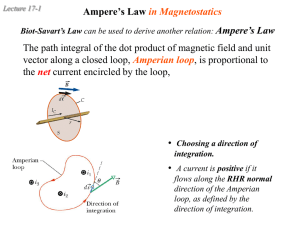
13 magnetic effects of electric current - class 10
... 2) Magnetic field due to a current carrying conductor :If a magnetic compass is placed near a conductor carrying current (wire), the needle is deflected. This shows that a conductor carrying current has a magnetic field around it. If the direction of the current is from north to south, the deflecti ...
... 2) Magnetic field due to a current carrying conductor :If a magnetic compass is placed near a conductor carrying current (wire), the needle is deflected. This shows that a conductor carrying current has a magnetic field around it. If the direction of the current is from north to south, the deflecti ...
Magnetic Levitation - 123SeminarsOnly.com
... Superconductors A superconductor is an element, inter-metallic alloy, or a compound that will conduct electricity without resistance below a certain temperature. Resistance produces losses in energy flowing through the material. In a closed loop, an electrical current will flow continuously i ...
... Superconductors A superconductor is an element, inter-metallic alloy, or a compound that will conduct electricity without resistance below a certain temperature. Resistance produces losses in energy flowing through the material. In a closed loop, an electrical current will flow continuously i ...
The Sun - The University Centre in Svalbard
... The Moon orbits the Earth, which in turn orbits the Sun. Thus, sometimes the Moon will be located between the Earth and the Sun and we will experience what we call a solar eclipse. By a coincidence he Sun and the Moon appear to have the same size in the sky as seen from the Earth. The shadow of the ...
... The Moon orbits the Earth, which in turn orbits the Sun. Thus, sometimes the Moon will be located between the Earth and the Sun and we will experience what we call a solar eclipse. By a coincidence he Sun and the Moon appear to have the same size in the sky as seen from the Earth. The shadow of the ...
Liquid Magnets Worksheet – Answers
... Individual nanoparticles align with magnetic field. Result is a three dimensional depiction of magnetic field directions and varying strengths. KEY: Single domain arrow is characteristic of the nanoparticle because of the particle size can only contain one domain. 5. Why do ferrofluid materials beha ...
... Individual nanoparticles align with magnetic field. Result is a three dimensional depiction of magnetic field directions and varying strengths. KEY: Single domain arrow is characteristic of the nanoparticle because of the particle size can only contain one domain. 5. Why do ferrofluid materials beha ...
CHAPTER - 13 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT CLASS
... periodically is called alternating current. Most power stations in our country produce alternating current. AC changes direction every 1/100 second and its frequency is 50 Hertz (Hz). One advantage of AC over DC is that it can be transmitted over long distances without much loss of energy. Direct cu ...
... periodically is called alternating current. Most power stations in our country produce alternating current. AC changes direction every 1/100 second and its frequency is 50 Hertz (Hz). One advantage of AC over DC is that it can be transmitted over long distances without much loss of energy. Direct cu ...
Lab 2: Magnetic Fields - Island Energy Inquiry
... Tell the class you are giving each student a magical rock. After distributing magnets to all students, ask students to convince you that what they are holding is more than a rock (a magnet). Ask students to work in pairs to come up with at least two concrete reasons. Have students share their exampl ...
... Tell the class you are giving each student a magical rock. After distributing magnets to all students, ask students to convince you that what they are holding is more than a rock (a magnet). Ask students to work in pairs to come up with at least two concrete reasons. Have students share their exampl ...
The Evolution of Coronal X
... Here is what I will speak about. First, how do we infer the past properties of the solar corona? One way is to look for archaeological evidence in the form of the composition of ancient meteorites or surface composition of the lunar surface or indirect evidence from planetary atmosphere histories. H ...
... Here is what I will speak about. First, how do we infer the past properties of the solar corona? One way is to look for archaeological evidence in the form of the composition of ancient meteorites or surface composition of the lunar surface or indirect evidence from planetary atmosphere histories. H ...
2.5. Types of Materials
... They magnetically saturate easily than multi-domains or even pseudo-single domains. The saturation means that no linear relation between the transmitted field and the received response. Although most of the superparamagnetic particles in the goldfields require intense transmitted field to cause satu ...
... They magnetically saturate easily than multi-domains or even pseudo-single domains. The saturation means that no linear relation between the transmitted field and the received response. Although most of the superparamagnetic particles in the goldfields require intense transmitted field to cause satu ...
Lecture 23 ppt
... • But if not strong enough, then on removing the permanent magnet, the domains in the iron piece thermally move back to a random arrangement. • Another way to make magnet: stroke iron piece with magnet – aligns domains. ...
... • But if not strong enough, then on removing the permanent magnet, the domains in the iron piece thermally move back to a random arrangement. • Another way to make magnet: stroke iron piece with magnet – aligns domains. ...
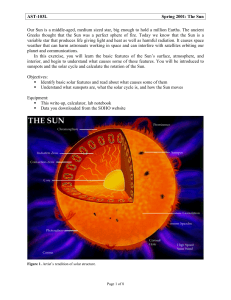
AST-103L Spring 2001 - University of Texas Astronomy Home Page
... What about our Sun, that sphere of glowing gas rising just beyond the eastern horizon? Does it rotate? To find out, we can use one of the Sun’s most prominent features, its sunspots. Sunspots occur in 11 year cycles where the number of visible spots increases from a minimum of almost zero to a maxim ...
... What about our Sun, that sphere of glowing gas rising just beyond the eastern horizon? Does it rotate? To find out, we can use one of the Sun’s most prominent features, its sunspots. Sunspots occur in 11 year cycles where the number of visible spots increases from a minimum of almost zero to a maxim ...
Appendix A. The Normal Geomagnetic Field in Hutchinson, Kansas ( ) Model: IGRF2000
... True bearing = 72 degrees + (-12 degrees declination) = 72 degrees - 12 degrees declination = 60 degrees East It should be noted that the magnetic declination becomes undefined at the North and South magnetic poles. These poles are by definition the two places where the magnetic field is vertical. M ...
... True bearing = 72 degrees + (-12 degrees declination) = 72 degrees - 12 degrees declination = 60 degrees East It should be noted that the magnetic declination becomes undefined at the North and South magnetic poles. These poles are by definition the two places where the magnetic field is vertical. M ...
Name
... 5. During this super storm of 1859 the Northern lights were seen as far _____________________ as _____________________________ and _____________________________ 6. What happened to the amount of sunlight after the mammoth solar flare was released on September 1, 1859? 7. What is coronal mass ejectio ...
... 5. During this super storm of 1859 the Northern lights were seen as far _____________________ as _____________________________ and _____________________________ 6. What happened to the amount of sunlight after the mammoth solar flare was released on September 1, 1859? 7. What is coronal mass ejectio ...
Section Summary
... Rocks containing the mineral magnetite attract materials that contain iron and also attract or repel other magnetic rocks. The attraction or repulsion of magnetic materials is called magnetism. Magnetic rocks are known as lodestones. Magnets have the same properties as magnetic rocks. Magnets attrac ...
... Rocks containing the mineral magnetite attract materials that contain iron and also attract or repel other magnetic rocks. The attraction or repulsion of magnetic materials is called magnetism. Magnetic rocks are known as lodestones. Magnets have the same properties as magnetic rocks. Magnets attrac ...
Geomagnetic storm

A geomagnetic storm is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere caused by a solar wind shock wave and/or cloud of magnetic field that interacts with the Earth's magnetic field. The increase in the solar wind pressure initially compresses the magnetosphere. The solar wind's magnetic field interacts with the Earth’s magnetic field and transfers an increased energy into the magnetosphere. Both interactions cause an increase in plasma movement through the magnetosphere (driven by increased electric fields inside the magnetosphere) and an increase in electric current in the magnetosphere and ionosphere.During the main phase of a geomagnetic storm, electric current in the magnetosphere creates a magnetic force that pushes out the boundary between the magnetosphere and the solar wind. The disturbance in the interplanetary medium that drives the storm may be due to a solar coronal mass ejection (CME) or a high speed stream (co-rotating interaction region or CIR) of the solar wind originating from a region of weak magnetic field on the Sun’s surface. The frequency of geomagnetic storms increases and decreases with the sunspot cycle. CME driven storms are more common during the maximum of the solar cycle, while CIR driven storms are more common during the minimum of the solar cycle.Several space weather phenomena tend to be associated with or are caused by a geomagnetic storm. These include: solar energetic Particle (SEP) events, geomagnetically induced currents (GIC), ionospheric disturbances that cause radio and radar scintillation, disruption of navigation by magnetic compass and auroral displays at much lower latitudes than normal. In 1989, a geomagnetic storm energized ground induced currents that disrupted electric power distribution throughout most of the province of Quebec and caused aurorae as far south as Texas.