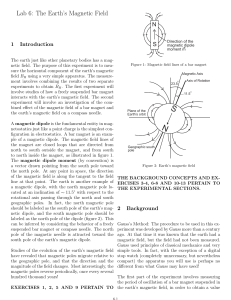
the magnetic field
... APPENDIX – Measuring the Magnetic Field in a Solenoid. We will use a PASCO device to measure the Magnetic Field inside a long coil. This device measures the magnetic field in units of GAUSS that is an older but still popular unit. We measure magnetic fields is TESLAs. You don’t know what either unit ...
... APPENDIX – Measuring the Magnetic Field in a Solenoid. We will use a PASCO device to measure the Magnetic Field inside a long coil. This device measures the magnetic field in units of GAUSS that is an older but still popular unit. We measure magnetic fields is TESLAs. You don’t know what either unit ...
Sources of Magnetic Fields (7/11)
... A circular loop of wire carries a constant current. If the loop is placed in a region of uniform magnetic field, the net magnetic torque on the loop A. tends to orient the loop so that its plane is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field. B. tends to orient the loop so that its plane is ...
... A circular loop of wire carries a constant current. If the loop is placed in a region of uniform magnetic field, the net magnetic torque on the loop A. tends to orient the loop so that its plane is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field. B. tends to orient the loop so that its plane is ...
investigation of measured distributions of local vector magnetic
... 2.2 VH sensor Fig.2 shows the construction of the V-H sensor. The sensor has the two sets of the needle probe for measuring the magnetic flux density B in each direction. The distance between the needles was 7 mm. In addition, the sensor has the double H-coils for measuring the magnetic field intens ...
... 2.2 VH sensor Fig.2 shows the construction of the V-H sensor. The sensor has the two sets of the needle probe for measuring the magnetic flux density B in each direction. The distance between the needles was 7 mm. In addition, the sensor has the double H-coils for measuring the magnetic field intens ...
magnetic field
... It is sometimes convenient to refer the value of magnetization to unit mass rather than unit volume. The mass of a small sample can be measured more accurately than its volume, and the mass is independent of temperature whereas the volume changes with temperature due to thermal expansion. The specif ...
... It is sometimes convenient to refer the value of magnetization to unit mass rather than unit volume. The mass of a small sample can be measured more accurately than its volume, and the mass is independent of temperature whereas the volume changes with temperature due to thermal expansion. The specif ...
Magnetism - APlusPhysics
... b. Use Ampere’s law, plus symmetry arguments and the right-hand rule, to relate magnetic field strength to current for planar or cylindrical symmetries. 2. Apply the superposition principle to determine the magnetic field produced by combinations of Biot-Savart and Ampere’s laws configurations liste ...
... b. Use Ampere’s law, plus symmetry arguments and the right-hand rule, to relate magnetic field strength to current for planar or cylindrical symmetries. 2. Apply the superposition principle to determine the magnetic field produced by combinations of Biot-Savart and Ampere’s laws configurations liste ...
M106 Vibrating Sample Magnetometry
... Macroscopic shape anisotropy has its origin in long range dipole interactions arising from free poles at surfaces. It can be represented in terms of the stray fields created external to the sample. In thin films stray field energy is minimized if the magnetization is in-plane and maximized if the ma ...
... Macroscopic shape anisotropy has its origin in long range dipole interactions arising from free poles at surfaces. It can be represented in terms of the stray fields created external to the sample. In thin films stray field energy is minimized if the magnetization is in-plane and maximized if the ma ...
Magnetometer

Magnetometers are measurement instruments used for two general purposes: to measure the magnetization of a magnetic material like a ferromagnet, or to measure the strength and, in some cases, the direction of the magnetic field at a point in space.The first magnetometer was invented by Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1833 and notable developments in the 19th century included the Hall Effect which is still widely used.Magnetometers are widely used for measuring the Earth's magnetic field and in geophysical surveys to detect magnetic anomalies of various types. They are also used militarily to detect submarines. Consequently, some countries, such as the USA, Canada and Australia classify the more sensitive magnetometers as military technology, and control their distribution.Magnetometers can be used as metal detectors: they can detect only magnetic (ferrous) metals, but can detect such metals at a much larger depth than conventional metal detectors; they are capable of detecting large objects, such as cars, at tens of metres, while a metal detector's range is rarely more than 2 metres.In recent years magnetometers have been miniaturized to the extent that they can be incorporated in integrated circuits at very low cost and are finding increasing use as compasses in consumer devices such as mobile phones and tablet computers.