PPT Slides
... (such as two negative charges) repel each other. This is why electrons remain spread out in the electron cloud. ...
... (such as two negative charges) repel each other. This is why electrons remain spread out in the electron cloud. ...
atomic number
... • neutron number varies with the type of isotope (more on this later) • electron number is the same as proton number for uncharged (neutral) atoms (also, more on this later) Part II: Atomic Structure • the atom has two distinct areas: the nucleus and the electron cloud. • nucleus = center of the ato ...
... • neutron number varies with the type of isotope (more on this later) • electron number is the same as proton number for uncharged (neutral) atoms (also, more on this later) Part II: Atomic Structure • the atom has two distinct areas: the nucleus and the electron cloud. • nucleus = center of the ato ...
September 20th, 2012
... Magnesium has three isotopes, with mass numbers 24, 25, and 26. a) write the complete chemical symbol (subscript and superscript) of each. b) how many neutrons are in an atom of ...
... Magnesium has three isotopes, with mass numbers 24, 25, and 26. a) write the complete chemical symbol (subscript and superscript) of each. b) how many neutrons are in an atom of ...
Name______________________________ (First and Last
... Are there pieces of matter that are smaller than atoms? Sure there are. You'll soon be learning that atoms are composed of pieces like neutrons, electrons, and protons. But guess what? There are even smaller particles moving around in atoms. These super-small particles can be found inside the proton ...
... Are there pieces of matter that are smaller than atoms? Sure there are. You'll soon be learning that atoms are composed of pieces like neutrons, electrons, and protons. But guess what? There are even smaller particles moving around in atoms. These super-small particles can be found inside the proton ...
Atomic Structure - OCPS TeacherPress
... The number of valence electrons in an atom will determine if an element will allow electricity to flow. The ability of an atom to draw electrons to itself (away from its neighbors) is called Electronegativity. ...
... The number of valence electrons in an atom will determine if an element will allow electricity to flow. The ability of an atom to draw electrons to itself (away from its neighbors) is called Electronegativity. ...
The Modern Atomic Model
... • Every atom of an element will always have the same number of protons • Carbon will always have 6 protons, oxygen will always have 8 protons, and iron will always have 26 protons. ...
... • Every atom of an element will always have the same number of protons • Carbon will always have 6 protons, oxygen will always have 8 protons, and iron will always have 26 protons. ...
Periodic Table Trends
... A hydrogen atom is so small that in a dash like this one: if that dash is 1 mm long, there would be about 20 million hydrogen atoms to make that length Hydrogen Atom ...
... A hydrogen atom is so small that in a dash like this one: if that dash is 1 mm long, there would be about 20 million hydrogen atoms to make that length Hydrogen Atom ...
Chp 4 slideshow notes - Lower Cape May Regional School District
... atom depends on the number of electrons. The electron(s) in the outermost energy level of an atom are called “valence electrons”. The most valence electrons that an atom can have is eight (8). Atoms with a filled valence energy level are the “stable” and don’t react chemically. Electron dot diagrams ...
... atom depends on the number of electrons. The electron(s) in the outermost energy level of an atom are called “valence electrons”. The most valence electrons that an atom can have is eight (8). Atoms with a filled valence energy level are the “stable” and don’t react chemically. Electron dot diagrams ...
atoms - schultz915
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
Lecture 2 - Unit 1 Part 2 Slides
... The atomic number, number of protons in the nucleus, differentiates the atoms of one element from the atoms of other elements. V. The state that matter is in depends on the kinetic energy of its particles ...
... The atomic number, number of protons in the nucleus, differentiates the atoms of one element from the atoms of other elements. V. The state that matter is in depends on the kinetic energy of its particles ...
atomic number on the periodic table
... • Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian scientist born in Siberia in 1834, is known as the father of the periodic table of the elements • The periodic table is designed to help you predict chemical and physical properties of elements ...
... • Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian scientist born in Siberia in 1834, is known as the father of the periodic table of the elements • The periodic table is designed to help you predict chemical and physical properties of elements ...
File
... - Each group is designated a number at the top of the group in Roman numeral which increases from left to right. The Roman numeral is followed by the letter A or B - Members of a group have similar properties. - The atomic numbers in a group increases from top to bottom - The groups of elements can ...
... - Each group is designated a number at the top of the group in Roman numeral which increases from left to right. The Roman numeral is followed by the letter A or B - Members of a group have similar properties. - The atomic numbers in a group increases from top to bottom - The groups of elements can ...
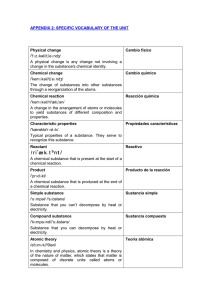
specific vocabulary of the unit
... Substance that you can decompose by heat or electricity. Atomic theory Teoría atómica /ə'tɒmɪk//'θiəri/ In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms or molecules. ...
... Substance that you can decompose by heat or electricity. Atomic theory Teoría atómica /ə'tɒmɪk//'θiəri/ In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms or molecules. ...
Review Questions
... How did Rutherford explain these results? 26. Explain how empirical data helped Thomson and Rutherford modify their view of the atom. Briefly explain how each viewed the atom after their experimentation. ...
... How did Rutherford explain these results? 26. Explain how empirical data helped Thomson and Rutherford modify their view of the atom. Briefly explain how each viewed the atom after their experimentation. ...
CHEMICAL FOUNDATIONS: ELEMENTS AND ATOMS
... • a substance that cannot be further decomposed into simpler substances by chemical or physical means. • consists of atoms that all have the same atomic number. • approximately 115 elements are known. • 88 elements occur naturally. • microscopic--single atom of an element. • macroscopic--enough atom ...
... • a substance that cannot be further decomposed into simpler substances by chemical or physical means. • consists of atoms that all have the same atomic number. • approximately 115 elements are known. • 88 elements occur naturally. • microscopic--single atom of an element. • macroscopic--enough atom ...
1 TEST DATE:
... The electron has very little mass compared to the ____________________________ or ___________________________ . The mass of the atom depends on the nucleus and how many _________________________ and _________________________ it has. The sum of the protons and neutrons is the mass ___________________ ...
... The electron has very little mass compared to the ____________________________ or ___________________________ . The mass of the atom depends on the nucleus and how many _________________________ and _________________________ it has. The sum of the protons and neutrons is the mass ___________________ ...
Chapter 4 Review ans.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... The particles of the nucleus are called nucleons and are either protons (p+) or neutrons (no). 10. What information does the atomic number of an atom give? Atomic number of an atom gives the number of protons in the nucleus; it gives the identity of the atom – which element. 11. What information doe ...
... The particles of the nucleus are called nucleons and are either protons (p+) or neutrons (no). 10. What information does the atomic number of an atom give? Atomic number of an atom gives the number of protons in the nucleus; it gives the identity of the atom – which element. 11. What information doe ...
Name Date Class DEFINING THE ATOM Section Review Objectives
... 9. According to Dalton’s atomic theory, atoms are composed of protons, electrons, and neutrons. 10. Atoms of elements are electrically neutral. 11. The mass of an electron is equal to the mass of a neutron. 12. The charge on all protons is the same. ...
... 9. According to Dalton’s atomic theory, atoms are composed of protons, electrons, and neutrons. 10. Atoms of elements are electrically neutral. 11. The mass of an electron is equal to the mass of a neutron. 12. The charge on all protons is the same. ...
1 Notes Ch. 4 and 25: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry
... II. Induced Transmutation • Before 1919, the only way to change the nucleus or cause transmutation was to wait for _______________________. • In 1919 Rutherford was the first to induce (_____________________) transmutation. • He proved that nuclear reactions can be produced _________________________ ...
... II. Induced Transmutation • Before 1919, the only way to change the nucleus or cause transmutation was to wait for _______________________. • In 1919 Rutherford was the first to induce (_____________________) transmutation. • He proved that nuclear reactions can be produced _________________________ ...
Explaining the Periodic Table (6.7)
... • each element has a unique atomic number • each element is identified by its atomic number and number of protons • (ex. the element carbon, and only carbon, has the atomic number of 6) • In a neutral atom, the number of positives must equal the number of negatives. • This means the # of electrons = ...
... • each element has a unique atomic number • each element is identified by its atomic number and number of protons • (ex. the element carbon, and only carbon, has the atomic number of 6) • In a neutral atom, the number of positives must equal the number of negatives. • This means the # of electrons = ...