Test Bank - The Joy of Stats
... (Answer: Students are sometimes confused about this, so stress that the frequency distribution displays only one variable. When we see it, we cannot identify the cases to which the values pertain; it only provides a summary of the distribution, not the full information or “raw data.” We do not know ...
... (Answer: Students are sometimes confused about this, so stress that the frequency distribution displays only one variable. When we see it, we cannot identify the cases to which the values pertain; it only provides a summary of the distribution, not the full information or “raw data.” We do not know ...
Outline of Levin and Fox, Chapter 1 (2003)
... Note that the slope is an asymmetrical measure of association because the denominator includes only the variance for x (i.e., the independent variable); whereas Pearson’s correlation is symmetrical because it includes the standard deviations for both x and y. What numbers do you need to draw a line? ...
... Note that the slope is an asymmetrical measure of association because the denominator includes only the variance for x (i.e., the independent variable); whereas Pearson’s correlation is symmetrical because it includes the standard deviations for both x and y. What numbers do you need to draw a line? ...
DOC - StatsTools
... film of a mock robbery, after which each participant was questioned about what he or she had seen. The four participants in the experimental group were questioned while they were hypnotized and gave 14, 22, 18, and 17 accurate responses. The four participants in the control group gave 20, 25, 24, an ...
... film of a mock robbery, after which each participant was questioned about what he or she had seen. The four participants in the experimental group were questioned while they were hypnotized and gave 14, 22, 18, and 17 accurate responses. The four participants in the control group gave 20, 25, 24, an ...
Chapter Ten
... to be larger in one direction than in the other. Tendency for one tail of the distribution to be heavier than the other. Kurtosis is a measure of the relative peakedness or flatness of the frequency distribution curve. The kurtosis of a normal distribution is zero. -kurtosis>0, then dist is more pea ...
... to be larger in one direction than in the other. Tendency for one tail of the distribution to be heavier than the other. Kurtosis is a measure of the relative peakedness or flatness of the frequency distribution curve. The kurtosis of a normal distribution is zero. -kurtosis>0, then dist is more pea ...
Multiple Regression - Basic Relationships
... The b coefficient associated with how often does r pray (-0.554) is negative, indicating an inverse relationship in which higher numeric values for how often does r pray are associated with lower numeric values for frequency of attendance at religious services. Since both variables are ordinal level ...
... The b coefficient associated with how often does r pray (-0.554) is negative, indicating an inverse relationship in which higher numeric values for how often does r pray are associated with lower numeric values for frequency of attendance at religious services. Since both variables are ordinal level ...
The Data
... Our conclusion from this is that there is a possibility that at least one of the explanatory variables within POPULATN, LITERACY and BIRTH_RT influences the value of the dependent variable GDP/CAP. ...
... Our conclusion from this is that there is a possibility that at least one of the explanatory variables within POPULATN, LITERACY and BIRTH_RT influences the value of the dependent variable GDP/CAP. ...
Hypothesis Testing
... Kruskal-Wallis test Like most non-parametric tests, it is performed on ranked data, so the measurement observations are converted to their ranks in the overall data set: the smallest value gets a rank of 1, the next smallest gets a rank of 2, and so on. The loss of information involved in substit ...
... Kruskal-Wallis test Like most non-parametric tests, it is performed on ranked data, so the measurement observations are converted to their ranks in the overall data set: the smallest value gets a rank of 1, the next smallest gets a rank of 2, and so on. The loss of information involved in substit ...
Class Notes - Wells` Math Classes
... B) Describe the shape, center, and spread of the distribution of gas mileages. Are there any potential outliers? The shape of the distribution is skewed to the left, with a major peak at 28 and a minor peak at 24. The spread is relatively narrow (21 to 32 mpg). The two observations at 21 and the obs ...
... B) Describe the shape, center, and spread of the distribution of gas mileages. Are there any potential outliers? The shape of the distribution is skewed to the left, with a major peak at 28 and a minor peak at 24. The spread is relatively narrow (21 to 32 mpg). The two observations at 21 and the obs ...
Biostatistics Quantitative Data • Descriptive Statistics • Statistical
... two parts: a systematic part which is of scientific interest and a random variation part which is due to biological and measurement error variation. To complete the specification of the model we also specify how the random variation ǫi varies. We do this by specifying its distribution. It is assumed ...
... two parts: a systematic part which is of scientific interest and a random variation part which is due to biological and measurement error variation. To complete the specification of the model we also specify how the random variation ǫi varies. We do this by specifying its distribution. It is assumed ...
Extended-answer questions (90 MARKS)
... C when the distribution is symmetric D when the distribution is symmetric with outliers E always 35 A student’s mark on a test is 75. The mean mark for their class is 68 and the standard deviation is 4. Their standardised score is: A –2.5 B –1.75 C 0 D 1.75 E 2.5 36 A student’s standardised score on ...
... C when the distribution is symmetric D when the distribution is symmetric with outliers E always 35 A student’s mark on a test is 75. The mean mark for their class is 68 and the standard deviation is 4. Their standardised score is: A –2.5 B –1.75 C 0 D 1.75 E 2.5 36 A student’s standardised score on ...
Chapter 3
... The first quartile, Q1, is the value for which 25% of the observations are smaller and 75% are larger Q2 is the same as the median (50% are smaller, 50% are ...
... The first quartile, Q1, is the value for which 25% of the observations are smaller and 75% are larger Q2 is the same as the median (50% are smaller, 50% are ...
Over the Skittles Rainbow A Statistical Analysis of 14 Bags of Candy
... It makes no sense to aim to be as “clever as a gizzard.” Making sense is very important statistics. In order to make sense, one must have a clear understanding of the differences between categorical and quantitative data. Categorical data encompasses groups or categories, such as political affiliati ...
... It makes no sense to aim to be as “clever as a gizzard.” Making sense is very important statistics. In order to make sense, one must have a clear understanding of the differences between categorical and quantitative data. Categorical data encompasses groups or categories, such as political affiliati ...
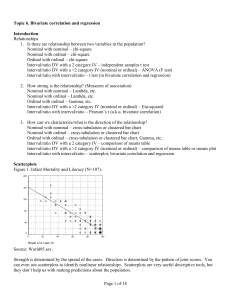
Topic 10: LEAST SQUARES REGRESSION 1 29
... The equation of a line can be represented as ŷ a bx where ŷ denotes the (response) variable being predicted (which is plotted on the vertical axis), x denotes the (explanatory) variable being used for the prediction (which is plotted on the horizontal axis), a is the value of the y-intercept o ...
... The equation of a line can be represented as ŷ a bx where ŷ denotes the (response) variable being predicted (which is plotted on the vertical axis), x denotes the (explanatory) variable being used for the prediction (which is plotted on the horizontal axis), a is the value of the y-intercept o ...
The invention of random variables
... Question 1. How did a quantity for which we have probabilities get to be a variable? Cournot (1843) used variable intermittently, along with other names. He also talked about the valeur moyenne and its linearity properties. He never applied an adjective such as aléatoire or fortuit to variable. ...
... Question 1. How did a quantity for which we have probabilities get to be a variable? Cournot (1843) used variable intermittently, along with other names. He also talked about the valeur moyenne and its linearity properties. He never applied an adjective such as aléatoire or fortuit to variable. ...
Excel and Calculator
... Central tendency People like to know, what are the central values? You can use central values to measure how you are ...
... Central tendency People like to know, what are the central values? You can use central values to measure how you are ...
Solutions Manual for Fundamental Statistics for the Behavioral
... I think it is a good idea to really think through this problem, rather than to just take the answer as given. It is important to see that looking at data can lead to conclusions to scientific questions, even without formal statistical tests. Many students have a hard time seeing the relationship bet ...
... I think it is a good idea to really think through this problem, rather than to just take the answer as given. It is important to see that looking at data can lead to conclusions to scientific questions, even without formal statistical tests. Many students have a hard time seeing the relationship bet ...
mean
... spread but it is very sensitive to the influence of extreme values. Measuring spread: interquartile range (IQR) p38 Quartiles: p33) The first quartile (Q1) is the median of the observations whose position in the ordered list is to the left of the median of the overall median. The 3rd quartile (Q3) i ...
... spread but it is very sensitive to the influence of extreme values. Measuring spread: interquartile range (IQR) p38 Quartiles: p33) The first quartile (Q1) is the median of the observations whose position in the ordered list is to the left of the median of the overall median. The 3rd quartile (Q3) i ...
Lecture 4
... the sample mean x is the difference between them, ( xi x ) ◦ Sum of all deviations is zero ◦ Therefore, we use either the sum of the absolute deviations or the sum of the squared deviations as a measure of variation ...
... the sample mean x is the difference between them, ( xi x ) ◦ Sum of all deviations is zero ◦ Therefore, we use either the sum of the absolute deviations or the sum of the squared deviations as a measure of variation ...
STA 291 Summer 2010
... the sample mean x is the difference between them, ( xi x ) ◦ Sum of all deviations is zero ◦ Therefore, we use either the sum of the absolute deviations or the sum of the squared deviations as a measure of variation ...
... the sample mean x is the difference between them, ( xi x ) ◦ Sum of all deviations is zero ◦ Therefore, we use either the sum of the absolute deviations or the sum of the squared deviations as a measure of variation ...
ameans - Stata
... Methods and formulas See Armitage, Berry, and Matthews (2002) or Snedecor and Cochran (1989). For a history of the concept of the mean, see Plackett (1958). When restricted to the same set of values (that is, to positive values), the arithmetic mean (x) is greater than or equal to the geometric mean ...
... Methods and formulas See Armitage, Berry, and Matthews (2002) or Snedecor and Cochran (1989). For a history of the concept of the mean, see Plackett (1958). When restricted to the same set of values (that is, to positive values), the arithmetic mean (x) is greater than or equal to the geometric mean ...
01/20/2010
... The third quartile (Q3) is the value from which 75% observations are smaller and 25% observations are larger. This is the median of the 2nd half of the ordered dataset. Nemours Biomedical Research ...
... The third quartile (Q3) is the value from which 75% observations are smaller and 25% observations are larger. This is the median of the 2nd half of the ordered dataset. Nemours Biomedical Research ...
Cover Sheet: Displaying Quantitative Data and
... skewed distribution and slight skew in the unimodal symmetric distribution. Correct reasoning for using median and IQR with a skewed distribution since mean and standard deviation are sensitive to outliers. Using outlier rule correctly (1.5*IQR below and above first and third quartiles). Class parti ...
... skewed distribution and slight skew in the unimodal symmetric distribution. Correct reasoning for using median and IQR with a skewed distribution since mean and standard deviation are sensitive to outliers. Using outlier rule correctly (1.5*IQR below and above first and third quartiles). Class parti ...
Doing Statistics with WinStat
... should these values be arranged for use with WinStat? In general, data are arranged in rows and colums. Observations (IQ-values from each test person) are arranged in rows, while variables (IQ values of all persons on a specific week) are arranged in columns. The data of this example are shown in Ta ...
... should these values be arranged for use with WinStat? In general, data are arranged in rows and colums. Observations (IQ-values from each test person) are arranged in rows, while variables (IQ values of all persons on a specific week) are arranged in columns. The data of this example are shown in Ta ...