Populations
... • The MEAN is the arithmetic average of the set of observations (can be used for both continuous and discrete data) • can be susceptible to influence of outliers (income example) ...
... • The MEAN is the arithmetic average of the set of observations (can be used for both continuous and discrete data) • can be susceptible to influence of outliers (income example) ...
1.1 Basic Equations
... Inferential Stats: making predictions or inferences about a population based on a sample ...
... Inferential Stats: making predictions or inferences about a population based on a sample ...
Descriptive Measures
... they are of little value in practical prediction situations. With correlation around 0.50, crude group prediction may be achieved. In describing the relationship between two variables, correlation coefficients that are this low do not suggest a good relationship. Correlation coefficients ranging ...
... they are of little value in practical prediction situations. With correlation around 0.50, crude group prediction may be achieved. In describing the relationship between two variables, correlation coefficients that are this low do not suggest a good relationship. Correlation coefficients ranging ...
Describing the Spread of Quantitative Data
... numbers or letters assigned to objects serve as labels for identification or classification. • For example, names and gender are categorical variables; – and one can put the level ‘M’ for Male and ‘F’ for Female, – or ‘1’ for male and ‘2’ for female, – or ‘1’ for female and ‘2’ for male. ...
... numbers or letters assigned to objects serve as labels for identification or classification. • For example, names and gender are categorical variables; – and one can put the level ‘M’ for Male and ‘F’ for Female, – or ‘1’ for male and ‘2’ for female, – or ‘1’ for female and ‘2’ for male. ...
In Depth: Descriptive Research
... Examples: finishers in a race, class ranking, small, medium, and large size Interval order and equal distance, but no true zero Zero is not the absence of the property Examples: Intelligence, degrees F or C ...
... Examples: finishers in a race, class ranking, small, medium, and large size Interval order and equal distance, but no true zero Zero is not the absence of the property Examples: Intelligence, degrees F or C ...
BIOSTATISTICS QUIZ ANSWERS
... a. False: Tests the null hypothesis that the mean of the differences in the population is zero. b. True (This is required in order to calculate the difference for each pair of observations.) c. False: the paired t-test makes the assumption that the differences between the pairs are normally distribu ...
... a. False: Tests the null hypothesis that the mean of the differences in the population is zero. b. True (This is required in order to calculate the difference for each pair of observations.) c. False: the paired t-test makes the assumption that the differences between the pairs are normally distribu ...
1. For a particular sample of 63 scores on a psychology exam, the
... 8. SAT I scores around the nation tend to have a mean scale score around 500, a standard deviation of about 100 points and are approximately normally distributed. A person who scores 700 on the SAT I has approximately what percentile rank within the population? Show all work as to how this is obtain ...
... 8. SAT I scores around the nation tend to have a mean scale score around 500, a standard deviation of about 100 points and are approximately normally distributed. A person who scores 700 on the SAT I has approximately what percentile rank within the population? Show all work as to how this is obtain ...
Chapter 3 Slides (PPT)
... been ordered from smallest to largest. Appropriate for interval and ordinal scales • Pth percentile - Value where P% of measurements fall below and (100-P)% lie above. Lower quartile(25th), Median(50th), Upper quartile(75th) often reported • Mode - Most frequently occurring outcome. Typically report ...
... been ordered from smallest to largest. Appropriate for interval and ordinal scales • Pth percentile - Value where P% of measurements fall below and (100-P)% lie above. Lower quartile(25th), Median(50th), Upper quartile(75th) often reported • Mode - Most frequently occurring outcome. Typically report ...
Bivariate Data
... Are there any unusual points? Outliers are points whose combination of values is unusual. They will affect what we perceive as the pattern, so they need investigation. If the data points fit a straight line well, we can use one of the variables to predict the other. Usually, one variable is diffic ...
... Are there any unusual points? Outliers are points whose combination of values is unusual. They will affect what we perceive as the pattern, so they need investigation. If the data points fit a straight line well, we can use one of the variables to predict the other. Usually, one variable is diffic ...
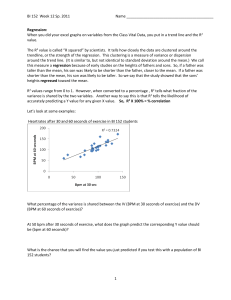
Regression
... Regression: When you did your excel graphs on variables from the Class Vital Data, you put in a trend line and the R2 value. The R2 value is called “R squared” by scientists. It tells how closely the data are clustered around the trendline, or the strength of the regression. This clustering is a mea ...
... Regression: When you did your excel graphs on variables from the Class Vital Data, you put in a trend line and the R2 value. The R2 value is called “R squared” by scientists. It tells how closely the data are clustered around the trendline, or the strength of the regression. This clustering is a mea ...
KING ABDULAZIZ UNVERSITY
... If a variable can take any value between 0 and 15, then this variable is called a …….. variable. (A) continuous (C) discrete and quantitative (B) discrete (D) continuous and qualitative ...
... If a variable can take any value between 0 and 15, then this variable is called a …….. variable. (A) continuous (C) discrete and quantitative (B) discrete (D) continuous and qualitative ...
data prep and descriptive stats
... • The process of systematically and consistently assigning each response a numerical score. • The key to a good coding system is for the coding categories to be mutually exclusive and the entire system to be collectively exhaustive. • To be mutually exclusive, every response must fit into only one c ...
... • The process of systematically and consistently assigning each response a numerical score. • The key to a good coding system is for the coding categories to be mutually exclusive and the entire system to be collectively exhaustive. • To be mutually exclusive, every response must fit into only one c ...
ANOVA & Regression
... The bigger the test statistic the more likely there is a relationship between the independent and dependent variables. Values greater than 3 are for every type of inferential statistic other than correlation are usually statistically significant. Relationships can be positive or negative. You need t ...
... The bigger the test statistic the more likely there is a relationship between the independent and dependent variables. Values greater than 3 are for every type of inferential statistic other than correlation are usually statistically significant. Relationships can be positive or negative. You need t ...
ANOVA & Regression
... The bigger the test statistic the more likely there is a relationship between the independent and dependent variables. Values greater than 3 are for every type of inferential statistic other than correlation are usually statistically significant. • Relationships can be positive or negative. You need ...
... The bigger the test statistic the more likely there is a relationship between the independent and dependent variables. Values greater than 3 are for every type of inferential statistic other than correlation are usually statistically significant. • Relationships can be positive or negative. You need ...
Chapter 3 outline notes
... • Cross classifications of categorical variables in which rows (typically) represent categories of explanatory variable and columns represent categories of response variable. • Numbers in “cells” of the table give the numbers of individuals at the corresponding combination of levels of the two varia ...
... • Cross classifications of categorical variables in which rows (typically) represent categories of explanatory variable and columns represent categories of response variable. • Numbers in “cells” of the table give the numbers of individuals at the corresponding combination of levels of the two varia ...
Chapter 1 Study Guide
... 2. Explain how to calculate the mean, x . 3. Explain how to calculate the median, M. 4. Explain why the median is resistant to extreme observations, but the mean is nonresistant. 5. In statistics, what is meant by spread? 6. Explain how to calculate Q1 and Q3. 7. What is the five-number summary? 8. ...
... 2. Explain how to calculate the mean, x . 3. Explain how to calculate the median, M. 4. Explain why the median is resistant to extreme observations, but the mean is nonresistant. 5. In statistics, what is meant by spread? 6. Explain how to calculate Q1 and Q3. 7. What is the five-number summary? 8. ...
META-ANALYSIS OF RESEARCH
... Procedures for reliability of coding Data analysis approach (eg. Lipsey & Wilson) ...
... Procedures for reliability of coding Data analysis approach (eg. Lipsey & Wilson) ...
KING ABDULAZIZ UNVERSITY
... Please: Make sure that the answer sheet form matches the question form. ...
... Please: Make sure that the answer sheet form matches the question form. ...
Handout for SPSS
... grouping variables. All levels of the grouping variable are crosstabulated. You can choose the order in which the statistics are displayed. Summary statistics for each variable across all categories are also displayed. Data values in each category can be listed or suppressed. With large data sets, y ...
... grouping variables. All levels of the grouping variable are crosstabulated. You can choose the order in which the statistics are displayed. Summary statistics for each variable across all categories are also displayed. Data values in each category can be listed or suppressed. With large data sets, y ...
chapter2A
... Studentized residuals – standardizing the residuals using the standard deviation of the data with the individual omitted from the data (helps to avoid having too big a standard deviation) Beware of lurking variables Correlation measures only linear association. Extrapolation can be inaccurate. Corre ...
... Studentized residuals – standardizing the residuals using the standard deviation of the data with the individual omitted from the data (helps to avoid having too big a standard deviation) Beware of lurking variables Correlation measures only linear association. Extrapolation can be inaccurate. Corre ...
Review Topics for
... prediction problems in XLMINER? What are some of the other predictive accuracy measures one could use? What loss function is implied by the RMSE accuracy measure in prediction problems? You should know the basic logic of the various data mining techniques. With respect to multiple linear regression ...
... prediction problems in XLMINER? What are some of the other predictive accuracy measures one could use? What loss function is implied by the RMSE accuracy measure in prediction problems? You should know the basic logic of the various data mining techniques. With respect to multiple linear regression ...
one-way anova
... Interaction effects(two indep. Variables separated by *): if Sig. less than 0.05 it means there is interaction effect—there is significant difference in first independent variable GIVEN the second one. Main Effects—check each of the indep. Variables and their Sig. value; if less than 0.05, that vari ...
... Interaction effects(two indep. Variables separated by *): if Sig. less than 0.05 it means there is interaction effect—there is significant difference in first independent variable GIVEN the second one. Main Effects—check each of the indep. Variables and their Sig. value; if less than 0.05, that vari ...
10 Chapter 01 Concept Sheet
... the median M is the center observation in the ordered list. The position of the center can be found at (n +1)/2. If the number of observations n is even, the median M is the mean of the two center observations in the ordered list. The position of the two middle values are n/2 and (n/2) + 1. The Fi ...
... the median M is the center observation in the ordered list. The position of the center can be found at (n +1)/2. If the number of observations n is even, the median M is the mean of the two center observations in the ordered list. The position of the two middle values are n/2 and (n/2) + 1. The Fi ...
Descriptive Statistics - University of Florida
... – If too cramped/narrow, break stems into two groups: low with leaves 0-4 and high with leaves 5-9 – When numbers have many digits, trim off right-most (less significant) digits. Leaves should always be a single digit. ...
... – If too cramped/narrow, break stems into two groups: low with leaves 0-4 and high with leaves 5-9 – When numbers have many digits, trim off right-most (less significant) digits. Leaves should always be a single digit. ...