Mole Relationships in chemistry
... Formulas from Mass % Pretend that you have a 100 gram sample of the compound ...
... Formulas from Mass % Pretend that you have a 100 gram sample of the compound ...
Science 10 Chem - Holy Trinity Academy
... Mixture: a combination of 2 or more different pure substances where the properties can vary depending on the quantities of the substances. Mechanical (Heterogeneous) Mixture: a mixture in which the different substances are visible. e.g., soil Solution (Homogeneous): a mixture in which the differ ...
... Mixture: a combination of 2 or more different pure substances where the properties can vary depending on the quantities of the substances. Mechanical (Heterogeneous) Mixture: a mixture in which the different substances are visible. e.g., soil Solution (Homogeneous): a mixture in which the differ ...
Atomic Structure Timeline
... Discovery of the Electron • In the late 1870’s many experiments were performed in which electric current was passed through gases at low pressures due to the fact that gases at atmospheric pressure don’t conduct electricity well. • These experiments were carried out in glass tubes called cathode-ra ...
... Discovery of the Electron • In the late 1870’s many experiments were performed in which electric current was passed through gases at low pressures due to the fact that gases at atmospheric pressure don’t conduct electricity well. • These experiments were carried out in glass tubes called cathode-ra ...
Chapter2Part1
... Example: CARBON and OXYGEN form two compounds: CO and CO2 Meaning: The masses of OXYGEN, in these two compounds, for the same mass of CARBON are in a ratio of small whole numbers. Carbon monoxide ...
... Example: CARBON and OXYGEN form two compounds: CO and CO2 Meaning: The masses of OXYGEN, in these two compounds, for the same mass of CARBON are in a ratio of small whole numbers. Carbon monoxide ...
1b Atomic Structure
... (O- oxygen, He- Helium) 2. The first letter is always capitalized any other letter must remain lower case. (Agsilver) Nuclear Symbols ...
... (O- oxygen, He- Helium) 2. The first letter is always capitalized any other letter must remain lower case. (Agsilver) Nuclear Symbols ...
chemistry ii chapter 2- atoms, molecules, and ions
... (protons), but different mass numbers are called isotopes of each other (isotopesdifferent mass number due to different number of neutrons) Only use the notation with superscripts only when referring to a particular isotope ...
... (protons), but different mass numbers are called isotopes of each other (isotopesdifferent mass number due to different number of neutrons) Only use the notation with superscripts only when referring to a particular isotope ...
Ch 3 notes ppt
... not all combinations of protons and neutrons create a stable nucleus protons in the nucleus should repel each other, but there is a strong nuclear force (that is an attractive force) that holds the nucleus together the nuclear force is only strong between subatomic particles that are extremely close ...
... not all combinations of protons and neutrons create a stable nucleus protons in the nucleus should repel each other, but there is a strong nuclear force (that is an attractive force) that holds the nucleus together the nuclear force is only strong between subatomic particles that are extremely close ...
Chemical Reactions
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
... – Chemical reactions occur when bonds between the outermost parts of atoms are formed or broken – Chemical reactions involve changes in matter, the making of new materials with new properties, and energy changes. – Symbols represent elements, formulas describe compounds, chemical equations describe ...
Chemistry
... The atomic mass unit (amu) is defined as 1/12 the mass of a carbon – 12 atom (element is named by its name and atomic mass number) C – 12 has 6 protons and 6 neutrons so the mass of a single proton or neutron is 1 amu Most mass numbers in the periodic table are not whole numbers because in nature mo ...
... The atomic mass unit (amu) is defined as 1/12 the mass of a carbon – 12 atom (element is named by its name and atomic mass number) C – 12 has 6 protons and 6 neutrons so the mass of a single proton or neutron is 1 amu Most mass numbers in the periodic table are not whole numbers because in nature mo ...
Matter and Atoms Notes
... If we did find out how to make matter, what would we create with it? What kind of matter are we made of, food atoms from before we were born or what?? How do scientists know about the Big Bang? Is the state of being alive made of atoms? Why can’t we ever send actual people into different planets? ...
... If we did find out how to make matter, what would we create with it? What kind of matter are we made of, food atoms from before we were born or what?? How do scientists know about the Big Bang? Is the state of being alive made of atoms? Why can’t we ever send actual people into different planets? ...
Chemistry: Fall Final Review 08
... 35) What are the temperature conversions from Celsius to Kelvin? °C + 273 = K Chapter 4 – Atomic Structure 36) What was Democritus’ contribution to the atomic structure? He came up with the idea of atoms. 37) Give all of Dalton’s laws. Elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms ...
... 35) What are the temperature conversions from Celsius to Kelvin? °C + 273 = K Chapter 4 – Atomic Structure 36) What was Democritus’ contribution to the atomic structure? He came up with the idea of atoms. 37) Give all of Dalton’s laws. Elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms ...
(8th) Chapter 4-1 Cornell Notes Key Questions How did atomic
... • 1913 Niels Bohr: described electrons having E, moving in orbit around nucleus; • electron movement depends on E level; • later the neutron is added in the nucleus; • Final model: nucleus has protons + neutrons, surrounded by electron cloud. ...
... • 1913 Niels Bohr: described electrons having E, moving in orbit around nucleus; • electron movement depends on E level; • later the neutron is added in the nucleus; • Final model: nucleus has protons + neutrons, surrounded by electron cloud. ...
chapter3 - AlvarezHChem
... a. sum all atoms of each type on a side, even if an element is in more than one substance b. work from left to right to stay organized c. if a polyatomic ion is present in the same form on both sides it can be counted as a unit rather than as individual elements d. look to balance H’s and O’s last i ...
... a. sum all atoms of each type on a side, even if an element is in more than one substance b. work from left to right to stay organized c. if a polyatomic ion is present in the same form on both sides it can be counted as a unit rather than as individual elements d. look to balance H’s and O’s last i ...
1st semester exam review
... • One or more substances changing into new substances • Chemical reactions • New substances have different composition & properties • Decompose, explode, rust, oxidize, corrode, burn ...
... • One or more substances changing into new substances • Chemical reactions • New substances have different composition & properties • Decompose, explode, rust, oxidize, corrode, burn ...
atomic number - s3.amazonaws.com
... might expect them to repel each other just as the north ends of two magnets tend to push each other apart. • It is true that they normally would do just that. • However, when they are packed together in the nucleus with the neutrons, an even stronger binding force takes over. • That force is called ...
... might expect them to repel each other just as the north ends of two magnets tend to push each other apart. • It is true that they normally would do just that. • However, when they are packed together in the nucleus with the neutrons, an even stronger binding force takes over. • That force is called ...
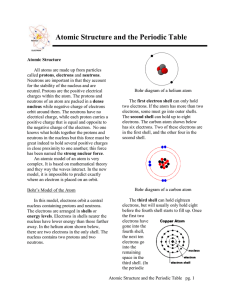
Atomic Structure
... Table is determined by its proton number. All elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons, which is the same as the Group number. All elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells. ...
... Table is determined by its proton number. All elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons, which is the same as the Group number. All elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells. ...
CHAPTER 2
... • If only 2 similar formula type anions exist, the one containing the greater number of oxygen atoms have an “–ate” ending, and the smaller number of oxygen atoms have an “-ite” ending NO3NO2SO42SO32• If more than two exist, the one with the largest number of oxygen atoms have a prefix “per-” and an ...
... • If only 2 similar formula type anions exist, the one containing the greater number of oxygen atoms have an “–ate” ending, and the smaller number of oxygen atoms have an “-ite” ending NO3NO2SO42SO32• If more than two exist, the one with the largest number of oxygen atoms have a prefix “per-” and an ...
atom - www .alexandria .k12 .mn .us
... – Mass the amount of particles making up a substance – Volume is the amount of space taken up by the particles ...
... – Mass the amount of particles making up a substance – Volume is the amount of space taken up by the particles ...
Atomic Structure Atoms. Summary Atomic Number.
... Everything is made of atoms. An atom is the smallest piece of a substance that can exist. 7 million atoms joined together in a straight line would be about 1mm long. All atoms have a nucleus (the big bit in the middle). The nucleus contains protons and neutrons. All atoms have electrons. For any neu ...
... Everything is made of atoms. An atom is the smallest piece of a substance that can exist. 7 million atoms joined together in a straight line would be about 1mm long. All atoms have a nucleus (the big bit in the middle). The nucleus contains protons and neutrons. All atoms have electrons. For any neu ...
Unit 2- The Atom
... Joseph Proust (1754‐1826) was a Frenchman that discovered a given compound always contains exactly the same proportions of the elements by weight. This law started being called Proust’s Law and is now named the Law of definite Proportion. John Dalton (1766‐1844) found the Law of Multiple Propor ...
... Joseph Proust (1754‐1826) was a Frenchman that discovered a given compound always contains exactly the same proportions of the elements by weight. This law started being called Proust’s Law and is now named the Law of definite Proportion. John Dalton (1766‐1844) found the Law of Multiple Propor ...
Unit 2- The Atom
... Joseph Proust (1754‐1826) was a Frenchman that discovered a given compound always contains exactly the same proportions of the elements by weight. This law started being called Proust’s Law and is now named the Law of definite Proportion. John Dalton (1766‐1844) found the Law of Multiple Propor ...
... Joseph Proust (1754‐1826) was a Frenchman that discovered a given compound always contains exactly the same proportions of the elements by weight. This law started being called Proust’s Law and is now named the Law of definite Proportion. John Dalton (1766‐1844) found the Law of Multiple Propor ...
Properties and Changes in Matter
... Groups of atoms at such low temperatures that they behave as a single unit or super atom. (0.001 K) ...
... Groups of atoms at such low temperatures that they behave as a single unit or super atom. (0.001 K) ...
SCI 10 REVIEW
... composed of molecules and therefore ionic charges are NOT a factor. • When two non-metallic elements combine there are often different possible combinations producing different compounds. • These different compounds must be distinguished between since they have different chemical and physical proper ...
... composed of molecules and therefore ionic charges are NOT a factor. • When two non-metallic elements combine there are often different possible combinations producing different compounds. • These different compounds must be distinguished between since they have different chemical and physical proper ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.