Announcement
... The median is the value of a variable that divides the observations on that variable in half. If we ordered our observations on a variable from lowest to highest, the median observation is the one in the middle. With an even number of observations there is no true median. The median is most commonly ...
... The median is the value of a variable that divides the observations on that variable in half. If we ordered our observations on a variable from lowest to highest, the median observation is the one in the middle. With an even number of observations there is no true median. The median is most commonly ...
Ethics & Research
... The mode is the most frequently observed value in the frequency distribution ie it is the score that occurs most frequently The mode is best used for nominal data and for data that are qualitative in nature such as gender, eye colour, ethnicity, school or group membership In the following list of nu ...
... The mode is the most frequently observed value in the frequency distribution ie it is the score that occurs most frequently The mode is best used for nominal data and for data that are qualitative in nature such as gender, eye colour, ethnicity, school or group membership In the following list of nu ...
Cheat Sheet for R and RStudio
... • t.test(X,Y) - Performs a t-test of means between two variables X and Y for the hypothesis H0 : µX = µY . Gives t-statistic, p-value and 95% confidence interval. ...
... • t.test(X,Y) - Performs a t-test of means between two variables X and Y for the hypothesis H0 : µX = µY . Gives t-statistic, p-value and 95% confidence interval. ...
Homework1
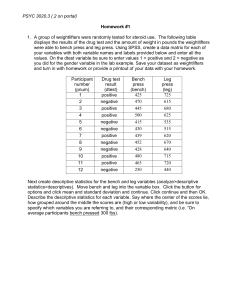
... options and click mean and standard deviation and continue. Click continue and then OK. Describe the descriptive statistics for each variable. Say where the center of the scores lie, how grouped around the middle the scores are (high or low variability), and be sure to specify which variables you ar ...
... options and click mean and standard deviation and continue. Click continue and then OK. Describe the descriptive statistics for each variable. Say where the center of the scores lie, how grouped around the middle the scores are (high or low variability), and be sure to specify which variables you ar ...
Powerpoint
... – Purpose: determining the empirical relationship between the two variables Multivariate analysis – Purpose: determining the empirical relationship among the variables ...
... – Purpose: determining the empirical relationship between the two variables Multivariate analysis – Purpose: determining the empirical relationship among the variables ...
Summarizing and exploring data
... Types of values that experimental variables can have. Categorial versus numerical values. Categorical values don’t have intrinsic numbers associated to them. For instance, a Bernoulli (also called binary) value is one of two values, such as Heads or Tails, Success or Failure, candidate A or candidat ...
... Types of values that experimental variables can have. Categorial versus numerical values. Categorical values don’t have intrinsic numbers associated to them. For instance, a Bernoulli (also called binary) value is one of two values, such as Heads or Tails, Success or Failure, candidate A or candidat ...
Unit 2: Research Methods NOTES
... 4. Longitudinal Study – collects data from same group over a long span of time 5. Cross-Sectional Studies – organizing groups according to age, gender, etc. and tested at the same time to see if there are differences 6. Correlational – research used to describe relationship between two variables 7. ...
... 4. Longitudinal Study – collects data from same group over a long span of time 5. Cross-Sectional Studies – organizing groups according to age, gender, etc. and tested at the same time to see if there are differences 6. Correlational – research used to describe relationship between two variables 7. ...
Statistics for teachers
... Types of Data Nominal Data -- Data that describe the presence or absence of some characteristic or attribute; data that name a characteristic without any regard to the value of the characteristic; also referred to as categorical data. Male = 1 Female = 2, blue, green, etc Ordinal Data -- Measur ...
... Types of Data Nominal Data -- Data that describe the presence or absence of some characteristic or attribute; data that name a characteristic without any regard to the value of the characteristic; also referred to as categorical data. Male = 1 Female = 2, blue, green, etc Ordinal Data -- Measur ...
Working with Data Part 3
... customers have JOB as ProfExe? The graphs also show that LOAN, MORTDUE, and VALUE all have extreme values significantly greater than their means. This means that each distribution is skewed to the right. Another useful feature in JMP is to click on the bar for bad risk customers in the BAD graph (BA ...
... customers have JOB as ProfExe? The graphs also show that LOAN, MORTDUE, and VALUE all have extreme values significantly greater than their means. This means that each distribution is skewed to the right. Another useful feature in JMP is to click on the bar for bad risk customers in the BAD graph (BA ...
Welcome to EDP 557 Educational Statistics
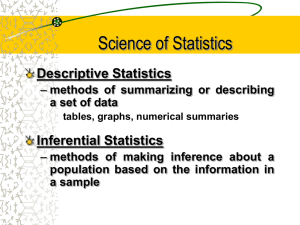
... Science of Statistics Descriptive Statistics – methods of summarizing or describing a set of data tables, graphs, numerical summaries ...
... Science of Statistics Descriptive Statistics – methods of summarizing or describing a set of data tables, graphs, numerical summaries ...
R Commands for Numeric Summaries of Data and Boxplots 1. Mean
... a. Exercise: Import the 4th-6th graders Popularity Study data from the course website. Use R Commander to computer the mean, median, standard deviation, etc. of the Sports variable for girls and boys. This variable represents how the student ranked sports as to its importance for popularity by assig ...
... a. Exercise: Import the 4th-6th graders Popularity Study data from the course website. Use R Commander to computer the mean, median, standard deviation, etc. of the Sports variable for girls and boys. This variable represents how the student ranked sports as to its importance for popularity by assig ...
Stats 1
... Why statistics are difficult to learn Deceptive terminology (significant, error, hypothesis) Statistical conclusions are never absolute (statistically significant) Statistics uses abstract concepts (populations, ...
... Why statistics are difficult to learn Deceptive terminology (significant, error, hypothesis) Statistical conclusions are never absolute (statistically significant) Statistics uses abstract concepts (populations, ...
Programmed Text onData Analysis (Appendix B)
... t-test (using the difference between the means and the standard error of this difference), and taking into account the number of degrees of freedom, one obtains a number which indicates whether or not there is a real difference between the two samples. GRAPHS When considering experimental observatio ...
... t-test (using the difference between the means and the standard error of this difference), and taking into account the number of degrees of freedom, one obtains a number which indicates whether or not there is a real difference between the two samples. GRAPHS When considering experimental observatio ...
Ch 3 Notes
... The fraction of the variation in the values of y that is explained by the least-squares regression of y on x Measures the contribution of x in predicting y If x is a poor predictor of y, then the sum of the squares of the deviations about the mean (SST) and the sum of the squares of deviations about ...
... The fraction of the variation in the values of y that is explained by the least-squares regression of y on x Measures the contribution of x in predicting y If x is a poor predictor of y, then the sum of the squares of the deviations about the mean (SST) and the sum of the squares of deviations about ...
Lecture 1 - University of Oregon
... • Causality is often difficult to determine—wait for the next slide—that’s that’s why research design is important. • An experiment is the gold standard. • If a treated subject and a control subject are the same in every respect (as they are in a perfect experiment), we can logically attribute any d ...
... • Causality is often difficult to determine—wait for the next slide—that’s that’s why research design is important. • An experiment is the gold standard. • If a treated subject and a control subject are the same in every respect (as they are in a perfect experiment), we can logically attribute any d ...
Summarizing the Relationship Between Two Variables with Tables
... whether or not the value is significant. In this case it is > .05. • Therefore we reject the hypothesis that the results we see are meaningfully different from what we could expect through simple probability • Therefore we also reject that there is any meaningful difference between the number of bat ...
... whether or not the value is significant. In this case it is > .05. • Therefore we reject the hypothesis that the results we see are meaningfully different from what we could expect through simple probability • Therefore we also reject that there is any meaningful difference between the number of bat ...
Quantitative analysis
... Likert scale eg. 1= never (disagree) 2 3 4 5 6 7 = always (agree) (odd - better) Dummy: dicotomic variables eg. Yes/no or gender ...
... Likert scale eg. 1= never (disagree) 2 3 4 5 6 7 = always (agree) (odd - better) Dummy: dicotomic variables eg. Yes/no or gender ...
Solutions
... study and randomly divides all subjects into two groups. He will treat one of the groups using the new drug and the other group placebo. This is an example of a(n): A. Observational study ...
... study and randomly divides all subjects into two groups. He will treat one of the groups using the new drug and the other group placebo. This is an example of a(n): A. Observational study ...
SUMMARY OF STATISTICAL PROCEDURES
... 1. one mean compared to a standard 2. two means compared to each other (independent samples with equal or unequal variances, dependent (matched pairs)) ...
... 1. one mean compared to a standard 2. two means compared to each other (independent samples with equal or unequal variances, dependent (matched pairs)) ...
Quantitative Data Analysis
... • Bar graph (column chart, histogram): best with fewer categories • Pie chart: good for displaying percentages; easily understood by general audience • Line graph: good for numerical variables with many values or for trend data ...
... • Bar graph (column chart, histogram): best with fewer categories • Pie chart: good for displaying percentages; easily understood by general audience • Line graph: good for numerical variables with many values or for trend data ...
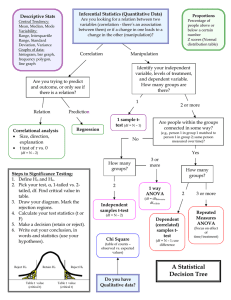
Statistical Test Decision Tree
... Deviation, Variance Graphs of data: histogram, bar graph, frequency polygon, line graph ...
... Deviation, Variance Graphs of data: histogram, bar graph, frequency polygon, line graph ...
1 STA 225: Exam 1 Instructor: Theo Ogunyemi July 19, 2004 Name
... (b) students who watch more TV tend to get lower grades. (c) Students who watch more TV tend to get higher grades. (d) There is little association between TV viewing and grade-point index. 2. In the regression equation, the value that gives the amount by which Y changes for one unit in X is called t ...
... (b) students who watch more TV tend to get lower grades. (c) Students who watch more TV tend to get higher grades. (d) There is little association between TV viewing and grade-point index. 2. In the regression equation, the value that gives the amount by which Y changes for one unit in X is called t ...
Homework 1
... 1.5. (a) All adult Americans. (b) Proportion of all adult Americans who would answer definitely or probably true. (c) The sample proportion 0.523 estimates the population proportion. (d) No, it is a prediction of the population value but will not equal it exactly, because the sample is only a very s ...
... 1.5. (a) All adult Americans. (b) Proportion of all adult Americans who would answer definitely or probably true. (c) The sample proportion 0.523 estimates the population proportion. (d) No, it is a prediction of the population value but will not equal it exactly, because the sample is only a very s ...