doc - Cornerstone Robotics
... Another definition is that a solenoid is a coil and a moveable iron core used to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. It is a coil of wire commonly in the form of a long cylinder that when carrying a current resembles a bar magnet so that a moveable core is drawn into the coil when a cu ...
... Another definition is that a solenoid is a coil and a moveable iron core used to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. It is a coil of wire commonly in the form of a long cylinder that when carrying a current resembles a bar magnet so that a moveable core is drawn into the coil when a cu ...
Magnetic Moments
... Find the field at a point at distance r from the center of the toroid The toroid has N turns of wire ...
... Find the field at a point at distance r from the center of the toroid The toroid has N turns of wire ...
Electromagnetism Unit 2014
... • Static discharge is the movement of charges from one object to another. – Think of this like shocking yourself when you drag your feet on the carpet and touch a door handle. – You feel the “shock.” – What you really experienced is static discharge. – Lightning is also a discharge of static electri ...
... • Static discharge is the movement of charges from one object to another. – Think of this like shocking yourself when you drag your feet on the carpet and touch a door handle. – You feel the “shock.” – What you really experienced is static discharge. – Lightning is also a discharge of static electri ...
Applied Magnetism
... the amplification factor for the internal field B due to an external field H. ...
... the amplification factor for the internal field B due to an external field H. ...
DSM: Thesis SL-DSM-16-0185 - instn
... The development of technology of early diagnosis, at the same time fast and sensitive, allowing the detection of very small quantities of (sub) micrometric biological objetcs (cells, bacteria, proteins etc…) is a real challenge in the medical domain. One possible method consists to label these biolo ...
... The development of technology of early diagnosis, at the same time fast and sensitive, allowing the detection of very small quantities of (sub) micrometric biological objetcs (cells, bacteria, proteins etc…) is a real challenge in the medical domain. One possible method consists to label these biolo ...
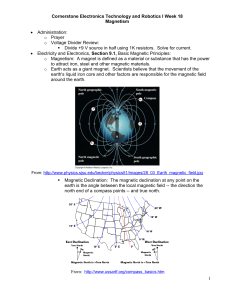
Measurement of the Horizontal Component (H) of Earth`s Magnetic
... The Earth's magnetic field is of interest to scientists due to its interaction with the Sun, its ability to protect us from harmful extraterrestrial radiation, its effect on compasses, and many other reasons. The magnitude of the field depends greatly on solar activity. When solar activity is high, ...
... The Earth's magnetic field is of interest to scientists due to its interaction with the Sun, its ability to protect us from harmful extraterrestrial radiation, its effect on compasses, and many other reasons. The magnitude of the field depends greatly on solar activity. When solar activity is high, ...
The Physics of MRI Scans
... conductor (the wire in this case) the stronger the magnetic field. The receiver coil picks up the RF electromagnetic relaxation produced by nuclear relaxation inside the ...
... conductor (the wire in this case) the stronger the magnetic field. The receiver coil picks up the RF electromagnetic relaxation produced by nuclear relaxation inside the ...
Magnetometer

Magnetometers are measurement instruments used for two general purposes: to measure the magnetization of a magnetic material like a ferromagnet, or to measure the strength and, in some cases, the direction of the magnetic field at a point in space.The first magnetometer was invented by Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1833 and notable developments in the 19th century included the Hall Effect which is still widely used.Magnetometers are widely used for measuring the Earth's magnetic field and in geophysical surveys to detect magnetic anomalies of various types. They are also used militarily to detect submarines. Consequently, some countries, such as the USA, Canada and Australia classify the more sensitive magnetometers as military technology, and control their distribution.Magnetometers can be used as metal detectors: they can detect only magnetic (ferrous) metals, but can detect such metals at a much larger depth than conventional metal detectors; they are capable of detecting large objects, such as cars, at tens of metres, while a metal detector's range is rarely more than 2 metres.In recent years magnetometers have been miniaturized to the extent that they can be incorporated in integrated circuits at very low cost and are finding increasing use as compasses in consumer devices such as mobile phones and tablet computers.