much if reflected. Dp = Newton’s law: ...
Chapter 22 - The Nature of Light
... When the electrons move back and forth, they give off a _________ of photons, making an ____ ___________ which carries the energy. Light has a __________ personality: it can be considered to have properties of both ____________ and _____________. The speed of light in a vacuum is ______________ or _ ...
... When the electrons move back and forth, they give off a _________ of photons, making an ____ ___________ which carries the energy. Light has a __________ personality: it can be considered to have properties of both ____________ and _____________. The speed of light in a vacuum is ______________ or _ ...
Single-Slit and Diffraction Grating
... According to Huygen’s principle, each portion of the slit acts as a source of waves The light from one portion of the slit can interfere with light from another portion The resultant intensity on the screen depends on the direction θ ...
... According to Huygen’s principle, each portion of the slit acts as a source of waves The light from one portion of the slit can interfere with light from another portion The resultant intensity on the screen depends on the direction θ ...
Chapter 24 Notes - Valdosta State University
... Visible light frequencies occupy a very small part of the complete electromagnetic spectrum. These are the frequencies we actually see. Our eyes and brain interpret different frequencies as different colors. We use ROYGBIV to help us remember the order of the colors with red being the lowest frequen ...
... Visible light frequencies occupy a very small part of the complete electromagnetic spectrum. These are the frequencies we actually see. Our eyes and brain interpret different frequencies as different colors. We use ROYGBIV to help us remember the order of the colors with red being the lowest frequen ...
PPT
... I1cos2(60o)= 1/4 I1 = 1/8 I0. • Now the light is again polarized, but at 60o. The last polarizer is horizontal, so I3 = I2cos2(30o) = 3/4 I2 =3 /32 I0 = 0.094 I0. • The exiting light is horizontally polarized, and has 9% of the original ...
... I1cos2(60o)= 1/4 I1 = 1/8 I0. • Now the light is again polarized, but at 60o. The last polarizer is horizontal, so I3 = I2cos2(30o) = 3/4 I2 =3 /32 I0 = 0.094 I0. • The exiting light is horizontally polarized, and has 9% of the original ...
Notes
... When certain metals are illuminated by light, they eject "photoelectrons." In the wave model of light, where energy was proportional to intensity squared, a brighter light should eject electrons that travel faster (from the extra energy). Instead, a brighter light just ejected more electrons with no ...
... When certain metals are illuminated by light, they eject "photoelectrons." In the wave model of light, where energy was proportional to intensity squared, a brighter light should eject electrons that travel faster (from the extra energy). Instead, a brighter light just ejected more electrons with no ...
Purdue University PHYS 221 EXAM II 11/6/03
... Which one of the following statements concerning the wavelength of an electromagnetic wave in a vacuum is true? ...
... Which one of the following statements concerning the wavelength of an electromagnetic wave in a vacuum is true? ...