elements of chemistry unit
... Sometimes it is useful to assign oxidation numbers to elements found in polar covalent species. By creating Lewis Dot Structures (LDS) diagrams for each element, it is possible to determine their oxidation numbers. OXIDATION NUMBERS AND LDS DIAGRAMS Next, combine the LDS diagrams for the elements an ...
... Sometimes it is useful to assign oxidation numbers to elements found in polar covalent species. By creating Lewis Dot Structures (LDS) diagrams for each element, it is possible to determine their oxidation numbers. OXIDATION NUMBERS AND LDS DIAGRAMS Next, combine the LDS diagrams for the elements an ...
atoms - WordPress.com
... All the positive charge, and almost all the mass is concentrated in a small area in the center. He called this a “nucleus” The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons (they make the nucleus!) The electrons distributed around the nucleus, and occupy most of the volume His model was called ...
... All the positive charge, and almost all the mass is concentrated in a small area in the center. He called this a “nucleus” The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons (they make the nucleus!) The electrons distributed around the nucleus, and occupy most of the volume His model was called ...
Chapter 5 - apel slice
... charged nucleus. But where exactly were the electrons in the atom? In 1913, the Danish scientist Niels Bohr proposed an irnprovement on the Rutherford model. In his model he placed each electron in a specific energy level. According to Bohr's atomic model, electrons move in definite orbits around th ...
... charged nucleus. But where exactly were the electrons in the atom? In 1913, the Danish scientist Niels Bohr proposed an irnprovement on the Rutherford model. In his model he placed each electron in a specific energy level. According to Bohr's atomic model, electrons move in definite orbits around th ...
Chemistry 11 – Course Review
... ___________________________ measured the charge/mass ratio of an electron and came up with the so-called “plum pudding” model of the atom. ...
... ___________________________ measured the charge/mass ratio of an electron and came up with the so-called “plum pudding” model of the atom. ...
regents chemistry midterm - irondequoit 2014_entire exam w key
... Which statement describes the type of change and the chemical properties of the product and reactants? 1) The equation represents a physical change, with the product and reactants having different chemical properties. 2) The equation represents a physical change, with the product and reactants havin ...
... Which statement describes the type of change and the chemical properties of the product and reactants? 1) The equation represents a physical change, with the product and reactants having different chemical properties. 2) The equation represents a physical change, with the product and reactants havin ...
Document
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 3. Atoms combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form molecules of compounds because atoms are unbreakable, they must combine as whole atoms the nature of the atom determines the ratios it combines in each molecule of a compound contains the exact same types and numbe ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 3. Atoms combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form molecules of compounds because atoms are unbreakable, they must combine as whole atoms the nature of the atom determines the ratios it combines in each molecule of a compound contains the exact same types and numbe ...
Fundamentals of Chemistry
... General Physics Corporation, Fundamentals of Chemistry, General Physics Corporation, ...
... General Physics Corporation, Fundamentals of Chemistry, General Physics Corporation, ...
atoms. - Unicam
... 2. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element in a chemical reaction. Elements can only be converted into other elements in nuclear reactions. 3. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determines the chemical behavior of the element. ...
... 2. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of another element in a chemical reaction. Elements can only be converted into other elements in nuclear reactions. 3. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determines the chemical behavior of the element. ...
Chemistry 5.12 Spring 2003 Lectures #1 & 2, 2/5,7/03
... atomic orbitals: unhybridized orbitals on an atom (s, p, d) Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals (LCAO): Individual wave functions (orbitals) combine to form hybrid atomic orbitals (sp, sp2, sp3) and molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) Hybrid Atomic Orbital: Combination of atomic orbitals from the sa ...
... atomic orbitals: unhybridized orbitals on an atom (s, p, d) Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals (LCAO): Individual wave functions (orbitals) combine to form hybrid atomic orbitals (sp, sp2, sp3) and molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) Hybrid Atomic Orbital: Combination of atomic orbitals from the sa ...
Introductory Chemistry, 2nd Edition Nivaldo Tro
... Determine the number of protons in a)Fe3+ b) P3• Fe is iron element #26. • Z = 26 = #p+s = #e-s in neutral atom • 3+ charge means 3 electrons lost 26 - 3 =23 e• P is phosphorus element #15. • Z = 15 = #p+s = #e-s in neutral atom • 3- charge means 3 electrons gained 15 + 3 =18 eTro's "Introductory C ...
... Determine the number of protons in a)Fe3+ b) P3• Fe is iron element #26. • Z = 26 = #p+s = #e-s in neutral atom • 3+ charge means 3 electrons lost 26 - 3 =23 e• P is phosphorus element #15. • Z = 15 = #p+s = #e-s in neutral atom • 3- charge means 3 electrons gained 15 + 3 =18 eTro's "Introductory C ...
Structure of the atom,english2009-08
... Define the atom explain the development of the atomic theory/ model Describe the structure of atom containing subatomic particles : protons, neutrons, and electrons. Define atomic number (Z) and mass number (A) Define isotopes, isotones, and isobars Write down the electron configuration ...
... Define the atom explain the development of the atomic theory/ model Describe the structure of atom containing subatomic particles : protons, neutrons, and electrons. Define atomic number (Z) and mass number (A) Define isotopes, isotones, and isobars Write down the electron configuration ...
Monday June 8, 2009
... Students describe atoms, understanding the structure of an atom. Students identify the symbol, atomic number, and atomic mass of the first 20 elements on the periodic table. Time Activity/Task Assessment Guiding Questions – Atomic Structure Students The teacher asks students three questions (see War ...
... Students describe atoms, understanding the structure of an atom. Students identify the symbol, atomic number, and atomic mass of the first 20 elements on the periodic table. Time Activity/Task Assessment Guiding Questions – Atomic Structure Students The teacher asks students three questions (see War ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table Atoms and the Periodic Table
... Metals shine because they are made of elements that reflect light. Another property of metals is that they do not shatter. Metals bend as they are pressed into thin, flat sheets during the coin-making process. All metals share some similarities, but each metal has its own unique chemical and physica ...
... Metals shine because they are made of elements that reflect light. Another property of metals is that they do not shatter. Metals bend as they are pressed into thin, flat sheets during the coin-making process. All metals share some similarities, but each metal has its own unique chemical and physica ...
Atoms
... • Not exactly correct because binding energy is needed to hold the parts of an atom together • Some mass converted to this binding energy in a nuclear reaction so the calculation gives a value that is a little larger than reality • (E = mc2) ...
... • Not exactly correct because binding energy is needed to hold the parts of an atom together • Some mass converted to this binding energy in a nuclear reaction so the calculation gives a value that is a little larger than reality • (E = mc2) ...
Balancing Reaction Equations Oxidation State Reduction
... Oxidation: Loss of electrons from an element. Oxidation number increases Reduction: Gain of electrons by an element. Oxidation number decreases ...
... Oxidation: Loss of electrons from an element. Oxidation number increases Reduction: Gain of electrons by an element. Oxidation number decreases ...
Oxidation
... Other nonmetals: the element closest to fluorine on the PT gets to keep its “usual” O.S. ...
... Other nonmetals: the element closest to fluorine on the PT gets to keep its “usual” O.S. ...
Atomic Structure
... Early Atomic Models Democritus was a Greek philosopher who lived from 460 B.C. until 370 B.C. He was among the first known individuals to suggest the idea of the atom as the basic unit of matter. The word atom comes from the Greek word atomos, meaning “indivisible.” Democritus ( Figure 1.1) was inde ...
... Early Atomic Models Democritus was a Greek philosopher who lived from 460 B.C. until 370 B.C. He was among the first known individuals to suggest the idea of the atom as the basic unit of matter. The word atom comes from the Greek word atomos, meaning “indivisible.” Democritus ( Figure 1.1) was inde ...
Chapter 4 PowerPoint - Southeast Online
... • The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number. Z is the short-hand designation for the atomic number. Because each element’s atoms have a unique number of protons, each element can be identified by its atomic number. The elements are arranged on the Periodic Tab ...
... • The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number. Z is the short-hand designation for the atomic number. Because each element’s atoms have a unique number of protons, each element can be identified by its atomic number. The elements are arranged on the Periodic Tab ...
Introductory Chemistry, 2nd Edition Nivaldo Tro
... • The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number. Z is the short-hand designation for the atomic number. Because each element’s atoms have a unique number of protons, each element can be identified by its atomic number. The elements are arranged on the Periodic Tab ...
... • The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number. Z is the short-hand designation for the atomic number. Because each element’s atoms have a unique number of protons, each element can be identified by its atomic number. The elements are arranged on the Periodic Tab ...
10 Chemistry
... 1. Atomic number (Z) – number of protons in the nucleus of an atom – neutral atom: number of protons = number of electrons ...
... 1. Atomic number (Z) – number of protons in the nucleus of an atom – neutral atom: number of protons = number of electrons ...
The d- and f- Block Element Block Elements The d- and f
... new electron enters a d orbital each time the nuclear charge increases by unity. It may be recalled that the shielding effect of a d electron is not that effective, hence the net electrostatic attraction between the nuclear charge and the outermost electron increases and the ionic radius decreases. ...
... new electron enters a d orbital each time the nuclear charge increases by unity. It may be recalled that the shielding effect of a d electron is not that effective, hence the net electrostatic attraction between the nuclear charge and the outermost electron increases and the ionic radius decreases. ...
the pdf
... radius of the nucleus is about 105 times less than the radius of the atom. On the basis of his experiment, Rutherford put forward the nuclear model of an atom, which had the following features: (i) There is a positively charged centre in an atom called the nucleus. Nearly all the mass of an atom res ...
... radius of the nucleus is about 105 times less than the radius of the atom. On the basis of his experiment, Rutherford put forward the nuclear model of an atom, which had the following features: (i) There is a positively charged centre in an atom called the nucleus. Nearly all the mass of an atom res ...
Science - Atom Structure
... From these activities, can we conclude that on rubbing two objects together, they become electrically charged? Where does this charge come from? This question can be answered by knowing that an atom is divisible and consists of charged particles. Many scientists contributed in revealing the presence ...
... From these activities, can we conclude that on rubbing two objects together, they become electrically charged? Where does this charge come from? This question can be answered by knowing that an atom is divisible and consists of charged particles. Many scientists contributed in revealing the presence ...
CHAP 4 - NCERT books
... Neils Bohr put forward the following postulates about the model of an atom: (i) Only certain special orbits known as discrete orbits of electrons, are allowed inside the atom. (ii) While revolving in discrete orbits the electrons do not radiate energy. ...
... Neils Bohr put forward the following postulates about the model of an atom: (i) Only certain special orbits known as discrete orbits of electrons, are allowed inside the atom. (ii) While revolving in discrete orbits the electrons do not radiate energy. ...
Boundless Study Slides
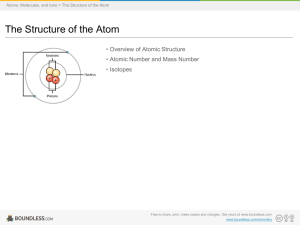
... • An atom is composed of two regions: the nucleus, which is in the center of the atom and contains protons and neutrons, and the outer region of the atom which holds its electrons in orbit around the nucleus. • Protons and neutrons have approximately the same mass, about 1.67 × 10-24 grams, which sc ...
... • An atom is composed of two regions: the nucleus, which is in the center of the atom and contains protons and neutrons, and the outer region of the atom which holds its electrons in orbit around the nucleus. • Protons and neutrons have approximately the same mass, about 1.67 × 10-24 grams, which sc ...