Data Quality Control in Multi-State, Multi-year, Multi-type Databases: A Method for Examining Year-to-Year Percentage Changes
... The “outlier” could be defined as being any number of standard deviations away from the mean within any particular roadway type. In this example use, we decided that we only wanted to look at the most extreme outliers (four and five standard deviations away). In other cases, the user could set at an ...
... The “outlier” could be defined as being any number of standard deviations away from the mean within any particular roadway type. In this example use, we decided that we only wanted to look at the most extreme outliers (four and five standard deviations away). In other cases, the user could set at an ...
Package `mapStats`
... mapStats will calculate statistics (mean, total, quantiles, variance, and standard deviation) for survey variables, by geography level (e.g. state, county), and optional class variables (such as year, if multiple years are included). The statistics for each variable are then plotted on a shapefile w ...
... mapStats will calculate statistics (mean, total, quantiles, variance, and standard deviation) for survey variables, by geography level (e.g. state, county), and optional class variables (such as year, if multiple years are included). The statistics for each variable are then plotted on a shapefile w ...
Chapter 3: Supply and Demand
... The Durbin-Watson statistic is used to identify the presence of autocorrelation. To correct autocorrelation consider: • Transforming the data into a different order of magnitude. ...
... The Durbin-Watson statistic is used to identify the presence of autocorrelation. To correct autocorrelation consider: • Transforming the data into a different order of magnitude. ...
Chapter 2-99. Homework Problem Solutions
... The scores simply represent labels or classifications, which have no natural rank ordering. Thus, the level of measure is “nominal” or an “unordered categorical scale.” All that can be done for unordered categories is to report the count, or frequency, for each category, along with the percent of th ...
... The scores simply represent labels or classifications, which have no natural rank ordering. Thus, the level of measure is “nominal” or an “unordered categorical scale.” All that can be done for unordered categories is to report the count, or frequency, for each category, along with the percent of th ...
Describing Your Data Using PROC MEANS PROC MEANS can be
... which data set to process. You can request that PROC FREQ print only one table per page by using the PAGE option (otherwise multiple tables per page will be printed, as space permits). The simplest form is PROC FREQ; and will produce frequency tables for all the variables in the most recently create ...
... which data set to process. You can request that PROC FREQ print only one table per page by using the PAGE option (otherwise multiple tables per page will be printed, as space permits). The simplest form is PROC FREQ; and will produce frequency tables for all the variables in the most recently create ...
Practice Exam Questions
... The answer is b) because both pie charts and bar graphs can be used for categorical data. A2. A study of 5000 university graduates recorded the sex of the graduates, the total university debt and the average annual salary of the university graduates. Which of the following is true? a) sex, universit ...
... The answer is b) because both pie charts and bar graphs can be used for categorical data. A2. A study of 5000 university graduates recorded the sex of the graduates, the total university debt and the average annual salary of the university graduates. Which of the following is true? a) sex, universit ...
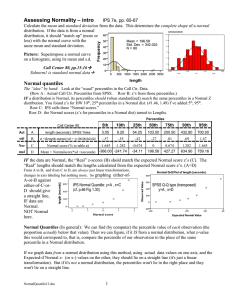
Normal quantile plots
... Normal Quantiles (In general): We can find (by computer) the percentile value of each observation (the proportion actually below that value). Then we can figure, if it IS from a normal distribution, what z-value this would correspond to, that is, compare the percentile of our observation to the plac ...
... Normal Quantiles (In general): We can find (by computer) the percentile value of each observation (the proportion actually below that value). Then we can figure, if it IS from a normal distribution, what z-value this would correspond to, that is, compare the percentile of our observation to the plac ...
An Introduction to Statistics used in Real Property Assessment
... The coefficients calculated would be used to estimate the carport's market value; e.g., a high quality carport is shown to add $1,915 to value. The first check in a regression calculation is to see if the coefficients have the expected signs (i.e., whether they are positive, adding to value, or nega ...
... The coefficients calculated would be used to estimate the carport's market value; e.g., a high quality carport is shown to add $1,915 to value. The first check in a regression calculation is to see if the coefficients have the expected signs (i.e., whether they are positive, adding to value, or nega ...
Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences
... is a statistical analysis used with one interval dependent variable and at least two nominal independent variables. a) factorial analysis of variance; two-way ANOVA b) one-way ANOVA; factorial ANOVA c) two-way ANOVA; factorial ANOVA d) between-groups ANOVA; within-groups ANOVA ...
... is a statistical analysis used with one interval dependent variable and at least two nominal independent variables. a) factorial analysis of variance; two-way ANOVA b) one-way ANOVA; factorial ANOVA c) two-way ANOVA; factorial ANOVA d) between-groups ANOVA; within-groups ANOVA ...
04/16/2009
... • Methods of repeated measures ANOVA Univariate - Uses a single outcome measure. Multivariate - Uses multiple outcome measures. Mixed Model Analysis - One or more factors (other than subject) are random effects. ...
... • Methods of repeated measures ANOVA Univariate - Uses a single outcome measure. Multivariate - Uses multiple outcome measures. Mixed Model Analysis - One or more factors (other than subject) are random effects. ...
Chapter 6: Graphics
... chart.” Dot plots can be one of the most useful ways of displaying and perusing data for neuroscience because sample sizes are usually small to moderate. The type of dot plot most useful in neuroscience has the groups on the horizontal axis and the values for the variable on the vertical axis. Each ...
... chart.” Dot plots can be one of the most useful ways of displaying and perusing data for neuroscience because sample sizes are usually small to moderate. The type of dot plot most useful in neuroscience has the groups on the horizontal axis and the values for the variable on the vertical axis. Each ...
Means & Medians
... Fancytown and Lowtown we can see that the mean, $295,000 appears to accurately represent the “center” of the data for Fancytown, but it is not representative of the Lowtown data. • Clearly, the mean can be greatly affected by the presence of even a single outlier. ...
... Fancytown and Lowtown we can see that the mean, $295,000 appears to accurately represent the “center” of the data for Fancytown, but it is not representative of the Lowtown data. • Clearly, the mean can be greatly affected by the presence of even a single outlier. ...
Introduction to statistical analysis of invertebrate monitoring data
... values and provide an indication of the variability within the data. The most common way to summarise data is in a table or in a graph using a program such as Excel or R. In Excel you can get an overall summary of your data by going to: ‘Tools > Data Analysis > Descriptive Statistics’. This also pro ...
... values and provide an indication of the variability within the data. The most common way to summarise data is in a table or in a graph using a program such as Excel or R. In Excel you can get an overall summary of your data by going to: ‘Tools > Data Analysis > Descriptive Statistics’. This also pro ...
Extended-answer questions (90 MARKS)
... c Use the information in the frequency table to construct a percentage frequency histogram to display the distribution of chest sizes of the militiamen. Comment on features of the distribution such a shape, centre and spread. d In what ways do you think that the distribution of chest sizes of soldie ...
... c Use the information in the frequency table to construct a percentage frequency histogram to display the distribution of chest sizes of the militiamen. Comment on features of the distribution such a shape, centre and spread. d In what ways do you think that the distribution of chest sizes of soldie ...
Comparing data sets
... The back-to-back stem plot allows us to make some visual comparisons of the two distributions. In Worked example 1, the centre of the distribution for the girls is higher than the centre of the distribution for the boys. The spread of each of the distributions seems to be about the same. For the boy ...
... The back-to-back stem plot allows us to make some visual comparisons of the two distributions. In Worked example 1, the centre of the distribution for the girls is higher than the centre of the distribution for the boys. The spread of each of the distributions seems to be about the same. For the boy ...
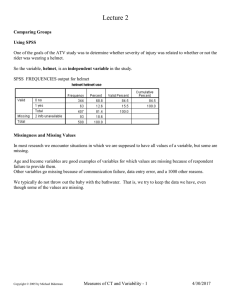
Comparing Groups
... The second important characteristic of collections of numbers is the variability of the values. It is also called the dispersion, heterogeneity or width of the values. This characteristic reflects the differences between the values. If all the values are close to each other we say that variability i ...
... The second important characteristic of collections of numbers is the variability of the values. It is also called the dispersion, heterogeneity or width of the values. This characteristic reflects the differences between the values. If all the values are close to each other we say that variability i ...
Running Head: Normality and Outliers in ANOVA and MANOVA
... If a dataset follows a normal distribution, then about 68% of the observations will fall within one standard deviation of the mean, 95% within 2 standard deviations and 99.7% will fall within 3 standard deviations of the mean. Although no method gives a definitive conclusion, two ways to evaluate no ...
... If a dataset follows a normal distribution, then about 68% of the observations will fall within one standard deviation of the mean, 95% within 2 standard deviations and 99.7% will fall within 3 standard deviations of the mean. Although no method gives a definitive conclusion, two ways to evaluate no ...
Characteristics of terrain, snow supply and forest cover
... In British Columbia, Canada, the primary method of harvesting timber is clear-cut logging which consists of removing all the timber in large tracts of land (typically areas of 1 0 100 ha). This practice has been banned from mountain slopes in the Alpine countries of Europe for > 100 years and is not ...
... In British Columbia, Canada, the primary method of harvesting timber is clear-cut logging which consists of removing all the timber in large tracts of land (typically areas of 1 0 100 ha). This practice has been banned from mountain slopes in the Alpine countries of Europe for > 100 years and is not ...
sm2
... 2.4 The total number of students who reported SAT scores is 355, so we have p̂ = 205/355 = 0.5775. We see that 57.75% have higher math SAT scores. 2.5 Since this describes a proportion for all residents of the US, the proportion is for a population and the correct notation is p. We see that the prop ...
... 2.4 The total number of students who reported SAT scores is 355, so we have p̂ = 205/355 = 0.5775. We see that 57.75% have higher math SAT scores. 2.5 Since this describes a proportion for all residents of the US, the proportion is for a population and the correct notation is p. We see that the prop ...
Measures of Location and Variability Spring, 2009
... The largest value for baseline cholesterol in the dataset weight.dta is 412. Try changing that to 1500 and comparing the mean of the original sample with the mean of the changed sample. Notice that there are 10,273 participants with baseline cholesterol values but there are 10,355 participants in th ...
... The largest value for baseline cholesterol in the dataset weight.dta is 412. Try changing that to 1500 and comparing the mean of the original sample with the mean of the changed sample. Notice that there are 10,273 participants with baseline cholesterol values but there are 10,355 participants in th ...
Powerpoint for Class Lecture
... pool of eligible employees. At time 1 we will measure both groups on their skill level. Group A will take the training, and Group B will not. At time 2 we will again measure the skill levels of both groups. In that way we can tell if the differences in the measures – both for comparing the two group ...
... pool of eligible employees. At time 1 we will measure both groups on their skill level. Group A will take the training, and Group B will not. At time 2 we will again measure the skill levels of both groups. In that way we can tell if the differences in the measures – both for comparing the two group ...
Z scores
... This is the inverse of the formula shown above in (2). It simply says “Start at the mean and go Z times the standard deviation above / below the mean” (above if Z is positive; below if Z is negative). In a spreadsheet, if the Z-score is in cell B1, the mean in B2, and the standard deviation in B3, t ...
... This is the inverse of the formula shown above in (2). It simply says “Start at the mean and go Z times the standard deviation above / below the mean” (above if Z is positive; below if Z is negative). In a spreadsheet, if the Z-score is in cell B1, the mean in B2, and the standard deviation in B3, t ...
Module 1: Fundamentals of Data Analysis
... and consistent. The process of measurement is often complex – don’t take it for granted. Levels of Measurement. There are various ways to characterize measurement of variables. An easy dichotomy in measurement is qualitative versus quantitative data. Qualitative data do not follow a natural numerica ...
... and consistent. The process of measurement is often complex – don’t take it for granted. Levels of Measurement. There are various ways to characterize measurement of variables. An easy dichotomy in measurement is qualitative versus quantitative data. Qualitative data do not follow a natural numerica ...
Measuring Dispersion
... Calculating the variance (2/2) 4. Sum up these squared deviations (SUM OF THE SQUARED DEVIATIONS) 5. Divide this SUM OF THE SQUARED DEVIATIONS by the total number of observations minus 1 (n-1) to give the VARIANCE • Why divide by n - 1 ? Adjustment for the fact that the mean is just an estimate o ...
... Calculating the variance (2/2) 4. Sum up these squared deviations (SUM OF THE SQUARED DEVIATIONS) 5. Divide this SUM OF THE SQUARED DEVIATIONS by the total number of observations minus 1 (n-1) to give the VARIANCE • Why divide by n - 1 ? Adjustment for the fact that the mean is just an estimate o ...
Find Measures of Central Tendency
... You have already found the mean or average of a data set. (Lesson 2–5) ...
... You have already found the mean or average of a data set. (Lesson 2–5) ...