1.1 Safety in the Science Classroom
... • The enhanced greenhouse effect increases thermal energy absorbed. More greenhouse gases in the atmosphere = increase of natural greenhouse effect Greenhouse gases include water vapour, CO2, methane, nitrous oxide, and CFCs. Global warming potential (GWP) refers to the ability to trap thermal ...
... • The enhanced greenhouse effect increases thermal energy absorbed. More greenhouse gases in the atmosphere = increase of natural greenhouse effect Greenhouse gases include water vapour, CO2, methane, nitrous oxide, and CFCs. Global warming potential (GWP) refers to the ability to trap thermal ...
The science behind climate change
... Climate change is one of the most pressing issues of our time. Though it has been a popular topic in recent years, interest in climate change has seemed to decline as the economic downturn felt across the globe has taken precedence. Nonetheless, action must urgently be taken, as the negative impact ...
... Climate change is one of the most pressing issues of our time. Though it has been a popular topic in recent years, interest in climate change has seemed to decline as the economic downturn felt across the globe has taken precedence. Nonetheless, action must urgently be taken, as the negative impact ...
for understanding the Strategic Framework
... Water: snowpacks are thinner and they melt earlier in spring—increasing drought ...
... Water: snowpacks are thinner and they melt earlier in spring—increasing drought ...
Slide 1
... What’s causing global warming? • Carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane • Naturally occurring, but increase with human activity • Rising CO2 since Industrial Revolution • Product of fossil fuels • 90-99% confidence (IPCC) ...
... What’s causing global warming? • Carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane • Naturally occurring, but increase with human activity • Rising CO2 since Industrial Revolution • Product of fossil fuels • 90-99% confidence (IPCC) ...
The science debate behind climate change
... the new crystal structure that forms when water molecules are under high pressure. Each layer of ice is observable using spectroscopic techniques, but in some cases, when there was a volcanic eruption, for example, the layers are even discernible to the naked eye. The snow that forms glacial ice hol ...
... the new crystal structure that forms when water molecules are under high pressure. Each layer of ice is observable using spectroscopic techniques, but in some cases, when there was a volcanic eruption, for example, the layers are even discernible to the naked eye. The snow that forms glacial ice hol ...
Global warming returns after two-year hiatus
... The eruption spewed dust and sulfur particles into the earth's atmosphere. These particles reflected the sun's heat and allowed the earth to cool. With much of this atmospheric dust now settled back to the ground, global warming has resumed. Although climatologists agree that a warming trend is unde ...
... The eruption spewed dust and sulfur particles into the earth's atmosphere. These particles reflected the sun's heat and allowed the earth to cool. With much of this atmospheric dust now settled back to the ground, global warming has resumed. Although climatologists agree that a warming trend is unde ...
Climate change vulnerability and adaptation research at TERI
... as the coastal districts where coastal ecosystems are already stressed due to extant human activity, and which are also the most vulnerable to sea level rise. These megacities already have pressing planning concerns due to high ground water needs, aggravated by salinity problems. For India's agricul ...
... as the coastal districts where coastal ecosystems are already stressed due to extant human activity, and which are also the most vulnerable to sea level rise. These megacities already have pressing planning concerns due to high ground water needs, aggravated by salinity problems. For India's agricul ...
climate change and ozone depletion
... 11. Which of the following statements about the greenhouse effect is false? a. The amount of heat trapped in the troposphere depends on concentrations of greenhouse gases. b. The greenhouse effect is a new theory that explains the warming of the atmosphere. c. Heat trapped by greenhouse gases keeps ...
... 11. Which of the following statements about the greenhouse effect is false? a. The amount of heat trapped in the troposphere depends on concentrations of greenhouse gases. b. The greenhouse effect is a new theory that explains the warming of the atmosphere. c. Heat trapped by greenhouse gases keeps ...
- Sustainable Loudoun
... 12. An even higher layer of the atmosphere, the ionosphere, is expected to cool and contract in response to greenhouse warming. This has been observed by satellites [16]. 13. The study considered temperature changes for the period of 1951–2010. During that time, global surface temperatures warmed ab ...
... 12. An even higher layer of the atmosphere, the ionosphere, is expected to cool and contract in response to greenhouse warming. This has been observed by satellites [16]. 13. The study considered temperature changes for the period of 1951–2010. During that time, global surface temperatures warmed ab ...
Chapter 9
... also implies that there will be variations of temperature and weather patterns on a regional basis. In fact, some have used global ‘weirding’ instead of warming to indicate that one outcome of GW is the unpredictable and often intense (hence damaging) regional weather patterns. How would one explain ...
... also implies that there will be variations of temperature and weather patterns on a regional basis. In fact, some have used global ‘weirding’ instead of warming to indicate that one outcome of GW is the unpredictable and often intense (hence damaging) regional weather patterns. How would one explain ...
PowerPoint - Columbia University
... 1. Chief mechanisms for paleoclimate change GHGs & ice sheet area, as feedbacks. 2. Chief instigator of climate change was earth orbital change, a very weak forcing. 3. Climate on long time scales is very sensitive to even small forcings. 4. Human-made forcings dwarf natural forcings that drove glac ...
... 1. Chief mechanisms for paleoclimate change GHGs & ice sheet area, as feedbacks. 2. Chief instigator of climate change was earth orbital change, a very weak forcing. 3. Climate on long time scales is very sensitive to even small forcings. 4. Human-made forcings dwarf natural forcings that drove glac ...
CASE STUDY - Climate change
... distribution. While there is potential catastrophic risk for everyone, the short and medium-term distribution of the costs and benefits will be far from uniform. The distributional challenge is made particularly difficult because those who have largely caused the problem— the rich countries—are not ...
... distribution. While there is potential catastrophic risk for everyone, the short and medium-term distribution of the costs and benefits will be far from uniform. The distributional challenge is made particularly difficult because those who have largely caused the problem— the rich countries—are not ...
APES CH 19 Power Point Presentation - for notes
... 5. Drought in some areas – fewer plants, more fires 6. Extreme storms in some areas due to increased water vapor in air 7. Changes in animal migration patterns and agricultural planting zones ...
... 5. Drought in some areas – fewer plants, more fires 6. Extreme storms in some areas due to increased water vapor in air 7. Changes in animal migration patterns and agricultural planting zones ...
greenhouse gases
... largest single contributor to climate forcing Carbon dioxide contributes about half of total climate forcing from greenhouse gases Other important greenhouse gases include methane, nitrous oxide, CFCs ...
... largest single contributor to climate forcing Carbon dioxide contributes about half of total climate forcing from greenhouse gases Other important greenhouse gases include methane, nitrous oxide, CFCs ...
Climate Change Overview
... the eastern tropical pacific and a reduction in external radiative forcings. Over this time, energy continues to accumulate in the ocean. • Antarctica is loosing a surprising amount of mass, with the potential for much larger and more rapid contributions to future sea level. These changes appear to ...
... the eastern tropical pacific and a reduction in external radiative forcings. Over this time, energy continues to accumulate in the ocean. • Antarctica is loosing a surprising amount of mass, with the potential for much larger and more rapid contributions to future sea level. These changes appear to ...
Climate Science Discussions_Day1_Nov2013
... How do we measure our carbon footprint in and out and what can we do about it? What will be the ability of any changes make in agriculture to effect change in climatesequestration/ mitigation of greenhouse gas composition We must address the gap between perception and reality Temperature dur ...
... How do we measure our carbon footprint in and out and what can we do about it? What will be the ability of any changes make in agriculture to effect change in climatesequestration/ mitigation of greenhouse gas composition We must address the gap between perception and reality Temperature dur ...
Dynamics of Climate Change slides
... Change: Adults' Mental Models of Climate Change Violate Conservation of Matter. ...
... Change: Adults' Mental Models of Climate Change Violate Conservation of Matter. ...
Recent Climate Observations Compared to Projections BREVIA
... Fig. 1. Changes in key global climate parameters since 1973, compared with the scenarios of the IPCC (shown as dashed lines and gray ranges). (Top) Monthly carbon dioxide concentration and its trend line at Mauna Loa, Hawaii (blue), up to January 2007, from Scripps in collaboration with NOAA. ppm, p ...
... Fig. 1. Changes in key global climate parameters since 1973, compared with the scenarios of the IPCC (shown as dashed lines and gray ranges). (Top) Monthly carbon dioxide concentration and its trend line at Mauna Loa, Hawaii (blue), up to January 2007, from Scripps in collaboration with NOAA. ppm, p ...
Climate Change - Capacity Center
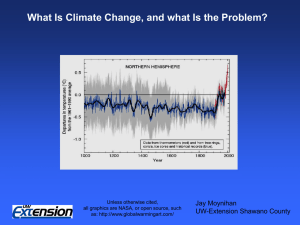
... Unless otherwise cited, all graphics are NASA, or open source, such as: http://www.globalwarmingart.com/ ...
... Unless otherwise cited, all graphics are NASA, or open source, such as: http://www.globalwarmingart.com/ ...
Global Warming - Florida International University
... the last 25 years: 1990s were the warmest decade of the 20th century – Based on 14,000 land and sea records from all over the world – Ice core patterns –varied between 180 and 280 ppm in the last half million years ...
... the last 25 years: 1990s were the warmest decade of the 20th century – Based on 14,000 land and sea records from all over the world – Ice core patterns –varied between 180 and 280 ppm in the last half million years ...
Evolution of the climate science
... • Several effects: increasing ocean acidification, ocean circulation changes, and water, temperature, and nutrient constraints on land CO2 uptake. • Also, danger of inert carbon pools mobilisation and released into the atmosphere either as CO2 or methane - peatland carbon, in Arctic permafrost, whic ...
... • Several effects: increasing ocean acidification, ocean circulation changes, and water, temperature, and nutrient constraints on land CO2 uptake. • Also, danger of inert carbon pools mobilisation and released into the atmosphere either as CO2 or methane - peatland carbon, in Arctic permafrost, whic ...
Unit-IV-Global Warming- Causes
... since the late 19th century The snow cover in the Northern Hemisphere and floating ice in the Arctic Ocean have decreased Sea level has risen 4-8 inches over the past century Global surface temp. could rise 1-4.5°F (0.6-2.5°C) in the next fifty years, and 2.2-10°F (1.4-5.8°C) in the next century ...
... since the late 19th century The snow cover in the Northern Hemisphere and floating ice in the Arctic Ocean have decreased Sea level has risen 4-8 inches over the past century Global surface temp. could rise 1-4.5°F (0.6-2.5°C) in the next fifty years, and 2.2-10°F (1.4-5.8°C) in the next century ...
Attribution of recent climate change
Attribution of recent climate change is the effort to scientifically ascertain mechanisms responsible for recent changes observed in the Earth's climate, commonly known as 'global warming'. The effort has focused on changes observed during the period of instrumental temperature record, when records are most reliable; particularly in the last 50 years, when human activity has grown fastest and observations of the troposphere have become available. The dominant mechanisms (to which recent climate change has been attributed) are anthropogenic, i.e., the result of human activity. They are: increasing atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases global changes to land surface, such as deforestation increasing atmospheric concentrations of aerosols.There are also natural mechanisms for variation including climate oscillations, changes in solar activity, and volcanic activity.According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), it is ""extremely likely"" that human influence was the dominant cause of global warming between 1951 and 2010. The IPCC defines ""extremely likely"" as indicating a probability of 95 to 100%, based on an expert assessment of all the available evidence.Multiple lines of evidence support attribution of recent climate change to human activities: A basic physical understanding of the climate system: greenhouse gas concentrations have increased and their warming properties are well-established. Historical estimates of past climate changes suggest that the recent changes in global surface temperature are unusual. Computer-based climate models are unable to replicate the observed warming unless human greenhouse gas emissions are included. Natural forces alone (such as solar and volcanic activity) cannot explain the observed warming.The IPCC's attribution of recent global warming to human activities is a view shared by most scientists, and is also supported by 196 other scientific organizations worldwide (see also: scientific opinion on climate change).