F15 - Tamu.edu
... 29b And the maximin strategies for each firm are that each firm picks Sedan. A maximin strategy chooses the option that makes the lowest payoff one can receive as large as possible. If Firm 1 picks Sedan, the worst payoff it can get is 500 but could get a lower payoff of 400 if picked SUV. Similarly ...
... 29b And the maximin strategies for each firm are that each firm picks Sedan. A maximin strategy chooses the option that makes the lowest payoff one can receive as large as possible. If Firm 1 picks Sedan, the worst payoff it can get is 500 but could get a lower payoff of 400 if picked SUV. Similarly ...
Chapter 1
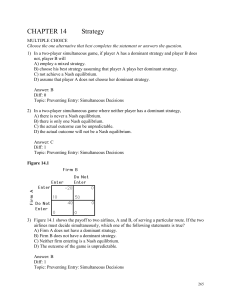
... does, a Nash equilibrium does not exist. Answer: False. There are two Nash equilibria. In each, the two players are doing the opposite of one another. The problem is, it is difficult to know which equilibrium is achieved without some form of collusion. Diff: 1 Topic: Preventing Entry: Simultaneous D ...
... does, a Nash equilibrium does not exist. Answer: False. There are two Nash equilibria. In each, the two players are doing the opposite of one another. The problem is, it is difficult to know which equilibrium is achieved without some form of collusion. Diff: 1 Topic: Preventing Entry: Simultaneous D ...
An Exact Solution Method for Binary Equilibrium
... equilibrium exists, but where a market operator or regulator can assign compensation payments in order to obtain an incentive-compatible outcome. These payments align the incentives of individual players with the objectives of the overall system, such as cost minimization or welfare maximization. A ...
... equilibrium exists, but where a market operator or regulator can assign compensation payments in order to obtain an incentive-compatible outcome. These payments align the incentives of individual players with the objectives of the overall system, such as cost minimization or welfare maximization. A ...
Lecture notes - Xiang Sun | 孙祥
... 1.4 In 1928, Zur Theorie der Gesellschaftsspiele (团队游戏之理论) by John von Neumann (约翰・冯・诺伊曼). ...
... 1.4 In 1928, Zur Theorie der Gesellschaftsspiele (团队游戏之理论) by John von Neumann (约翰・冯・诺伊曼). ...
Peering Equilibrium Multipath Routing: A Game Theory Framework
... Nevertheless, the lack of routing collaboration among neighboring carriers causes BGP Multipath to produce unilateral routing choices that, even if potentially efficient for the upstream carrier with respect to load distribution, may lead to an inefficient situation for the downstream carrier. In th ...
... Nevertheless, the lack of routing collaboration among neighboring carriers causes BGP Multipath to produce unilateral routing choices that, even if potentially efficient for the upstream carrier with respect to load distribution, may lead to an inefficient situation for the downstream carrier. In th ...
Chapter 11 Equilibrium - Farmingdale State College
... equilibrium states that for a body to be in equilibrium, the vector sum of all the forces acting on that body must be zero. But equation 11.1, the first condition of equilibrium, is just a special case of equation 5.9, Newton’s second law of motion. Hence, bodies in equilibrium are nothing more than ...
... equilibrium states that for a body to be in equilibrium, the vector sum of all the forces acting on that body must be zero. But equation 11.1, the first condition of equilibrium, is just a special case of equation 5.9, Newton’s second law of motion. Hence, bodies in equilibrium are nothing more than ...