Topic 2 Atomic Structure File
... 6. If the mass number of the atom of a given element is known, the number of neutrons in its nucleus can be calculated by subtracting the _______________________ from the _______________________. For example, if an atom of the element sodium, atomic number 11, has a mass of 23, the atom has ________ ...
... 6. If the mass number of the atom of a given element is known, the number of neutrons in its nucleus can be calculated by subtracting the _______________________ from the _______________________. For example, if an atom of the element sodium, atomic number 11, has a mass of 23, the atom has ________ ...
Chapter 10 Section 1 Development of the Atomic Theory
... •Matter is made of particles, which we call atoms. • An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the chemical properties of that element. ...
... •Matter is made of particles, which we call atoms. • An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the chemical properties of that element. ...
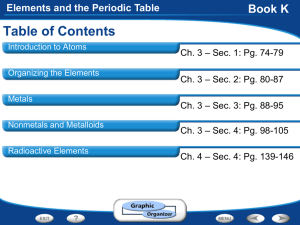
Chapter 4 Elements and the Periodic Table The Periodic Table
... The elements below the lanthanides are called actinides. Many of these elements are so unstable that they last for only a fraction of a second after they are made. ...
... The elements below the lanthanides are called actinides. Many of these elements are so unstable that they last for only a fraction of a second after they are made. ...
Q1. This question is about the first ionisation energies of some
... By reference to the relevant part of the mass spectrometer, explain how the abundance of an isotope in a sample of rubidium is determined. Name of relevant part .................................................................................... ...
... By reference to the relevant part of the mass spectrometer, explain how the abundance of an isotope in a sample of rubidium is determined. Name of relevant part .................................................................................... ...
Student Copy Study Guide Introduction to Periodic
... 19.The atomic number of an element is the total number of which particles in the nucleus? a. neutrons b. protons c. electrons d. protons and electrons 20. Who was the man who lived from 460 B.C.–370 B.C. and was among the first to suggest the idea of atoms? a. Atomos b. Dalton c. Democritus d. Thoms ...
... 19.The atomic number of an element is the total number of which particles in the nucleus? a. neutrons b. protons c. electrons d. protons and electrons 20. Who was the man who lived from 460 B.C.–370 B.C. and was among the first to suggest the idea of atoms? a. Atomos b. Dalton c. Democritus d. Thoms ...
ion
... Experiments done in Ernest Rutherford’s laboratory used positively charged alpha particles to bombard very thin gold (and other metals) foil. Most alpha particles passed through the foil, but a few were scattered at large angles, sometimes almost straight backward. Based on these findings, Rutherfor ...
... Experiments done in Ernest Rutherford’s laboratory used positively charged alpha particles to bombard very thin gold (and other metals) foil. Most alpha particles passed through the foil, but a few were scattered at large angles, sometimes almost straight backward. Based on these findings, Rutherfor ...
Atomic Energy for Military Purposes
... natural hydrogen to one part in 5,000. Because of its special importance this heavy species of hydrogen is given a name of its own, deuterium, and the corresponding nucleus is called the deuteron. Like the alpha particle the deuteron is not one of the fundamental particles but does play an important ...
... natural hydrogen to one part in 5,000. Because of its special importance this heavy species of hydrogen is given a name of its own, deuterium, and the corresponding nucleus is called the deuteron. Like the alpha particle the deuteron is not one of the fundamental particles but does play an important ...
- Angelo State University
... • Dalton’s atomic hypothesis had an uphill struggle — many scientists didn’t like the idea of using small, invisible entities to explain phenomena. • Most (but not all) chemists had accepted the existence of atoms by the early 20th century; however, many influential physicists did not accept the ato ...
... • Dalton’s atomic hypothesis had an uphill struggle — many scientists didn’t like the idea of using small, invisible entities to explain phenomena. • Most (but not all) chemists had accepted the existence of atoms by the early 20th century; however, many influential physicists did not accept the ato ...
AP Chemistry
... determine that a beaker has a mass of 250 g by weighing it on a scale. Using a different scale might give you a mass of 249.9 g for the same beaker. Yet another scale might report the mass as 249.89 g. Whenever you use an instrument (such as a scale or a graduated cylinder or a thermometer) to measu ...
... determine that a beaker has a mass of 250 g by weighing it on a scale. Using a different scale might give you a mass of 249.9 g for the same beaker. Yet another scale might report the mass as 249.89 g. Whenever you use an instrument (such as a scale or a graduated cylinder or a thermometer) to measu ...
Dalton`s atomic theory
... of the spectral phenomena that Bohr's model failed to explain. Although this concept was mathematically convenient, it was difficult to visualize, and faced opposition. One of its critics, Max Born, proposed instead that Schrödinger's wavefunction described not the electron but rather all its possib ...
... of the spectral phenomena that Bohr's model failed to explain. Although this concept was mathematically convenient, it was difficult to visualize, and faced opposition. One of its critics, Max Born, proposed instead that Schrödinger's wavefunction described not the electron but rather all its possib ...
atomic number - iGCSE Science Courses
... only one or two stable ones. The other isotopes tend to be radioactive, which means that they decay into other elements and give out radiation. This is where all radioactivity comes from – unstable radioactive isotopes undergoing nuclear decay and spitting out high energy particles. ...
... only one or two stable ones. The other isotopes tend to be radioactive, which means that they decay into other elements and give out radiation. This is where all radioactivity comes from – unstable radioactive isotopes undergoing nuclear decay and spitting out high energy particles. ...
Multivalent Ionic Compounds
... 4.2 PRACTICE: Names and Formulas of Compounds 1. Complete Names and Formulas of Compounds challenge, 4.2 crossword, 4.2 Quiz, and 4.2 Check Your Understanding. 2. Determine the formula of each of the following monovalent ionic compounds. Use your periodic table to look up the charge on each ion. If ...
... 4.2 PRACTICE: Names and Formulas of Compounds 1. Complete Names and Formulas of Compounds challenge, 4.2 crossword, 4.2 Quiz, and 4.2 Check Your Understanding. 2. Determine the formula of each of the following monovalent ionic compounds. Use your periodic table to look up the charge on each ion. If ...
No Slide Title
... 1) The atomic number (Z) is equal to the number of protons in the atom. 2) Since atoms are electrically neutral, the number of electrons in an atom is also equal to Z, the atomic number. 3) The mass number (A) is equal to the number of protons + neutrons in the atom. ...
... 1) The atomic number (Z) is equal to the number of protons in the atom. 2) Since atoms are electrically neutral, the number of electrons in an atom is also equal to Z, the atomic number. 3) The mass number (A) is equal to the number of protons + neutrons in the atom. ...
Elements and the Periodic Table
... • The elements below the lanthanides are called actinides. Many of these elements are so unstable that they last for only a fraction of a second after they are made. ...
... • The elements below the lanthanides are called actinides. Many of these elements are so unstable that they last for only a fraction of a second after they are made. ...
atom - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... Electronic structure The number and disposition of an atom’s electrons influence its tendency to join other atoms. ...
... Electronic structure The number and disposition of an atom’s electrons influence its tendency to join other atoms. ...
Chemistry SOL Review Test
... surrounded by a soup of positive charge to balance the electrons' negative charges (Plum Pudding Model). 17) What experiment did Thomson do? The cathode rays tube 18) What was his model called? Plum Pudding Model 19) Describe Rutherford’s model. Atoms have a center nucleus and the rest of the atom i ...
... surrounded by a soup of positive charge to balance the electrons' negative charges (Plum Pudding Model). 17) What experiment did Thomson do? The cathode rays tube 18) What was his model called? Plum Pudding Model 19) Describe Rutherford’s model. Atoms have a center nucleus and the rest of the atom i ...
Subatomic Particles
... isotopes, they need an efficient way to specify the number of neutrons in any particular nucleus. The mass number of an atom is the sum of the numbers of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Given the mass number for a nucleus (and knowing the atomic number of that particular atom), you can determi ...
... isotopes, they need an efficient way to specify the number of neutrons in any particular nucleus. The mass number of an atom is the sum of the numbers of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Given the mass number for a nucleus (and knowing the atomic number of that particular atom), you can determi ...
presentation1-elements-atoms-and-isotopes
... Each element has a definite and fixed number of protons. If the number of protons changes, then the atom becomes a different element. Changes in the number of particles in the nucleus (protons or neutrons) are very rare. They only take place in nuclear processes such as: ...
... Each element has a definite and fixed number of protons. If the number of protons changes, then the atom becomes a different element. Changes in the number of particles in the nucleus (protons or neutrons) are very rare. They only take place in nuclear processes such as: ...
Year End Review
... of element X, but one less electron than a neutral atom of element Z. b. Element X could be a halogen. c. Elements X, Y, and Z would all be in the same chemical family of the periodic table. d. Elements X, Y, and Z could be those elements with atomic numbers 9, 10, and 11 respectively. 11. Which of ...
... of element X, but one less electron than a neutral atom of element Z. b. Element X could be a halogen. c. Elements X, Y, and Z would all be in the same chemical family of the periodic table. d. Elements X, Y, and Z could be those elements with atomic numbers 9, 10, and 11 respectively. 11. Which of ...
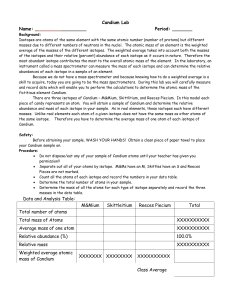
Candium Lab - OCPS TeacherPress
... 1.) Write a formula for each of the steps listed in calculations section. Example: Avg. mass of one atom = total mass of all atoms of an isotope total number of atoms of that isotope Relative Abundance = ...
... 1.) Write a formula for each of the steps listed in calculations section. Example: Avg. mass of one atom = total mass of all atoms of an isotope total number of atoms of that isotope Relative Abundance = ...
Itty-Bitty Atoms
... teeny-weeny. You could fit 100 million on the tip of your little finger! They are so small that no one has ever seen an atom all by itself. Atoms are what chemistry is all about. Chemistry is the study of substances and what they are made of. All substances are made of atoms. However, you can see lo ...
... teeny-weeny. You could fit 100 million on the tip of your little finger! They are so small that no one has ever seen an atom all by itself. Atoms are what chemistry is all about. Chemistry is the study of substances and what they are made of. All substances are made of atoms. However, you can see lo ...
chapter2-bur.2886332..
... Example: 3416S = 34S We can omit the subscript because all sulfur atoms contain 16 protons. ...
... Example: 3416S = 34S We can omit the subscript because all sulfur atoms contain 16 protons. ...
Subject Area Assessment Guides
... metals (Group 1), such as sodium and potassium, which are soft and white and extremely reactive chemically. Alkaline earth metals (Group 2), such as magnesium and calcium, are found in the second column of the periodic table. The transition metals (Groups 3 through 12) are represented by some of the ...
... metals (Group 1), such as sodium and potassium, which are soft and white and extremely reactive chemically. Alkaline earth metals (Group 2), such as magnesium and calcium, are found in the second column of the periodic table. The transition metals (Groups 3 through 12) are represented by some of the ...