Statistics 1: tests and linear models
... – If xn is numeric variable, then increment of xn with one unit increases the value of Y with bn – If xn is a factor, then parameter bn gets different value for each factor level, so that Y increases with the value bn corresponding to the level of xn • Note, reference level of x is included to the i ...
... – If xn is numeric variable, then increment of xn with one unit increases the value of Y with bn – If xn is a factor, then parameter bn gets different value for each factor level, so that Y increases with the value bn corresponding to the level of xn • Note, reference level of x is included to the i ...
April 21
... comparative experiment with two treatments the same as sampling from two independent populations. (b) Unlike the last section, in the case that we sample from one population and then use a categorical variable to categorize observations as X’s or Y ’s, we will also analyze the data as sampling from ...
... comparative experiment with two treatments the same as sampling from two independent populations. (b) Unlike the last section, in the case that we sample from one population and then use a categorical variable to categorize observations as X’s or Y ’s, we will also analyze the data as sampling from ...
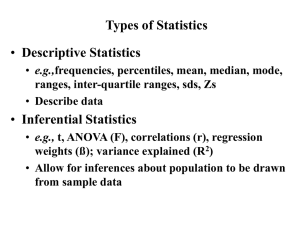
Descriptive Statistics
... Choosing a Statistic • Deciding on the appropriate statistical test requires understanding the level of measurement and the type of variable. • categorical(discrete) vs. continuous ...
... Choosing a Statistic • Deciding on the appropriate statistical test requires understanding the level of measurement and the type of variable. • categorical(discrete) vs. continuous ...
Chapter ___ Review: Type the Subject of the Chapter
... Key Topics Covered in this Chapter Graph categorical data on pie charts and bar graphs. Graph quantitative data on stemplots and histograms, Ogive or relative cumulative frequency graphs and timeplots are quantitative Describe Shape: symmetric or skewed, unimodal or no modes Describe Center ...
... Key Topics Covered in this Chapter Graph categorical data on pie charts and bar graphs. Graph quantitative data on stemplots and histograms, Ogive or relative cumulative frequency graphs and timeplots are quantitative Describe Shape: symmetric or skewed, unimodal or no modes Describe Center ...
Factor Analysis: dealing with missing values
... substantial number of cases. 3) One way around this is to construct scales that have average scores based on those items for which there are valid data. 4) The first step is to make sure all your variables have missing values assigned. Then standardize all the variables by subtracting the mean and d ...
... substantial number of cases. 3) One way around this is to construct scales that have average scores based on those items for which there are valid data. 4) The first step is to make sure all your variables have missing values assigned. Then standardize all the variables by subtracting the mean and d ...
Solution
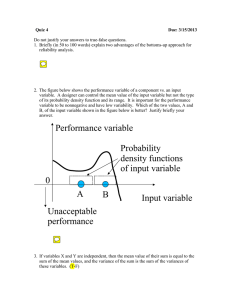
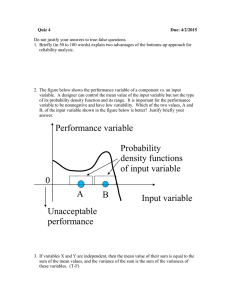
... 2. The figure below shows the performance variable of a component vs. an input variable. A designer can control the mean value of the input variable but not the type of its probability density function and its range. It is important for the performance variable to be nonnegative and have low variabi ...
... 2. The figure below shows the performance variable of a component vs. an input variable. A designer can control the mean value of the input variable but not the type of its probability density function and its range. It is important for the performance variable to be nonnegative and have low variabi ...
Performance variable Input variable A B 0 Unacceptable
... 2. The figure below shows the performance variable of a component vs. an input variable. A designer can control the mean value of the input variable but not the type of its probability density function and its range. It is important for the performance variable to be nonnegative and have low variabi ...
... 2. The figure below shows the performance variable of a component vs. an input variable. A designer can control the mean value of the input variable but not the type of its probability density function and its range. It is important for the performance variable to be nonnegative and have low variabi ...
AP STATISTIC EXAM REVIEW I: EXPLORING DATA (20–30
... • If you learn to distinguish categorical from quantitative variables now, it will pay big rewards later. You will be expected to analyze categorical and quantitative variables correctly on the AP exam. • When comparing distributions of quantitative data, it’s not enough just to list values for the ...
... • If you learn to distinguish categorical from quantitative variables now, it will pay big rewards later. You will be expected to analyze categorical and quantitative variables correctly on the AP exam. • When comparing distributions of quantitative data, it’s not enough just to list values for the ...
Standardize Variables
... Standardize Variables The STANDARDIZE V ARIABLES command transforms variables using selected normalization method. The command can be used to make variables comparable to each other. ...
... Standardize Variables The STANDARDIZE V ARIABLES command transforms variables using selected normalization method. The command can be used to make variables comparable to each other. ...
day2
... Categorical, Continuous and Discontinuous • Categorical (nominal) – Gender, party affiliation, etc. ...
... Categorical, Continuous and Discontinuous • Categorical (nominal) – Gender, party affiliation, etc. ...
ch7 slides
... E: Density Curves and Normal Distributions Know that areas under a density curve represent proportions of all observations and that the total area under a density curve is 1. Approximate the median and mean on a density curve. Know that the mean and median both lie at the center of a symmetric d ...
... E: Density Curves and Normal Distributions Know that areas under a density curve represent proportions of all observations and that the total area under a density curve is 1. Approximate the median and mean on a density curve. Know that the mean and median both lie at the center of a symmetric d ...
Stats handouts
... groups - does not tell us which groups are different from one another Post-hoc analysis with Tukey’s multiple comparison test A vs B p < 0.001 A vs C p > 0.05 (not significantly different) B vs C p < 0.001 ...
... groups - does not tell us which groups are different from one another Post-hoc analysis with Tukey’s multiple comparison test A vs B p < 0.001 A vs C p > 0.05 (not significantly different) B vs C p < 0.001 ...
qualitative data analysis - the political economy of war
... between all scores and the mean score. It helps you make comparisons in distributions- for example a low or zero standard deviation means that all cases are very close to or identical with the mean, while a large standard deviation implies that individual scores are in general quite different to t ...
... between all scores and the mean score. It helps you make comparisons in distributions- for example a low or zero standard deviation means that all cases are very close to or identical with the mean, while a large standard deviation implies that individual scores are in general quite different to t ...
April 21
... compare two data sets is to express all scores in terms of the distance from the mean. ...
... compare two data sets is to express all scores in terms of the distance from the mean. ...
Math4020 Statistics Worksheet # hours study per week
... (a) 68% of the teachers will have a salary on what interval centered about the mean? (b) 84% of the teachers have salaries below what amount? (c) How many teachers will make more than $28,600? 3. Suppose there are four third-grade classes in your school containing 25, 28, 30, and 27 students. These ...
... (a) 68% of the teachers will have a salary on what interval centered about the mean? (b) 84% of the teachers have salaries below what amount? (c) How many teachers will make more than $28,600? 3. Suppose there are four third-grade classes in your school containing 25, 28, 30, and 27 students. These ...
Chapter 1 of Gleitman et al
... two independent means (between-groups design) paired means (within-subjects design) Analysis of variance (ANOVA, F-test) comparisons involving more than two means one independent variable with more than two levels more than one independent variable ...
... two independent means (between-groups design) paired means (within-subjects design) Analysis of variance (ANOVA, F-test) comparisons involving more than two means one independent variable with more than two levels more than one independent variable ...
Province, Gender, Language, Height, Physical Days, Smoke
... Mean, Median, SD (Standard deviation) ...
... Mean, Median, SD (Standard deviation) ...
Key Terms - The Joy of Stats
... One-sample t-test (select a specific test value for the null hypothesis) Independent-samples t-test (two groups, not matched or paired, which might have different sample sizes and variances) ANOVA: F-test, ratio of “between-groups” to “within-groups” mean sum of squares, and post-hoc measures ...
... One-sample t-test (select a specific test value for the null hypothesis) Independent-samples t-test (two groups, not matched or paired, which might have different sample sizes and variances) ANOVA: F-test, ratio of “between-groups” to “within-groups” mean sum of squares, and post-hoc measures ...
Slides. - Rasmusen, Eric
... 1. Only present relevant and meaningful numbers. 2. Do not write 1.23423 when rounding to 1.23 will do just as well. Fewer digits yield greater clarity. 3. Use correlation matrices to show the simple correlations between important variables. 4. Give summary statistics. Think about which are most use ...
... 1. Only present relevant and meaningful numbers. 2. Do not write 1.23423 when rounding to 1.23 will do just as well. Fewer digits yield greater clarity. 3. Use correlation matrices to show the simple correlations between important variables. 4. Give summary statistics. Think about which are most use ...
Longitudinal Studies - Ball State University
... Mean • What we normally call the “average” • Denoted as “xbar” • Calculated as ...
... Mean • What we normally call the “average” • Denoted as “xbar” • Calculated as ...
Chap 2 Biv
... • Parallel Boxplots – To display a relationship between a numerical variable and categorical variable with more than two categories. – Same process as constructing a single boxplot, except that they share a common scale. – Comparing distributions of a number of boxplots. ...
... • Parallel Boxplots – To display a relationship between a numerical variable and categorical variable with more than two categories. – Same process as constructing a single boxplot, except that they share a common scale. – Comparing distributions of a number of boxplots. ...
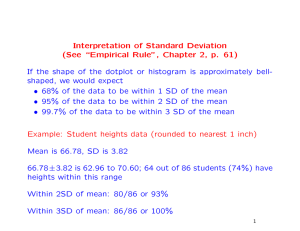
Interpretation of Standard Deviation (See “Empirical Rule”, Chapter
... The response variable is the outcome variable on which comparisons are made. The explanatory variable defines the groups to be compared with respect to values of the response variable. Association means that the values of the response in some way depend on the explanatory variable. At this level of ...
... The response variable is the outcome variable on which comparisons are made. The explanatory variable defines the groups to be compared with respect to values of the response variable. Association means that the values of the response in some way depend on the explanatory variable. At this level of ...
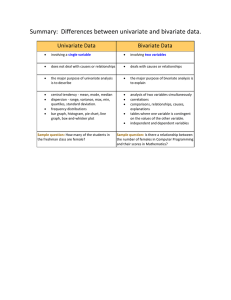
Summary: Differences between univariate and bivariate data.
... deals with causes or relationships ...
... deals with causes or relationships ...