Standard 1:Atomic Structure + Elements, Compounds, Mixtures
... Draw and label a diagram that has an electron cloud and a nucleus What 2 particles are found in the nucleus What particle is in the electron cloud? Which region has all the mass and takes up almost no space? Which region takes up all the space but has no mass? What is all matter in the universe made ...
... Draw and label a diagram that has an electron cloud and a nucleus What 2 particles are found in the nucleus What particle is in the electron cloud? Which region has all the mass and takes up almost no space? Which region takes up all the space but has no mass? What is all matter in the universe made ...
Need
... 6. A heating curve (or cooling curve) traces the changes in temperature of a substance as it changes from solid to liquid to gas (or gas to liquid to solid). When the substance undergoes a phase change, there is no change in temperature. The line “flattens” until the phase change is complete. Wh ...
... 6. A heating curve (or cooling curve) traces the changes in temperature of a substance as it changes from solid to liquid to gas (or gas to liquid to solid). When the substance undergoes a phase change, there is no change in temperature. The line “flattens” until the phase change is complete. Wh ...
Atom - Perry Local Schools
... -atom is mostly empty space through which electrons move -most of atom's positive charge and almost all of its mass were contained in a tiny dense region in the center of the atom-called the nucleus -negative particles are held within the atom by their attraction to positive nucleus Nucleus is very ...
... -atom is mostly empty space through which electrons move -most of atom's positive charge and almost all of its mass were contained in a tiny dense region in the center of the atom-called the nucleus -negative particles are held within the atom by their attraction to positive nucleus Nucleus is very ...
What You Need To Know for the Chemistry Regents Exam
... 6. A heating curve (or cooling curve) traces the changes in temperature of a substance as it changes from solid to liquid to gas (or gas to liquid to solid). When the substance undergoes a phase change, there is no change in temperature. The line “flattens” until the phase change is complete. Wh ...
... 6. A heating curve (or cooling curve) traces the changes in temperature of a substance as it changes from solid to liquid to gas (or gas to liquid to solid). When the substance undergoes a phase change, there is no change in temperature. The line “flattens” until the phase change is complete. Wh ...
Catalyst
... The Beginnings of Chemistry Another 460 BCGreek philosopher, Heraclitus, suggested everything was made out of fire ...
... The Beginnings of Chemistry Another 460 BCGreek philosopher, Heraclitus, suggested everything was made out of fire ...
Speed of reactions
... All the atoms of elements in the one group have the same number of electrons in the outer shell, e.g. 1 electron for all the atoms of the alkali metals. The chemical reactions of an element depend on the number of electrons in the outer shell. This is the reason for all the elements in the one group ...
... All the atoms of elements in the one group have the same number of electrons in the outer shell, e.g. 1 electron for all the atoms of the alkali metals. The chemical reactions of an element depend on the number of electrons in the outer shell. This is the reason for all the elements in the one group ...
Chapter 2 Worksheet: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... All samples of a given substance will have the same ratio of atoms by mass (e.g., carbon dioxide is always CO2). c. Dalton’s Atomic Theory 4 postulates: all matter is made of atoms (once thought to be indivisible); all atoms of a given elements are identical (atoms of different elements are differen ...
... All samples of a given substance will have the same ratio of atoms by mass (e.g., carbon dioxide is always CO2). c. Dalton’s Atomic Theory 4 postulates: all matter is made of atoms (once thought to be indivisible); all atoms of a given elements are identical (atoms of different elements are differen ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... In the presence of electric and magnetic forces, when the two forces are balanced, the charge to mass ratio can be calculated (see the handout to look at the math) and Thompson found it to be: charge/mass ratio = 1.76 108 coulombs/g. Robert Millikan determined the charge on the electron in 1909. ( ...
... In the presence of electric and magnetic forces, when the two forces are balanced, the charge to mass ratio can be calculated (see the handout to look at the math) and Thompson found it to be: charge/mass ratio = 1.76 108 coulombs/g. Robert Millikan determined the charge on the electron in 1909. ( ...
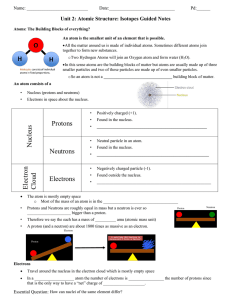
Nucleus Protons Neutrons Electron Cloud Electrons
... Isotope – atoms of the same element that have the same number of _______________but a different number of _________________________ Ions – atoms of the same element that have the same number of __________________ but different number of _________________________ ...
... Isotope – atoms of the same element that have the same number of _______________but a different number of _________________________ Ions – atoms of the same element that have the same number of __________________ but different number of _________________________ ...
Bio_130_files/Chemistry Review
... • A substance that is composed of only one type of atom is called an element. – Elements are the simplest form of matter with unique chemical properties. They are charted on the periodic table based on some of their chemical characteristics. • There are 24 major elements that have various roles in t ...
... • A substance that is composed of only one type of atom is called an element. – Elements are the simplest form of matter with unique chemical properties. They are charted on the periodic table based on some of their chemical characteristics. • There are 24 major elements that have various roles in t ...
Bio_130_files/Chemistry Review
... • A substance that is composed of only one type of atom is called an element. – Elements are the simplest form of matter with unique chemical properties. They are charted on the periodic table based on some of their chemical characteristics. • There are 24 major elements that have various roles in t ...
... • A substance that is composed of only one type of atom is called an element. – Elements are the simplest form of matter with unique chemical properties. They are charted on the periodic table based on some of their chemical characteristics. • There are 24 major elements that have various roles in t ...
File - LSAmockscience
... • When one element replaces another element in a compound A + BC AC + B Element + compound new element + new compound ...
... • When one element replaces another element in a compound A + BC AC + B Element + compound new element + new compound ...
know thy reference tables!
... An atom of argon in the ground state tends not to bond with an atom of a different element because the argon atom has (1) more protons than neutrons (2) more neutrons than protons (3) a total of two valence electrons (4) a total of eight valence electrons Which compound has the lowest vapor pressure ...
... An atom of argon in the ground state tends not to bond with an atom of a different element because the argon atom has (1) more protons than neutrons (2) more neutrons than protons (3) a total of two valence electrons (4) a total of eight valence electrons Which compound has the lowest vapor pressure ...
The Development of the Atomic Theory
... Same size, mass and chemical properties Atoms are indivisible in chemical processes. They can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction A chemical reaction simply changes the way the atom is grouped together A compound has a constant composition of its elements Different atoms ...
... Same size, mass and chemical properties Atoms are indivisible in chemical processes. They can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction A chemical reaction simply changes the way the atom is grouped together A compound has a constant composition of its elements Different atoms ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... By the early 1900’s scientists already new atoms contain electrons (negatively charged), but they are neutral overall… (i.e. they must contain something that neutralizes the charge). Thomson’s Model J.J. Thomson proposed the Plum Pudding Model (didn’t last long…): He thought of the atom as a sphere ...
... By the early 1900’s scientists already new atoms contain electrons (negatively charged), but they are neutral overall… (i.e. they must contain something that neutralizes the charge). Thomson’s Model J.J. Thomson proposed the Plum Pudding Model (didn’t last long…): He thought of the atom as a sphere ...
Atoms Family - The Science Queen
... The first energy street can only hold only two Electron brothers. The second energy street, called the Energy Freeway, can hold 8 brothers. The third energy street, called the Energy Superhighway, can hold 18 of the ...
... The first energy street can only hold only two Electron brothers. The second energy street, called the Energy Freeway, can hold 8 brothers. The third energy street, called the Energy Superhighway, can hold 18 of the ...
Ch 2 PowerPoint
... • The total mass of materials present after a chemical rxn is the same as the total mass present before the rxn ...
... • The total mass of materials present after a chemical rxn is the same as the total mass present before the rxn ...
Atomic Mass
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element having different masses, due to varying numbers of neutrons. Soddy won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1921 for his work with isotopes and radioactive materials. ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element having different masses, due to varying numbers of neutrons. Soddy won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1921 for his work with isotopes and radioactive materials. ...
Chapter 3 - Blair Community Schools
... Experiments support laws: Law of definite proportions: Chemical compounds always contain the same elements in exactly the same proportion by mass ...
... Experiments support laws: Law of definite proportions: Chemical compounds always contain the same elements in exactly the same proportion by mass ...
Sub-Atomic Particles and the Nuclear Atom - Chemistry-at-PA
... c. Write the nuclear reaction of polonium-210 decaying into lead-206 via an alpha decay. ...
... c. Write the nuclear reaction of polonium-210 decaying into lead-206 via an alpha decay. ...
Directed Reading A
... a. Atoms are small, soft particles. b. Atoms are always standing still. c. Atoms are made of a single material. d. Atoms are small particles that can be cut in half again and again. 3. We know that Democritus was right to say that all matter was made up of atoms. So why did people ignore Democritus’ ...
... a. Atoms are small, soft particles. b. Atoms are always standing still. c. Atoms are made of a single material. d. Atoms are small particles that can be cut in half again and again. 3. We know that Democritus was right to say that all matter was made up of atoms. So why did people ignore Democritus’ ...
Valence Electrons
... Some metals may form several different ions They are all metals and good conductors of heat and electricity and have high luster. Properties vary greatly. ...
... Some metals may form several different ions They are all metals and good conductors of heat and electricity and have high luster. Properties vary greatly. ...
Introduction to Atoms
... Electrons move around the nucleus, which contains the protons and neutrons. This area is called an electron cloud because electrons may move anywhere within it. Comparing Particle Masses: Although electrons occupy most of an atom’s volume, they don’t account for much of its mass. A proton and ...
... Electrons move around the nucleus, which contains the protons and neutrons. This area is called an electron cloud because electrons may move anywhere within it. Comparing Particle Masses: Although electrons occupy most of an atom’s volume, they don’t account for much of its mass. A proton and ...
Isotopes - Wando High School
... different number of protons. • However even atoms of the same element are not exactly the same. • Atoms of the same element can have different number of neutrons. These are called Isotopes. ...
... different number of protons. • However even atoms of the same element are not exactly the same. • Atoms of the same element can have different number of neutrons. These are called Isotopes. ...
Chemical element
A chemical element (or element) is a chemical substance consisting of atoms having the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei (i.e. the same atomic number, Z). There are 118 elements that have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. There are 80 elements that have at least one stable isotope and 38 that have exclusively radioactive isotopes, which decay over time into other elements. Iron is the most abundant element (by mass) making up the Earth, while oxygen is the most common element in the crust of the earth.Chemical elements constitute approximately 15% of the matter in the universe: the remainder is dark matter, the composition of it is unknown, but it is not composed of chemical elements.The two lightest elements, hydrogen and helium were mostly formed in the Big Bang and are the most common elements in the universe. The next three elements (lithium, beryllium and boron) were formed mostly by cosmic ray spallation, and are thus more rare than those that follow. Formation of elements with from six to twenty six protons occurred and continues to occur in main sequence stars via stellar nucleosynthesis. The high abundance of oxygen, silicon, and iron on Earth reflects their common production in such stars. Elements with greater than twenty six protons are formed by supernova nucleosynthesis in supernovae, which, when they explode, blast these elements far into space as planetary nebulae, where they may become incorporated into planets when they are formed.When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds. Only a minority of elements are found uncombined as relatively pure minerals. Among the more common of such ""native elements"" are copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite, or diamonds), and sulfur. All but a few of the most inert elements, such as noble gases and noble metals, are usually found on Earth in chemically combined form, as chemical compounds. While about 32 of the chemical elements occur on Earth in native uncombined forms, most of these occur as mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as that of iron and nickel.The history of the discovery and use of the elements began with primitive human societies that found native elements like carbon, sulfur, copper and gold. Later civilizations extracted elemental copper, tin, lead and iron from their ores by smelting, using charcoal. Alchemists and chemists subsequently identified many more, with almost all of the naturally-occurring elements becoming known by 1900. The properties of the chemical elements are summarized on the periodic table, which organizes the elements by increasing atomic number into rows (""periods"") in which the columns (""groups"") share recurring (""periodic"") physical and chemical properties. Save for unstable radioactive elements with short half-lives, all of the elements are available industrially, most of them in high degrees of purity.