physics – magnetism - Strive for Excellence Tutoring
... How a DC motor works A DC motor is a device that converts electrical energy into kinetic energy. It does this by using the electrical energy from a battery to create a magnetic field in a coil. The current in the coil creates a magnetic field which creates a force with the permanent magnets. This in ...
... How a DC motor works A DC motor is a device that converts electrical energy into kinetic energy. It does this by using the electrical energy from a battery to create a magnetic field in a coil. The current in the coil creates a magnetic field which creates a force with the permanent magnets. This in ...
Magnetic Activity
... Magnetic fields are generated by motions inside stars and greatly affect the movement and heating of the outer regions of stars ...
... Magnetic fields are generated by motions inside stars and greatly affect the movement and heating of the outer regions of stars ...
Superconductors - Bryn Mawr College
... The Meissner effect in superconductors like this black ceramic yttrium based superconductor acts to exclude magnetic fields from the material. Since the electrical resistance is zero, supercurrents are generated in the material to exclude the magnetic fields from a magnet brought near it. The curren ...
... The Meissner effect in superconductors like this black ceramic yttrium based superconductor acts to exclude magnetic fields from the material. Since the electrical resistance is zero, supercurrents are generated in the material to exclude the magnetic fields from a magnet brought near it. The curren ...
An electromagnetic wave in vacuum has the electric and magnetic
... In an electromagnetic wave electrical and magnetic fields are perpendicular to each other. Wave propagates in a direction perpendicular to both electric and magnetic filed as given by E⃗ B⃗ . Direction of polarization is perpendicular to direction of oscillation. Optical phenomena are due to electr ...
... In an electromagnetic wave electrical and magnetic fields are perpendicular to each other. Wave propagates in a direction perpendicular to both electric and magnetic filed as given by E⃗ B⃗ . Direction of polarization is perpendicular to direction of oscillation. Optical phenomena are due to electr ...
Physics 2102 Lecture 15
... Rail guns in the “Eraser” movie "Rail guns are hyper-velocity weapons that shoot aluminum or clay rounds at just below the speed of light. In our film, we've taken existing stealth technology one step further and given them an X-ray scope sighting system," notes director Russell. "These guns repres ...
... Rail guns in the “Eraser” movie "Rail guns are hyper-velocity weapons that shoot aluminum or clay rounds at just below the speed of light. In our film, we've taken existing stealth technology one step further and given them an X-ray scope sighting system," notes director Russell. "These guns repres ...
15 HW 5.1 Magnetism.pub
... 10. Which describes magnetic declination? a. the angle between Earth's magnetic field and the Earth's surface b. the Earth's magnetic field strength at the equator c. the tendency for the Earth's magnetic field to reverse itself d. the angle between the geographic north and magnetic south poles ...
... 10. Which describes magnetic declination? a. the angle between Earth's magnetic field and the Earth's surface b. the Earth's magnetic field strength at the equator c. the tendency for the Earth's magnetic field to reverse itself d. the angle between the geographic north and magnetic south poles ...
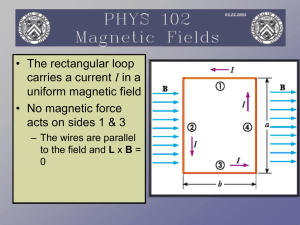
Magnetic Fields
... • The right-hand rule can be used to determine the direction of A for a closed loop. • Curl your fingers in the direction of the current in the loop • Your thumb points in the direction of A ...
... • The right-hand rule can be used to determine the direction of A for a closed loop. • Curl your fingers in the direction of the current in the loop • Your thumb points in the direction of A ...
Lodestones Magnetic Poles
... Direction of field is direction in which the testcompass needle will point at that location. Draw field lines so that compass always points tangent to the field lines. Field lines point from N to S outside the magnet Field lines point from S to N inside the magnet ...
... Direction of field is direction in which the testcompass needle will point at that location. Draw field lines so that compass always points tangent to the field lines. Field lines point from N to S outside the magnet Field lines point from S to N inside the magnet ...
Magnetism and Induction Review
... Ignoring energy losses due to heating of the coils, how do secondary and primary power compare? What about energy? What about currents? Is secondary voltage higher or lower than primary voltage in a step-up transformer? Why do power companies transmit energy as ac rather than dc? What is the smalles ...
... Ignoring energy losses due to heating of the coils, how do secondary and primary power compare? What about energy? What about currents? Is secondary voltage higher or lower than primary voltage in a step-up transformer? Why do power companies transmit energy as ac rather than dc? What is the smalles ...
Magnetometer

Magnetometers are measurement instruments used for two general purposes: to measure the magnetization of a magnetic material like a ferromagnet, or to measure the strength and, in some cases, the direction of the magnetic field at a point in space.The first magnetometer was invented by Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1833 and notable developments in the 19th century included the Hall Effect which is still widely used.Magnetometers are widely used for measuring the Earth's magnetic field and in geophysical surveys to detect magnetic anomalies of various types. They are also used militarily to detect submarines. Consequently, some countries, such as the USA, Canada and Australia classify the more sensitive magnetometers as military technology, and control their distribution.Magnetometers can be used as metal detectors: they can detect only magnetic (ferrous) metals, but can detect such metals at a much larger depth than conventional metal detectors; they are capable of detecting large objects, such as cars, at tens of metres, while a metal detector's range is rarely more than 2 metres.In recent years magnetometers have been miniaturized to the extent that they can be incorporated in integrated circuits at very low cost and are finding increasing use as compasses in consumer devices such as mobile phones and tablet computers.