2 – Atomic Structure - Science at St. Dominics
... Describe the experiment carried out by Rutherford that led to the discovery of the nucleus. Explain how Rutherford interpreted the results of this experiment to conclude that the atom has a nucleus. ...
... Describe the experiment carried out by Rutherford that led to the discovery of the nucleus. Explain how Rutherford interpreted the results of this experiment to conclude that the atom has a nucleus. ...
PROPERTIES_OF_MATTER
... • Every sample of a given substance has identical intensive properties because every sample has the same composition • Elements CANNOT be broken down into simpler components • Compounds CAN be broken down into elements ...
... • Every sample of a given substance has identical intensive properties because every sample has the same composition • Elements CANNOT be broken down into simpler components • Compounds CAN be broken down into elements ...
CCH 3 Mole Notes
... Law of Definite Proportions –it does not matter how much you have of a specific compound or where it comes from the mass ratios are always the same. If you have a 1.0 grams of NaCl or 100 grams of NaCl their mass ratios will always be 39.3 % by mass Na combining with 60.7% by mass Cl. (% mass of NaC ...
... Law of Definite Proportions –it does not matter how much you have of a specific compound or where it comes from the mass ratios are always the same. If you have a 1.0 grams of NaCl or 100 grams of NaCl their mass ratios will always be 39.3 % by mass Na combining with 60.7% by mass Cl. (% mass of NaC ...
Name
... • The standard used by scientists to compare units of atomic mass is the carbon-12 atom, which has been arbitrarily assigned a mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units, or 12 amu. • One atomic mass unit, or 1 amu, is exactly 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom. • The atomic mass of any atom is determined ...
... • The standard used by scientists to compare units of atomic mass is the carbon-12 atom, which has been arbitrarily assigned a mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units, or 12 amu. • One atomic mass unit, or 1 amu, is exactly 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom. • The atomic mass of any atom is determined ...
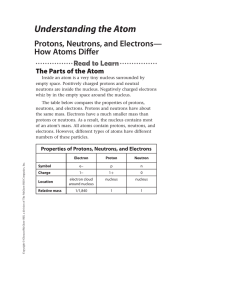
Understanding the Atom
... You have read that atoms of the same element have the same numbers of protons. However, atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons. For example, all carbon atoms have six protons. However, some carbon atoms have six neutrons, some have seven neutrons, and some have eight neutro ...
... You have read that atoms of the same element have the same numbers of protons. However, atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons. For example, all carbon atoms have six protons. However, some carbon atoms have six neutrons, some have seven neutrons, and some have eight neutro ...
Chapter 4 Structure of Atoms Isotopes and Ions KEY
... 1. List the charge and location of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom. protons positive one, Nucleus Elecrons- negative one, -1, in electron cloud neutrons no charge, nucleus 2. List the relative mass of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom. Relative mass means the mass compared to the ...
... 1. List the charge and location of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom. protons positive one, Nucleus Elecrons- negative one, -1, in electron cloud neutrons no charge, nucleus 2. List the relative mass of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom. Relative mass means the mass compared to the ...
Atomic Structure DEMOCRITUS JOHN DALTON
... __________ _________, similarities in their properties occur in a regular pattern. a) Atomic mass b) Atomic number c) Atomic radius Moseley created the modern periodic table when he determined that elements should be placed in order of increasing atomic number (# of protons). It’s a shame that WWI t ...
... __________ _________, similarities in their properties occur in a regular pattern. a) Atomic mass b) Atomic number c) Atomic radius Moseley created the modern periodic table when he determined that elements should be placed in order of increasing atomic number (# of protons). It’s a shame that WWI t ...
How Many Protons do I have? How Many Neutrons do I have?
... 4. The average mass of the isotopes is called the ______________________ Atomic Mass. 5. An unstable nucleus will undergo ______________________ ______________________ in order to become more stable. 6. The three types of radiation from largest to smallest are: _________________, ________________ & ...
... 4. The average mass of the isotopes is called the ______________________ Atomic Mass. 5. An unstable nucleus will undergo ______________________ ______________________ in order to become more stable. 6. The three types of radiation from largest to smallest are: _________________, ________________ & ...
Atomic Theory
... __________ _________, similarities in their properties occur in a regular pattern. a) Atomic mass b) Atomic number c) Atomic radius ...
... __________ _________, similarities in their properties occur in a regular pattern. a) Atomic mass b) Atomic number c) Atomic radius ...
Chapter 2 Powerpoint
... only 2.88 Å. How many silver atoms could be arranged side by side in a straight line across the diameter of a penny? The diameter of a carbon atom is 1.54 Å. Express this diameter in picometers. How many carbon atoms could be aligned side by side in a straight line across the width of a pencil line ...
... only 2.88 Å. How many silver atoms could be arranged side by side in a straight line across the diameter of a penny? The diameter of a carbon atom is 1.54 Å. Express this diameter in picometers. How many carbon atoms could be aligned side by side in a straight line across the width of a pencil line ...
PKUESJX Grade 10 Chemistry Pre
... The Grade 10 Chemistry Pre-IB course encompasses carefully selected content from the Standard Level IB programme, with an emphasis on skills acquisition in order to scaffold progression towards the IB Diploma in Grade 11/12. This course will advance pupils understanding of concepts in which they sho ...
... The Grade 10 Chemistry Pre-IB course encompasses carefully selected content from the Standard Level IB programme, with an emphasis on skills acquisition in order to scaffold progression towards the IB Diploma in Grade 11/12. This course will advance pupils understanding of concepts in which they sho ...
chapter 3 notes
... People have always wondered about what things are made of and what makes one substance different from another. ...
... People have always wondered about what things are made of and what makes one substance different from another. ...
Unit 7: Atomic Theory
... •The mass of a proton and a neutron are about the same and are both much more massive than an electron. •The electron has so little mass that it is not considered when determining the mass of an atom. ...
... •The mass of a proton and a neutron are about the same and are both much more massive than an electron. •The electron has so little mass that it is not considered when determining the mass of an atom. ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... a. Atoms of the same element must always have the same mass b. Atoms of isotopes of an element have different numbers of neutrons. c. The nucleus of an atom has a positive charge. d. Atoms are mostly empty space ____ 35) Which of the following particles are free to drift in metals? a. protons b. ele ...
... a. Atoms of the same element must always have the same mass b. Atoms of isotopes of an element have different numbers of neutrons. c. The nucleus of an atom has a positive charge. d. Atoms are mostly empty space ____ 35) Which of the following particles are free to drift in metals? a. protons b. ele ...
Chapter 2 Review - Garnet Valley School District
... Macromolecules Many of the carbon molecules in living things are so large they are called macromolecules. Macromolecules form by polymerization, in which smaller units called monomers join together to form polymers. Biochemists sort the macromolecules in living things into groups based on their chem ...
... Macromolecules Many of the carbon molecules in living things are so large they are called macromolecules. Macromolecules form by polymerization, in which smaller units called monomers join together to form polymers. Biochemists sort the macromolecules in living things into groups based on their chem ...
File
... Coefficients Interpretation of above example: 2 atoms of solid iron (metal) react with 3 molecules of chlorine gas to produce 2 formula units of solid iron (III) chloride. Coefficients can also be interpreted in a more useful way: MOLES! This is just as if we multiplied the whole equation by 6.02 x ...
... Coefficients Interpretation of above example: 2 atoms of solid iron (metal) react with 3 molecules of chlorine gas to produce 2 formula units of solid iron (III) chloride. Coefficients can also be interpreted in a more useful way: MOLES! This is just as if we multiplied the whole equation by 6.02 x ...
Lecture note 3
... An important feature of Dalton’s atomic theory is the idea that an atom of an element has a characteristic mass. Because he cannot measure the exact mass of individual atoms, Dalton measured the relative mass of elements required to form compound, and from this, deduced relative atomic masses. E.g. ...
... An important feature of Dalton’s atomic theory is the idea that an atom of an element has a characteristic mass. Because he cannot measure the exact mass of individual atoms, Dalton measured the relative mass of elements required to form compound, and from this, deduced relative atomic masses. E.g. ...
Scientific Principles: Chemical Properties
... (monatomic ion)or multiple atoms (polyatomic ion) – ions of many elements and compounds exist such as hydrogen, sodium, ammonium and sulfate ...
... (monatomic ion)or multiple atoms (polyatomic ion) – ions of many elements and compounds exist such as hydrogen, sodium, ammonium and sulfate ...
CHH Review Unit 3
... Protons, electrons, and neutrons are evenly distributed throughout the atom. The nucleus is made of protons, electrons, and neutrons. Electrons are located around the nucleus and occupy most of the volume. The nucleus is made of electrons and protons. ...
... Protons, electrons, and neutrons are evenly distributed throughout the atom. The nucleus is made of protons, electrons, and neutrons. Electrons are located around the nucleus and occupy most of the volume. The nucleus is made of electrons and protons. ...
1 - VCE Chemistry
... 17. What is metal fatigue, how does it occur and what consequences can result from it? 18. List and describe the three methods of heat treatment? 19. How does an atom become an ion? 20. How many protons, neutrons and electrons does (16O8)-2 have? The test will consist of multiple-choice questions an ...
... 17. What is metal fatigue, how does it occur and what consequences can result from it? 18. List and describe the three methods of heat treatment? 19. How does an atom become an ion? 20. How many protons, neutrons and electrons does (16O8)-2 have? The test will consist of multiple-choice questions an ...
Chapter 4 Section 1: Introduction to atoms
... Isotopes and mass number • Atoms with the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. All atoms of an element have the same number of PROTONS, but neutron number can vary. • Examples: Carbon 13 has 7 neutrons, carbon 14 has 8 neutrons. • Isotopes are identified by ...
... Isotopes and mass number • Atoms with the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. All atoms of an element have the same number of PROTONS, but neutron number can vary. • Examples: Carbon 13 has 7 neutrons, carbon 14 has 8 neutrons. • Isotopes are identified by ...
110 exam i material
... Metric metric conversion factors are exact numbers and have an infinite number of significant figures English english conversion factors are exact numbers and have an infinite number of significant figures English metric conversion factors are measured numbers and have a finite number of signi ...
... Metric metric conversion factors are exact numbers and have an infinite number of significant figures English english conversion factors are exact numbers and have an infinite number of significant figures English metric conversion factors are measured numbers and have a finite number of signi ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.