statistics and biometrics
... Some phenomena are easily quantified and can be easily measured. Other natural phenomena are not that easy to measure. In all these cases, we resort to the use of statistics so that we can know how to handle each case we come across. In this module we shall learn how to analyze facts and figures, an ...
... Some phenomena are easily quantified and can be easily measured. Other natural phenomena are not that easy to measure. In all these cases, we resort to the use of statistics so that we can know how to handle each case we come across. In this module we shall learn how to analyze facts and figures, an ...
Sociology 3211 - Central Web Server 2
... 2. Ordinal: also discrete, but the categories have a meaningful order. For example, there is a question about general health: 1=excellent, 2=very good, 3=good, 4=fair, 5=poor. Clearly there is a natural order to these categories. It makes sense to say that ‘2’ is in between ‘1’ and ‘3’. The variabl ...
... 2. Ordinal: also discrete, but the categories have a meaningful order. For example, there is a question about general health: 1=excellent, 2=very good, 3=good, 4=fair, 5=poor. Clearly there is a natural order to these categories. It makes sense to say that ‘2’ is in between ‘1’ and ‘3’. The variabl ...
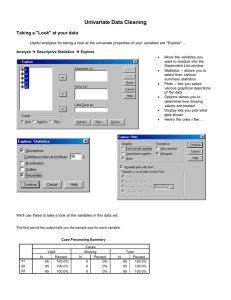
Univariate Data Cleaning
... Let's start with X1 -- Statistics and graphs are shown above. Not much to do with this one. Very low skewness value, Normal distribution tests are null, the histogram and the Q-Q plot look good. Before decide we can safely use the mean and std of this distribution we should check for outliers. To do ...
... Let's start with X1 -- Statistics and graphs are shown above. Not much to do with this one. Very low skewness value, Normal distribution tests are null, the histogram and the Q-Q plot look good. Before decide we can safely use the mean and std of this distribution we should check for outliers. To do ...
doc - Rossman/Chance
... Let μ represent the average guess of her age by all current at the university and suppose the sample constitutes a representative sample of all students at this school on this issue. Because there is just one variable and we are not comparing groups, a “one-sample t-interval” could be used. This pro ...
... Let μ represent the average guess of her age by all current at the university and suppose the sample constitutes a representative sample of all students at this school on this issue. Because there is just one variable and we are not comparing groups, a “one-sample t-interval” could be used. This pro ...
Minitab Orientation - Austin Community College
... interpretation of the output, see the Minitab Manual. One sample t test and confidence intervals In order to compute confidence intervals or hypothesis tests, click on Stat>Basic Statistics>1-Sample t…, (similar to Chapter 14 commands). It is different from the Chapter 14-15 commands because it uses ...
... interpretation of the output, see the Minitab Manual. One sample t test and confidence intervals In order to compute confidence intervals or hypothesis tests, click on Stat>Basic Statistics>1-Sample t…, (similar to Chapter 14 commands). It is different from the Chapter 14-15 commands because it uses ...
Preview Sample 1
... 9. Which of the following is the correct function for calculating the score occurring most often in a distribution? a. MEAN(A1:A15) b. MEDIAN(A1+A2+A3)/3 c. MODE (A1:A12) d. MEDIAN(A1:A10) Ans: c ...
... 9. Which of the following is the correct function for calculating the score occurring most often in a distribution? a. MEAN(A1:A15) b. MEDIAN(A1+A2+A3)/3 c. MODE (A1:A12) d. MEDIAN(A1:A10) Ans: c ...
Chapter 2: Statistics Part II
... The location of the center of a data set is important, but also important is how much variability or spread there is in the data. If a teacher gives an exam and tells you that the mean score was 75% that might make you happy. But then if the teacher says that the spread was only 2%, then that means ...
... The location of the center of a data set is important, but also important is how much variability or spread there is in the data. If a teacher gives an exam and tells you that the mean score was 75% that might make you happy. But then if the teacher says that the spread was only 2%, then that means ...
Chapter 2: Statistics: Part 2
... The location of the center of a data set is important, but also important is how much variability or spread there is in the data. If a teacher gives an exam and tells you that the mean score was 75% that might make you happy. But then if the teacher says that the spread was only 2%, then that means ...
... The location of the center of a data set is important, but also important is how much variability or spread there is in the data. If a teacher gives an exam and tells you that the mean score was 75% that might make you happy. But then if the teacher says that the spread was only 2%, then that means ...
Statistics, Data Analysis, and Decision Modelin Descriptive Statistics
... 2) All of the following are examples of measures of central tendency except ________. A) mean B) median C) standard deviation D) mode Answer: C 3) All of the following are examples of measures of dispersion except ________. A) range B) variance C) standard deviation D) mode Answer: D 4) In Microsoft ...
... 2) All of the following are examples of measures of central tendency except ________. A) mean B) median C) standard deviation D) mode Answer: C 3) All of the following are examples of measures of dispersion except ________. A) range B) variance C) standard deviation D) mode Answer: D 4) In Microsoft ...
Describing Numbers
... Median requires ordered data, either numerical or ordered categorical Problem with the mean: it is distorted by a change in one value on either side (change one 50 to 5,000,000 and note the mean changes) Median is a more “robust” estimate (jargon: high ’breakdown point’) ...
... Median requires ordered data, either numerical or ordered categorical Problem with the mean: it is distorted by a change in one value on either side (change one 50 to 5,000,000 and note the mean changes) Median is a more “robust” estimate (jargon: high ’breakdown point’) ...
Package `tigerstats`
... Crime: You are on a jury for a manslaughter case in Lewistown, PA. The defendant has been found guilty, and in Pennsylvania it is part of the job of the jury to recommend a sentence to the judge. The facts of the case are as follows. The defendant, Tyrone Marcus Watson, a 35-year old native of Lewis ...
... Crime: You are on a jury for a manslaughter case in Lewistown, PA. The defendant has been found guilty, and in Pennsylvania it is part of the job of the jury to recommend a sentence to the judge. The facts of the case are as follows. The defendant, Tyrone Marcus Watson, a 35-year old native of Lewis ...
A Little Book of Python for Multivariate Analysis
... on principal components analysis (PCA) and linear discriminant analysis (LDA). This booklet assumes that the reader has some basic knowledge of multivariate analyses, and the principal focus of the booklet is not to explain multivariate analyses, but rather to explain how to carry out these analyses ...
... on principal components analysis (PCA) and linear discriminant analysis (LDA). This booklet assumes that the reader has some basic knowledge of multivariate analyses, and the principal focus of the booklet is not to explain multivariate analyses, but rather to explain how to carry out these analyses ...
Statistics, Data Analysis, and Decision Modeling Descriptive
... 2) All of the following are examples of measures of central tendency except ________. A) mean B) median C) standard deviation D) mode Answer: C 3) All of the following are examples of measures of dispersion except ________. A) range B) variance C) standard deviation D) mode Answer: D 4) In Microsoft ...
... 2) All of the following are examples of measures of central tendency except ________. A) mean B) median C) standard deviation D) mode Answer: C 3) All of the following are examples of measures of dispersion except ________. A) range B) variance C) standard deviation D) mode Answer: D 4) In Microsoft ...
1-26
... Categorical data: Data that takes on distinct values (i.e., it falls into categories), such as sex (male/female), alive/dead, blood type (A/B/AB/O), stages of cancer Continuous data: Data that takes on a spectrum of fractional values, such as time, age, temperature, cholesterol levels ...
... Categorical data: Data that takes on distinct values (i.e., it falls into categories), such as sex (male/female), alive/dead, blood type (A/B/AB/O), stages of cancer Continuous data: Data that takes on a spectrum of fractional values, such as time, age, temperature, cholesterol levels ...
Statistics – Theory
... In this diverse world of ours, no two things are exactly the same. A statistician is interested in both the differences and the similarities; i.e., both departures and patterns. The actuarial tables published by insurance companies reflect their statistical analysis of the average life expectancy of ...
... In this diverse world of ours, no two things are exactly the same. A statistician is interested in both the differences and the similarities; i.e., both departures and patterns. The actuarial tables published by insurance companies reflect their statistical analysis of the average life expectancy of ...
Evaluation of Discrepant Data
... • This gives the result: 10936 75 days • However, the unweighted mean is influenced by outliers in the data, in particular the first, low value of 9715 days • Secondly, the unweighted mean takes no account of the fact that different authors made measurements of different precision, so we have lost ...
... • This gives the result: 10936 75 days • However, the unweighted mean is influenced by outliers in the data, in particular the first, low value of 9715 days • Secondly, the unweighted mean takes no account of the fact that different authors made measurements of different precision, so we have lost ...
One-Way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
... variability: the sum of squares. Table 8.4 shows that doing that here gives us a sum of squares of 280. The total amount of variability that needs to be explained is a sum of squares of 280.We can refer to this amount of variability as the Sum of Squares Total. Determining the amount of variability ...
... variability: the sum of squares. Table 8.4 shows that doing that here gives us a sum of squares of 280. The total amount of variability that needs to be explained is a sum of squares of 280.We can refer to this amount of variability as the Sum of Squares Total. Determining the amount of variability ...
Using response probabilities for assessing representativity
... The questionnaire is put on the web, and it is left to the visitors of the website to decide whether or not they will participate in the survey. No random sampling is involved. Survey respondents are those people that happen to know that the survey is being conducted, happen to have Internet access ...
... The questionnaire is put on the web, and it is left to the visitors of the website to decide whether or not they will participate in the survey. No random sampling is involved. Survey respondents are those people that happen to know that the survey is being conducted, happen to have Internet access ...
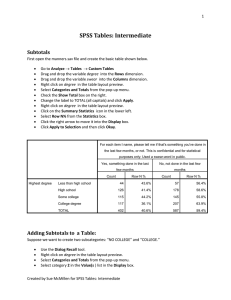
Adding Subtotals to a Table
... Select the COLLEGE category in the Display box. Click the Edit button. Check the Hide box and click Continue. Select the No COLLEGE category in the Display box. Click the Edit button. Check the Hide box and click Continue. Click Apply and then click Okay. For each item I name, please tell me if that ...
... Select the COLLEGE category in the Display box. Click the Edit button. Check the Hide box and click Continue. Select the No COLLEGE category in the Display box. Click the Edit button. Check the Hide box and click Continue. Click Apply and then click Okay. For each item I name, please tell me if that ...
QNT 275 Entire Course
... very large sizes, and substituting an online ordering service to dropship rare sizes directly from suppliers. How should the manager communicate those results to the store owner? ...
... very large sizes, and substituting an online ordering service to dropship rare sizes directly from suppliers. How should the manager communicate those results to the store owner? ...
Data reporting and visualization in ecology
... chapter 2), aimed at biologists. In this example we would like to know how the means would vary when computed for repeated (hypothetical) samples of size 15 from the same original distribution, in other words what other possible values of the mean could have been obtained. Intuitively, means based r ...
... chapter 2), aimed at biologists. In this example we would like to know how the means would vary when computed for repeated (hypothetical) samples of size 15 from the same original distribution, in other words what other possible values of the mean could have been obtained. Intuitively, means based r ...
Chapter 3: Central Tendency
... simplified, concise form. • In addition, it is possible to compare two (or more) sets of data by simply comparing the average score (central tendency) for one set versus the average score for another set. ...
... simplified, concise form. • In addition, it is possible to compare two (or more) sets of data by simply comparing the average score (central tendency) for one set versus the average score for another set. ...
I BSC MICRO STAT maths - E
... data, they should be classified and converted into a frequency distribution ( number of times or frequency with which a particular data occurs in the given mass of data.). This type of condensation of data reduces their bulk and gives a clear picture of their structure. If you want to know any speci ...
... data, they should be classified and converted into a frequency distribution ( number of times or frequency with which a particular data occurs in the given mass of data.). This type of condensation of data reduces their bulk and gives a clear picture of their structure. If you want to know any speci ...
Chapter 2: Descriptive Statistics _____ provide facts and figures that
... Feedback: In an experimental study, a variable of interest is first identified. Then one or more other variables are identified and controlled or manipulated so that data can be obtained about how they influence the variable of interest. 13. The data collected from the customers in restaurants abou ...
... Feedback: In an experimental study, a variable of interest is first identified. Then one or more other variables are identified and controlled or manipulated so that data can be obtained about how they influence the variable of interest. 13. The data collected from the customers in restaurants abou ...