
Magnetism - Physical Science
... – 2. A magnetic field, which exerts the magnetic force, surrounds a magnet, and is closest to the magnet. ...
... – 2. A magnetic field, which exerts the magnetic force, surrounds a magnet, and is closest to the magnet. ...
The Sun, from Core to Corona and Solar Wind
... The history of the formation and evolution of the Solar System is encoded in the composition (particularly of the isotopes) of its bodies relative to this baseline7. But how can the solar composition be measured? After all it is not possible to go and scoop up a solar sample and analyse it in the la ...
... The history of the formation and evolution of the Solar System is encoded in the composition (particularly of the isotopes) of its bodies relative to this baseline7. But how can the solar composition be measured? After all it is not possible to go and scoop up a solar sample and analyse it in the la ...
Scientific Justification
... of the solar wind were not possible, due to competing measurements requiring a different spacecraft orientation. Since no instrument on Cassini could image the aurora, HST observations were scheduled with a spacing of several days to a week. With this separation, no large solar wind variations were ...
... of the solar wind were not possible, due to competing measurements requiring a different spacecraft orientation. Since no instrument on Cassini could image the aurora, HST observations were scheduled with a spacing of several days to a week. With this separation, no large solar wind variations were ...
Solar radioastronomy with the LOFAR (LOw Frequency ARray) radio
... feasible. Microwave frequencies have two crucial advantages over longer wavelengths: for a given array dimension the spatial resolution is better; and microwave frequencies do not suffer from the ionospheric effects (perturbations of the ray paths from a straight line due to inhomogeneities in the i ...
... feasible. Microwave frequencies have two crucial advantages over longer wavelengths: for a given array dimension the spatial resolution is better; and microwave frequencies do not suffer from the ionospheric effects (perturbations of the ray paths from a straight line due to inhomogeneities in the i ...
Habitability potential of icy moons around giant planets and the
... Classes I-II: habitable zones on the surface, not much water, small domain Beyond the snow-line: deep habitats within the hydrospheres. Icy moons, Ganymede and Europa and Titan and Enceladus, are the archetypes of classes III-IV of habitable worlds ...
... Classes I-II: habitable zones on the surface, not much water, small domain Beyond the snow-line: deep habitats within the hydrospheres. Icy moons, Ganymede and Europa and Titan and Enceladus, are the archetypes of classes III-IV of habitable worlds ...
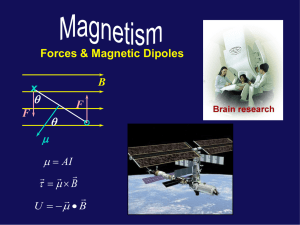
When a current-carrying loop is placed in a
... electrons to their domain. Some domains may even reorient to be aligned with the magnetic field. ...
... electrons to their domain. Some domains may even reorient to be aligned with the magnetic field. ...
ES_CH3_L1 - AFJROTC Ar/Ld 4
... We know a great deal about the Sun through the many discoveries that scientists have made. Think about how you might view the Sun differently if you did not have access to any scientific data. ...
... We know a great deal about the Sun through the many discoveries that scientists have made. Think about how you might view the Sun differently if you did not have access to any scientific data. ...
CHP 19
... b. the sun c. volcanic eruptions d. tidal forces e. impacts of small meteorites The condensation sequence suggests that _______________ should condense closest to the sun. a. Jovian planets b. metals and metal oxides c. silicates d. ices of water, methane, and ammonia e. low density materials. Conde ...
... b. the sun c. volcanic eruptions d. tidal forces e. impacts of small meteorites The condensation sequence suggests that _______________ should condense closest to the sun. a. Jovian planets b. metals and metal oxides c. silicates d. ices of water, methane, and ammonia e. low density materials. Conde ...
ch-6 [Magnetism]
... Magnetism • Magnetism was known from long times ago • Ancient Greek and Chinese used stones exist in nature that have “magical” attractive properties later known as lodestone and magnetite (iron oxide Fe203) • These stones used in navigation • Today we know that iron, cobalt, and nickel are magneti ...
... Magnetism • Magnetism was known from long times ago • Ancient Greek and Chinese used stones exist in nature that have “magical” attractive properties later known as lodestone and magnetite (iron oxide Fe203) • These stones used in navigation • Today we know that iron, cobalt, and nickel are magneti ...
Life on Other Worlds
... The condensation sequence suggests that _______________ should condense closest to the sun. a. Jovian planets b. metals and metal oxides c. silicates d. ices of water, methane, and ammonia e. low density materials. Condensation in the solar nebula probably led to the formation of a. icy grains beyon ...
... The condensation sequence suggests that _______________ should condense closest to the sun. a. Jovian planets b. metals and metal oxides c. silicates d. ices of water, methane, and ammonia e. low density materials. Condensation in the solar nebula probably led to the formation of a. icy grains beyon ...
Answers for Student notes page
... If you suspend a bar magnet from its center by a piece of string, it will act as a compass. • The end that points northward is called the north-seeking pole. • The end that points southward is called the south-seeking pole. • More simply, these are called the north and south poles. • All magnets h ...
... If you suspend a bar magnet from its center by a piece of string, it will act as a compass. • The end that points northward is called the north-seeking pole. • The end that points southward is called the south-seeking pole. • More simply, these are called the north and south poles. • All magnets h ...
Chapter 8 Formation of the Solar System What properties of our
... The nebular theory states that our solar system formed from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar gas cloud—the solar nebula ...
... The nebular theory states that our solar system formed from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar gas cloud—the solar nebula ...
PSCI 1414 General Astronomy
... With elongated orbits, the planets gravitationally interact with each other more strongly. In many computer simulations, this nearly doubles the orbital distance of Neptune, sending Neptune out to its current distance of about 30 AU. As Neptune moves outward, its gravity flings nearby planetesimals ...
... With elongated orbits, the planets gravitationally interact with each other more strongly. In many computer simulations, this nearly doubles the orbital distance of Neptune, sending Neptune out to its current distance of about 30 AU. As Neptune moves outward, its gravity flings nearby planetesimals ...
Atmosphere-Ionosphere Response to the M9 Tohoku Earthquake
... these pre-earthquake atmospheric transient phenomenon (Ouzounov et al., 2007; Inan et al., 2008; Němec et al., 2009; Kon et al., 2011), there is still lack of consistent data necessary to understanding the connection between atmospheric and ionospheric associated with major earthquakes. In this pres ...
... these pre-earthquake atmospheric transient phenomenon (Ouzounov et al., 2007; Inan et al., 2008; Němec et al., 2009; Kon et al., 2011), there is still lack of consistent data necessary to understanding the connection between atmospheric and ionospheric associated with major earthquakes. In this pres ...
Geomagnetic storm

A geomagnetic storm is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere caused by a solar wind shock wave and/or cloud of magnetic field that interacts with the Earth's magnetic field. The increase in the solar wind pressure initially compresses the magnetosphere. The solar wind's magnetic field interacts with the Earth’s magnetic field and transfers an increased energy into the magnetosphere. Both interactions cause an increase in plasma movement through the magnetosphere (driven by increased electric fields inside the magnetosphere) and an increase in electric current in the magnetosphere and ionosphere.During the main phase of a geomagnetic storm, electric current in the magnetosphere creates a magnetic force that pushes out the boundary between the magnetosphere and the solar wind. The disturbance in the interplanetary medium that drives the storm may be due to a solar coronal mass ejection (CME) or a high speed stream (co-rotating interaction region or CIR) of the solar wind originating from a region of weak magnetic field on the Sun’s surface. The frequency of geomagnetic storms increases and decreases with the sunspot cycle. CME driven storms are more common during the maximum of the solar cycle, while CIR driven storms are more common during the minimum of the solar cycle.Several space weather phenomena tend to be associated with or are caused by a geomagnetic storm. These include: solar energetic Particle (SEP) events, geomagnetically induced currents (GIC), ionospheric disturbances that cause radio and radar scintillation, disruption of navigation by magnetic compass and auroral displays at much lower latitudes than normal. In 1989, a geomagnetic storm energized ground induced currents that disrupted electric power distribution throughout most of the province of Quebec and caused aurorae as far south as Texas.















![ch-6 [Magnetism]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004366853_1-cbc1ce7a74752c20e1a6e456bd1e46ed-300x300.png)






