1-Electromagnetic Forces - MrD-Home
... Fingers: Direction of current through solenoid Thumb: Points to north pole ...
... Fingers: Direction of current through solenoid Thumb: Points to north pole ...
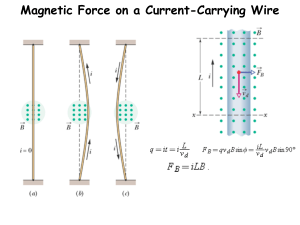
Hall Effect
... one side of the conductor. This is most evident in a thin flat conductor as illustrated. A build up of charge at the sides of the conductors will balance this magnetic influence, producing a measurable voltage between the two sides of the conductor. The presence of this measurable transverse voltage ...
... one side of the conductor. This is most evident in a thin flat conductor as illustrated. A build up of charge at the sides of the conductors will balance this magnetic influence, producing a measurable voltage between the two sides of the conductor. The presence of this measurable transverse voltage ...
The Abstract Title Should be in Title Case and Should be
... the presence of a magnetic field. In order to implement magnetofection in the brain we have constructed two adenoviral vectors, RAd-DsRed2 which expresses DsRed2, a red fluorescent protein from Discosoma, and RAd-GFP a vector expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP). The vectors were constructed b ...
... the presence of a magnetic field. In order to implement magnetofection in the brain we have constructed two adenoviral vectors, RAd-DsRed2 which expresses DsRed2, a red fluorescent protein from Discosoma, and RAd-GFP a vector expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP). The vectors were constructed b ...
Introduction to NMR Spectroscopy and Imaging
... field is removed (turned off), or the sample is removed from the magnet. c. Normally, an NMR sample is diamagnetic, i.e., all electrons in the molecule are paired up, or, there is no net magnetization from the electrons. d. A quadrupole spin means it has very large magnetic moment. e. The majority o ...
... field is removed (turned off), or the sample is removed from the magnet. c. Normally, an NMR sample is diamagnetic, i.e., all electrons in the molecule are paired up, or, there is no net magnetization from the electrons. d. A quadrupole spin means it has very large magnetic moment. e. The majority o ...
Skeleton
... from either pole. Zero the magnetometer on the calculator application. e) Carefully point the surface of the detector downward and try to find the angle which maximized the reading. Since we are in the northern hemisphere, the magnetic field vectors here are on eddy field lines and thus, we should e ...
... from either pole. Zero the magnetometer on the calculator application. e) Carefully point the surface of the detector downward and try to find the angle which maximized the reading. Since we are in the northern hemisphere, the magnetic field vectors here are on eddy field lines and thus, we should e ...
Student
... ________________________ the north pole and ________________________ the south pole of a magnet. e) Electricity can be used to make magnets. The interaction between magnetism and electricity is called “________________________.” An electric current can generate a magnetic field, and the ____________ ...
... ________________________ the north pole and ________________________ the south pole of a magnet. e) Electricity can be used to make magnets. The interaction between magnetism and electricity is called “________________________.” An electric current can generate a magnetic field, and the ____________ ...
Magnetic Effects of Electric Currents
... magnetic field is produced around the wire. If the wire is wound into a coil the resulting field is similar to that of a bar magnet wit north and south poles. ...
... magnetic field is produced around the wire. If the wire is wound into a coil the resulting field is similar to that of a bar magnet wit north and south poles. ...
Magnetism Webquest
... b. What was the principal constituent of the ore that such magnets were composed of? AF. a. Where does the name “magnet” come from? This is the historical name of a geographical location. b. In what modern day country is this place? BG. a. What’s the difference between true north and magnetic north? ...
... b. What was the principal constituent of the ore that such magnets were composed of? AF. a. Where does the name “magnet” come from? This is the historical name of a geographical location. b. In what modern day country is this place? BG. a. What’s the difference between true north and magnetic north? ...
Value Based Questions Magnetic effects of current and Magnetism
... Magnetic effects of current and Magnetism 1)While watching Discovery Channel.Sheela was impressed that certain organisms have the ability to sense the field lines of earth’s magnetic field. They use this ability to travel from one location to another. Sheela wanted to find the angle of dip at her pl ...
... Magnetic effects of current and Magnetism 1)While watching Discovery Channel.Sheela was impressed that certain organisms have the ability to sense the field lines of earth’s magnetic field. They use this ability to travel from one location to another. Sheela wanted to find the angle of dip at her pl ...
Magnetometer

Magnetometers are measurement instruments used for two general purposes: to measure the magnetization of a magnetic material like a ferromagnet, or to measure the strength and, in some cases, the direction of the magnetic field at a point in space.The first magnetometer was invented by Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1833 and notable developments in the 19th century included the Hall Effect which is still widely used.Magnetometers are widely used for measuring the Earth's magnetic field and in geophysical surveys to detect magnetic anomalies of various types. They are also used militarily to detect submarines. Consequently, some countries, such as the USA, Canada and Australia classify the more sensitive magnetometers as military technology, and control their distribution.Magnetometers can be used as metal detectors: they can detect only magnetic (ferrous) metals, but can detect such metals at a much larger depth than conventional metal detectors; they are capable of detecting large objects, such as cars, at tens of metres, while a metal detector's range is rarely more than 2 metres.In recent years magnetometers have been miniaturized to the extent that they can be incorporated in integrated circuits at very low cost and are finding increasing use as compasses in consumer devices such as mobile phones and tablet computers.