SOCIAL CAPITAL AND IMMIGRANT RELIGION1
... he takes their human capital with them. In contrast, social capital represents resources that reside in specific social relationships in which individuals are imbedded. When social capital is viewed as an individual variable, it is seen as one form of human capital along with education and organizat ...
... he takes their human capital with them. In contrast, social capital represents resources that reside in specific social relationships in which individuals are imbedded. When social capital is viewed as an individual variable, it is seen as one form of human capital along with education and organizat ...
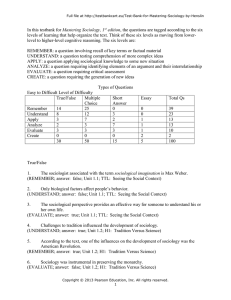
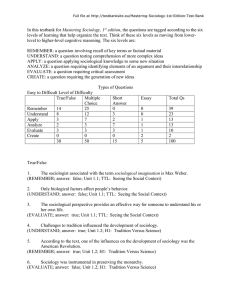
In this testbank for Mastering Sociology, 1st edition, the questions
... Sociologists can safely press for social reform because they are protected by tenure. (UNDERSTAND; answer: false; Unit 1.3; H1: The Tension Today: Basic, Applied, and Public ...
... Sociologists can safely press for social reform because they are protected by tenure. (UNDERSTAND; answer: false; Unit 1.3; H1: The Tension Today: Basic, Applied, and Public ...
FREE Sample Here
... Full file at http://testbanksite.eu/Mastering-Sociology-1st-Edition-Test-Bank ...
... Full file at http://testbanksite.eu/Mastering-Sociology-1st-Edition-Test-Bank ...
View/Open - Dora.dmu.ac.uk
... favour of more powerful interests in mental health contexts. To illustrate this, let us consider the work of theologian and philosopher Martin Buber. He is well known for his popularisation of the so-called ‘I-thou’ relationship, which has been of interest to scholars of nursing (Briant and Freshwat ...
... favour of more powerful interests in mental health contexts. To illustrate this, let us consider the work of theologian and philosopher Martin Buber. He is well known for his popularisation of the so-called ‘I-thou’ relationship, which has been of interest to scholars of nursing (Briant and Freshwat ...
FREE Sample Here - We can offer most test bank and
... Full file at http://testbanksite.eu/Social-Problems-in-a-Diverse-Society-3rd-Edition-Test-Bank ...
... Full file at http://testbanksite.eu/Social-Problems-in-a-Diverse-Society-3rd-Edition-Test-Bank ...
GROUP DYNAMICS 6. The Sociology of Georg Simmel 6.1
... the mind. In other words, Simmel does not quite say that the big city has an overall negative effect on the mind or the self, even as he suggests that it undergoes permanent changes. It is perhaps this ambiguity that gave the essay a lasting place in the discourse on the metropolis. The deepest pro ...
... the mind. In other words, Simmel does not quite say that the big city has an overall negative effect on the mind or the self, even as he suggests that it undergoes permanent changes. It is perhaps this ambiguity that gave the essay a lasting place in the discourse on the metropolis. The deepest pro ...
Document
... have been migrant integration (assimilation) and political practices across borders (diasporas). First, it is noteworthy that the pioneers of this understanding of the transnational challenged the notion that the incorporation of immigrants takes place in the container of the respective nation-state ...
... have been migrant integration (assimilation) and political practices across borders (diasporas). First, it is noteworthy that the pioneers of this understanding of the transnational challenged the notion that the incorporation of immigrants takes place in the container of the respective nation-state ...
introduction to sociology
... discipline in which we often set aside our personal view of the world to look more carefully at the influences that shape our lives and those of others. Sociology helps us to know not only our society but also others, their motives, aspirations, traditions, customs, etc. Sociology emerged as a disti ...
... discipline in which we often set aside our personal view of the world to look more carefully at the influences that shape our lives and those of others. Sociology helps us to know not only our society but also others, their motives, aspirations, traditions, customs, etc. Sociology emerged as a disti ...